Hemanth Kandula
QueryBuilder: Human-in-the-Loop Query Development for Information Retrieval
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:Frequently, users of an Information Retrieval (IR) system start with an overarching information need (a.k.a., an analytic task) and proceed to define finer-grained queries covering various important aspects (i.e., sub-topics) of that analytic task. We present a novel, interactive system called $\textit{QueryBuilder}$, which allows a novice, English-speaking user to create queries with a small amount of effort, through efficient exploration of an English development corpus in order to rapidly develop cross-lingual information retrieval queries corresponding to the user's information needs. QueryBuilder performs near real-time retrieval of documents based on user-entered search terms; the user looks through the retrieved documents and marks sentences as relevant to the information needed. The marked sentences are used by the system as additional information in query formation and refinement: query terms (and, optionally, event features, which capture event $'triggers'$ (indicator terms) and agent/patient roles) are appropriately weighted, and a neural-based system, which better captures textual meaning, retrieves other relevant content. The process of retrieval and marking is repeated as many times as desired, giving rise to increasingly refined queries in each iteration. The final product is a fine-grained query used in Cross-Lingual Information Retrieval (CLIR). Our experiments using analytic tasks and requests from the IARPA BETTER IR datasets show that with a small amount of effort (at most 10 minutes per sub-topic), novice users can form $\textit{useful}$ fine-grained queries including in languages they don't understand. QueryBuilder also provides beneficial capabilities to the traditional corpus exploration and query formation process. A demonstration video is released at https://vimeo.com/734795835
Evaluation of deep convolutional neural networks in classifying human embryo images based on their morphological quality
May 21, 2020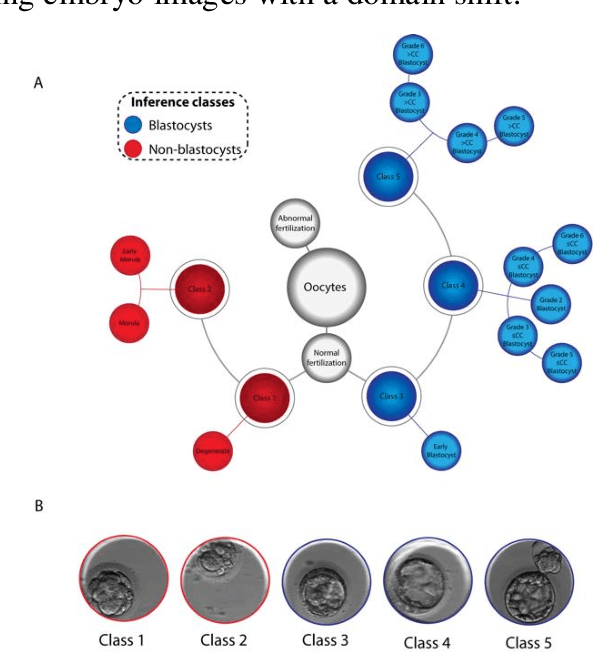
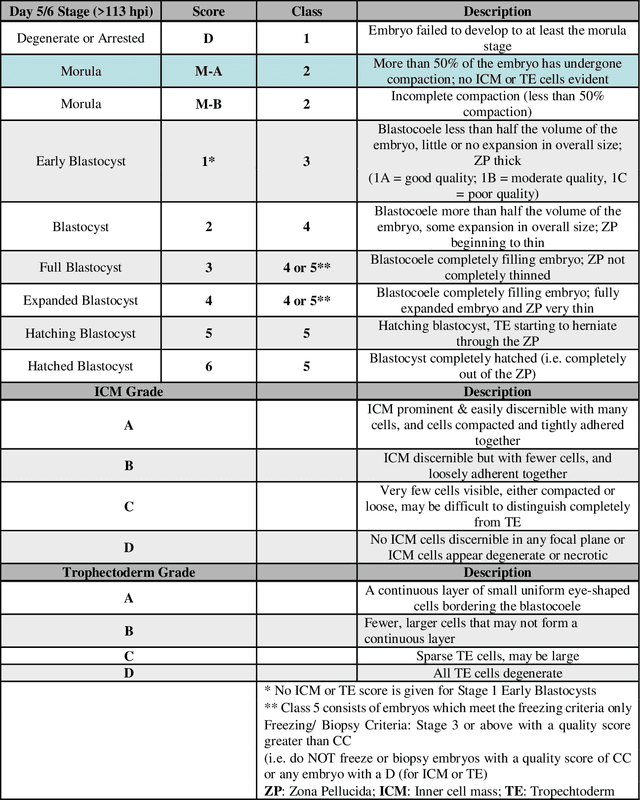

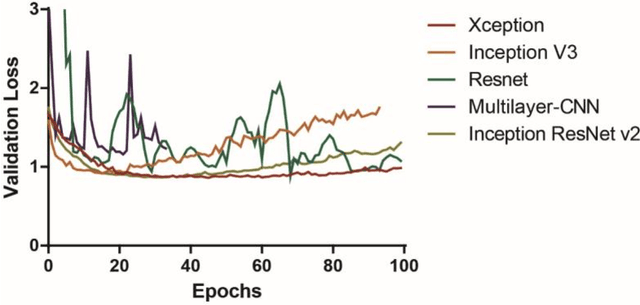
Abstract:A critical factor that influences the success of an in-vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure is the quality of the transferred embryo. Embryo morphology assessments, conventionally performed through manual microscopic analysis suffer from disparities in practice, selection criteria, and subjectivity due to the experience of the embryologist. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are powerful, promising algorithms with significant potential for accurate classifications across many object categories. Network architectures and hyper-parameters affect the efficiency of CNNs for any given task. Here, we evaluate multi-layered CNNs developed from scratch and popular deep-learning architectures such as Inception v3, ResNET, Inception-ResNET-v2, and Xception in differentiating between embryos based on their morphological quality at 113 hours post insemination (hpi). Xception performed the best in differentiating between the embryos based on their morphological quality.
Deep learning mediated single time-point image-based prediction of embryo developmental outcome at the cleavage stage
May 21, 2020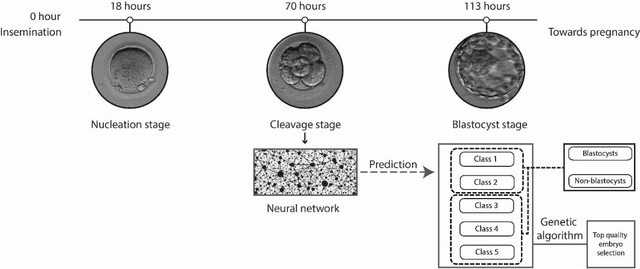

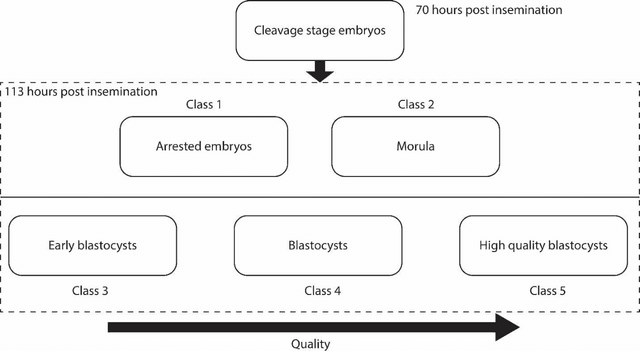
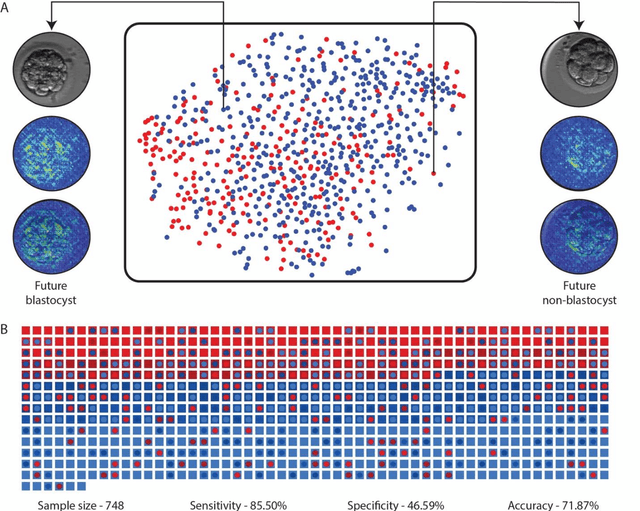
Abstract:In conventional clinical in-vitro fertilization practices embryos are transferred either at the cleavage or blastocyst stages of development. Cleavage stage transfers, particularly, are beneficial for patients with relatively poor prognosis and at fertility centers in resource-limited settings where there is a higher chance of developmental failure in embryos in-vitro. However, one of the major limitations of embryo selections at the cleavage stage is the availability of very low number of manually discernable features to predict developmental outcomes. Although, time-lapse imaging systems have been proposed as possible solutions, they are cost-prohibitive and require bulky and expensive hardware, and labor-intensive. Advances in convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been utilized to provide accurate classifications across many medical and non-medical object categories. Here, we report an automated system for classification and selection of human embryos at the cleavage stage using a trained CNN combined with a genetic algorithm. The system selected the cleavage stage embryo at 70 hours post insemination (hpi) that ultimately developed into top-quality blastocyst at 70 hpi with 64% accuracy, outperforming the abilities of embryologists in identifying embryos with the highest developmental potential. Such systems can have a significant impact on IVF procedures by empowering embryologists for accurate and consistent embryo assessment in both resource-poor and resource-rich settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge