Heejeong Nam
When AI Co-Scientists Fail: SPOT-a Benchmark for Automated Verification of Scientific Research
May 17, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have fueled the vision of automated scientific discovery, often called AI Co-Scientists. To date, prior work casts these systems as generative co-authors responsible for crafting hypotheses, synthesizing code, or drafting manuscripts. In this work, we explore a complementary application: using LLMs as verifiers to automate the \textbf{academic verification of scientific manuscripts}. To that end, we introduce SPOT, a dataset of 83 published papers paired with 91 errors significant enough to prompt errata or retraction, cross-validated with actual authors and human annotators. Evaluating state-of-the-art LLMs on SPOT, we find that none surpasses 21.1\% recall or 6.1\% precision (o3 achieves the best scores, with all others near zero). Furthermore, confidence estimates are uniformly low, and across eight independent runs, models rarely rediscover the same errors, undermining their reliability. Finally, qualitative analysis with domain experts reveals that even the strongest models make mistakes resembling student-level misconceptions derived from misunderstandings. These findings highlight the substantial gap between current LLM capabilities and the requirements for dependable AI-assisted academic verification.
An Adversarial Learning Approach to Irregular Time-Series Forecasting
Nov 28, 2024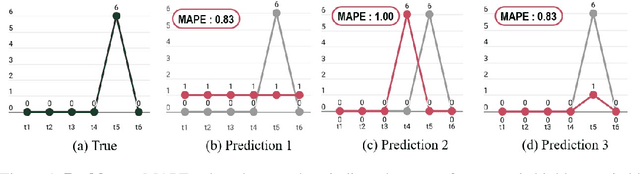
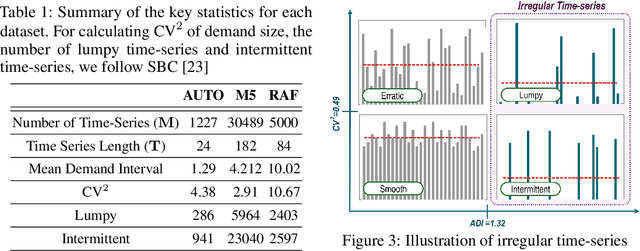
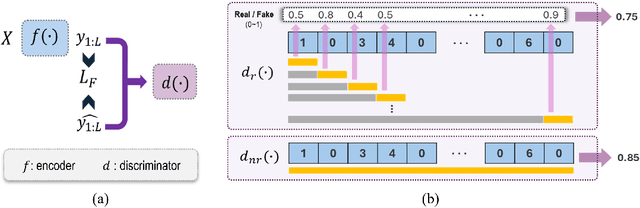
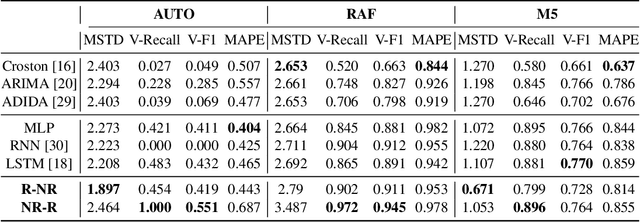
Abstract:Forecasting irregular time series presents significant challenges due to two key issues: the vulnerability of models to mean regression, driven by the noisy and complex nature of the data, and the limitations of traditional error-based evaluation metrics, which fail to capture meaningful patterns and penalize unrealistic forecasts. These problems result in forecasts that often misalign with human intuition. To tackle these challenges, we propose an adversarial learning framework with a deep analysis of adversarial components. Specifically, we emphasize the importance of balancing the modeling of global distribution (overall patterns) and transition dynamics (localized temporal changes) to better capture the nuances of irregular time series. Overall, this research provides practical insights for improving models and evaluation metrics, and pioneers the application of adversarial learning in the domian of irregular time-series forecasting.
Visual Contexts Clarify Ambiguous Expressions: A Benchmark Dataset
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:The ability to perform complex reasoning across multimodal inputs is essential for models to effectively interact with humans in real-world scenarios. Advancements in vision-language models have significantly improved performance on tasks that require processing explicit and direct textual inputs, such as Visual Question Answering (VQA) and Visual Grounding (VG). However, less attention has been given to improving the model capabilities to comprehend nuanced and ambiguous forms of communication. This presents a critical challenge, as human language in real-world interactions often convey hidden intentions that rely on context for accurate interpretation. To address this gap, we propose VAGUE, a multimodal benchmark comprising 3.9K indirect human utterances paired with corresponding scenes. Additionally, we contribute a model-based pipeline for generating prompt-solution pairs from input images. Our work aims to delve deeper into the ability of models to understand indirect communication and seek to contribute to the development of models capable of more refined and human-like interactions. Extensive evaluation on multiple VLMs reveals that mainstream models still struggle with indirect communication when required to perform complex linguistic and visual reasoning. We release our code and data at https://github.com/Hazel-Heejeong-Nam/VAGUE.git.
Compact and De-biased Negative Instance Embedding for Multi-Instance Learning on Whole-Slide Image Classification
Feb 16, 2024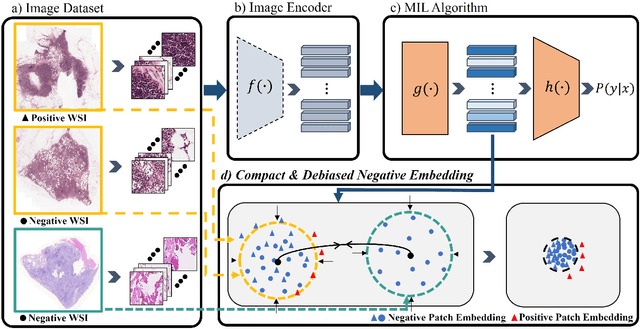
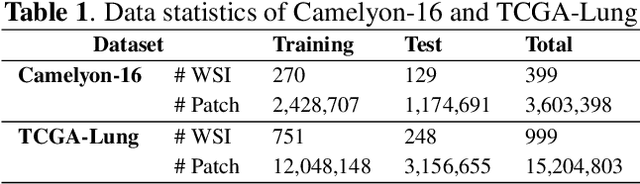
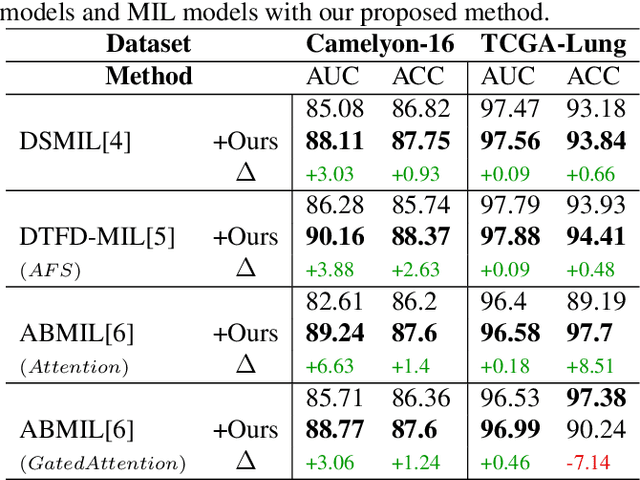
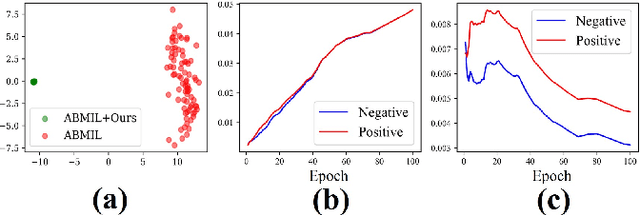
Abstract:Whole-slide image (WSI) classification is a challenging task because 1) patches from WSI lack annotation, and 2) WSI possesses unnecessary variability, e.g., stain protocol. Recently, Multiple-Instance Learning (MIL) has made significant progress, allowing for classification based on slide-level, rather than patch-level, annotations. However, existing MIL methods ignore that all patches from normal slides are normal. Using this free annotation, we introduce a semi-supervision signal to de-bias the inter-slide variability and to capture the common factors of variation within normal patches. Because our method is orthogonal to the MIL algorithm, we evaluate our method on top of the recently proposed MIL algorithms and also compare the performance with other semi-supervised approaches. We evaluate our method on two public WSI datasets including Camelyon-16 and TCGA lung cancer and demonstrate that our approach significantly improves the predictive performance of existing MIL algorithms and outperforms other semi-supervised algorithms. We release our code at https://github.com/AITRICS/pathology_mil.
SCADI: Self-supervised Causal Disentanglement in Latent Variable Models
Nov 11, 2023



Abstract:Causal disentanglement has great potential for capturing complex situations. However, there is a lack of practical and efficient approaches. It is already known that most unsupervised disentangling methods are unable to produce identifiable results without additional information, often leading to randomly disentangled output. Therefore, most existing models for disentangling are weakly supervised, providing information about intrinsic factors, which incurs excessive costs. Therefore, we propose a novel model, SCADI(SElf-supervised CAusal DIsentanglement), that enables the model to discover semantic factors and learn their causal relationships without any supervision. This model combines a masked structural causal model (SCM) with a pseudo-label generator for causal disentanglement, aiming to provide a new direction for self-supervised causal disentanglement models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge