Heng Gao
Detecting OOD Samples via Optimal Transport Scoring Function
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:To deploy machine learning models in the real world, researchers have proposed many OOD detection algorithms to help models identify unknown samples during the inference phase and prevent them from making untrustworthy predictions. Unlike methods that rely on extra data for outlier exposure training, post hoc methods detect Out-of-Distribution (OOD) samples by developing scoring functions, which are model agnostic and do not require additional training. However, previous post hoc methods may fail to capture the geometric cues embedded in network representations. Thus, in this study, we propose a novel score function based on the optimal transport theory, named OTOD, for OOD detection. We utilize information from features, logits, and the softmax probability space to calculate the OOD score for each test sample. Our experiments show that combining this information can boost the performance of OTOD with a certain margin. Experiments on the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of our method. Notably, OTOD outperforms the state-of-the-art method GEN by 7.19% in the mean FPR@95 on the CIFAR-10 benchmark using ResNet-18 as the backbone, and by 12.51% in the mean FPR@95 using WideResNet-28 as the backbone. In addition, we provide theoretical guarantees for OTOD. The code is available in https://github.com/HengGao12/OTOD.
Towards Open-set Camera 3D Object Detection
Jun 25, 2024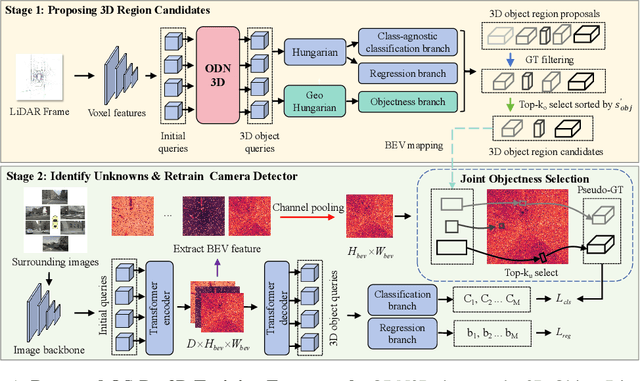

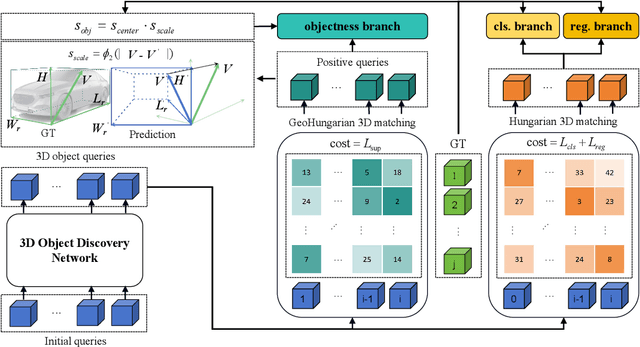

Abstract:Traditional camera 3D object detectors are typically trained to recognize a predefined set of known object classes. In real-world scenarios, these detectors may encounter unknown objects outside the training categories and fail to identify them correctly. To address this gap, we present OS-Det3D (Open-set Camera 3D Object Detection), a two-stage training framework enhancing the ability of camera 3D detectors to identify both known and unknown objects. The framework involves our proposed 3D Object Discovery Network (ODN3D), which is specifically trained using geometric cues such as the location and scale of 3D boxes to discover general 3D objects. ODN3D is trained in a class-agnostic manner, and the provided 3D object region proposals inherently come with data noise. To boost accuracy in identifying unknown objects, we introduce a Joint Objectness Selection (JOS) module. JOS selects the pseudo ground truth for unknown objects from the 3D object region proposals of ODN3D by combining the ODN3D objectness and camera feature attention objectness. Experiments on the nuScenes and KITTI datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework in enabling camera 3D detectors to successfully identify unknown objects while also improving their performance on known objects.
OAML: Outlier Aware Metric Learning for OOD Detection Enhancement
Jun 24, 2024



Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection methods have been developed to identify objects that a model has not seen during training. The Outlier Exposure (OE) methods use auxiliary datasets to train OOD detectors directly. However, the collection and learning of representative OOD samples may pose challenges. To tackle these issues, we propose the Outlier Aware Metric Learning (OAML) framework. The main idea of our method is to use the k-NN algorithm and Stable Diffusion model to generate outliers for training at the feature level without making any distributional assumptions. To increase feature discrepancies in the semantic space, we develop a mutual information-based contrastive learning approach for learning from OOD data effectively. Both theoretical and empirical results confirm the effectiveness of this contrastive learning technique. Furthermore, we incorporate knowledge distillation into our learning framework to prevent degradation of in-distribution classification accuracy. The combination of contrastive learning and knowledge distillation algorithms significantly enhances the performance of OOD detection. Experimental results across various datasets show that our method significantly outperforms previous OE methods.
Knowledge Distillation from 3D to Bird's-Eye-View for LiDAR Semantic Segmentation
Apr 22, 2023



Abstract:LiDAR point cloud segmentation is one of the most fundamental tasks for autonomous driving scene understanding. However, it is difficult for existing models to achieve both high inference speed and accuracy simultaneously. For example, voxel-based methods perform well in accuracy, while Bird's-Eye-View (BEV)-based methods can achieve real-time inference. To overcome this issue, we develop an effective 3D-to-BEV knowledge distillation method that transfers rich knowledge from 3D voxel-based models to BEV-based models. Our framework mainly consists of two modules: the voxel-to-pillar distillation module and the label-weight distillation module. Voxel-to-pillar distillation distills sparse 3D features to BEV features for middle layers to make the BEV-based model aware of more structural and geometric information. Label-weight distillation helps the model pay more attention to regions with more height information. Finally, we conduct experiments on the SemanticKITTI dataset and Paris-Lille-3D. The results on SemanticKITTI show more than 5% improvement on the test set, especially for classes such as motorcycle and person, with more than 15% improvement. The code can be accessed at https://github.com/fengjiang5/Knowledge-Distillation-from-Cylinder3D-to-PolarNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge