Hechuan Wen
Efficient Content-based Recommendation Model Training via Noise-aware Coreset Selection
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Content-based recommendation systems (CRSs) utilize content features to predict user-item interactions, serving as essential tools for helping users navigate information-rich web services. However, ensuring the effectiveness of CRSs requires large-scale and even continuous model training to accommodate diverse user preferences, resulting in significant computational costs and resource demands. A promising approach to this challenge is coreset selection, which identifies a small but representative subset of data samples that preserves model quality while reducing training overhead. Yet, the selected coreset is vulnerable to the pervasive noise in user-item interactions, particularly when it is minimally sized. To this end, we propose Noise-aware Coreset Selection (NaCS), a specialized framework for CRSs. NaCS constructs coresets through submodular optimization based on training gradients, while simultaneously correcting noisy labels using a progressively trained model. Meanwhile, we refine the selected coreset by filtering out low-confidence samples through uncertainty quantification, thereby avoid training with unreliable interactions. Through extensive experiments, we show that NaCS produces higher-quality coresets for CRSs while achieving better efficiency than existing coreset selection techniques. Notably, NaCS recovers 93-95\% of full-dataset training performance using merely 1\% of the training data. The source code is available at \href{https://github.com/chenxing1999/nacs}{https://github.com/chenxing1999/nacs}.
Enhancing Treatment Effect Estimation via Active Learning: A Counterfactual Covering Perspective
May 08, 2025Abstract:Although numerous complex algorithms for treatment effect estimation have been developed in recent years, their effectiveness remains limited when handling insufficiently labeled training sets due to the high cost of labeling the effect after treatment, e.g., expensive tumor imaging or biopsy procedures needed to evaluate treatment effects. Therefore, it becomes essential to actively incorporate more high-quality labeled data, all while adhering to a constrained labeling budget. To enable data-efficient treatment effect estimation, we formalize the problem through rigorous theoretical analysis within the active learning context, where the derived key measures -- \textit{factual} and \textit{counterfactual covering radius} determine the risk upper bound. To reduce the bound, we propose a greedy radius reduction algorithm, which excels under an idealized, balanced data distribution. To generalize to more realistic data distributions, we further propose FCCM, which transforms the optimization objective into the \textit{Factual} and \textit{Counterfactual Coverage Maximization} to ensure effective radius reduction during data acquisition. Furthermore, benchmarking FCCM against other baselines demonstrates its superiority across both fully synthetic and semi-synthetic datasets.
Progressive Generalization Risk Reduction for Data-Efficient Causal Effect Estimation
Nov 18, 2024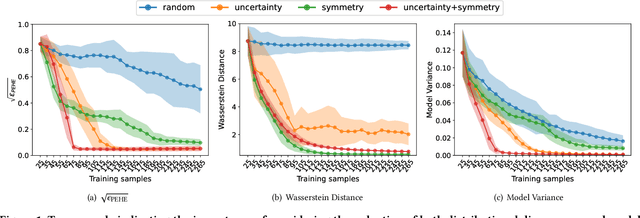
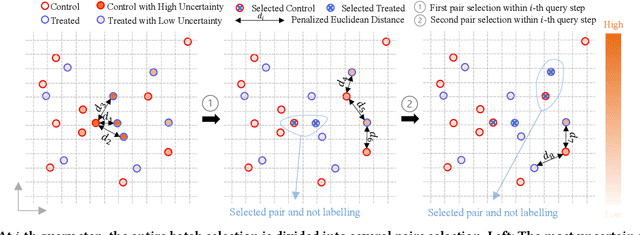
Abstract:Causal effect estimation (CEE) provides a crucial tool for predicting the unobserved counterfactual outcome for an entity. As CEE relaxes the requirement for ``perfect'' counterfactual samples (e.g., patients with identical attributes and only differ in treatments received) that are impractical to obtain and can instead operate on observational data, it is usually used in high-stake domains like medical treatment effect prediction. Nevertheless, in those high-stake domains, gathering a decently sized, fully labelled observational dataset remains challenging due to hurdles associated with costs, ethics, expertise and time needed, etc., of which medical treatment surveys are a typical example. Consequently, if the training dataset is small in scale, low generalization risks can hardly be achieved on any CEE algorithms. Unlike existing CEE methods that assume the constant availability of a dataset with abundant samples, in this paper, we study a more realistic CEE setting where the labelled data samples are scarce at the beginning, while more can be gradually acquired over the course of training -- assuredly under a limited budget considering their expensive nature. Then, the problem naturally comes down to actively selecting the best possible samples to be labelled, e.g., identifying the next subset of patients to conduct the treatment survey. However, acquiring quality data for reducing the CEE risk under limited labelling budgets remains under-explored until now. To fill the gap, we theoretically analyse the generalization risk from an intriguing perspective of progressively shrinking its upper bound, and develop a principled label acquisition pipeline exclusively for CEE tasks. With our analysis, we propose the Model Agnostic Causal Active Learning (MACAL) algorithm for batch-wise label acquisition, which aims to reduce both the CEE model's uncertainty and the post-acquisition ...
To Predict or to Reject: Causal Effect Estimation with Uncertainty on Networked Data
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:Due to the imbalanced nature of networked observational data, the causal effect predictions for some individuals can severely violate the positivity/overlap assumption, rendering unreliable estimations. Nevertheless, this potential risk of individual-level treatment effect estimation on networked data has been largely under-explored. To create a more trustworthy causal effect estimator, we propose the uncertainty-aware graph deep kernel learning (GraphDKL) framework with Lipschitz constraint to model the prediction uncertainty with Gaussian process and identify unreliable estimations. To the best of our knowledge, GraphDKL is the first framework to tackle the violation of positivity assumption when performing causal effect estimation with graphs. With extensive experiments, we demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method in uncertainty-aware causal effect estimation on networked data.
Variational Counterfactual Prediction under Runtime Domain Corruption
Jun 23, 2023



Abstract:To date, various neural methods have been proposed for causal effect estimation based on observational data, where a default assumption is the same distribution and availability of variables at both training and inference (i.e., runtime) stages. However, distribution shift (i.e., domain shift) could happen during runtime, and bigger challenges arise from the impaired accessibility of variables. This is commonly caused by increasing privacy and ethical concerns, which can make arbitrary variables unavailable in the entire runtime data and imputation impractical. We term the co-occurrence of domain shift and inaccessible variables runtime domain corruption, which seriously impairs the generalizability of a trained counterfactual predictor. To counter runtime domain corruption, we subsume counterfactual prediction under the notion of domain adaptation. Specifically, we upper-bound the error w.r.t. the target domain (i.e., runtime covariates) by the sum of source domain error and inter-domain distribution distance. In addition, we build an adversarially unified variational causal effect model, named VEGAN, with a novel two-stage adversarial domain adaptation scheme to reduce the latent distribution disparity between treated and control groups first, and between training and runtime variables afterwards. We demonstrate that VEGAN outperforms other state-of-the-art baselines on individual-level treatment effect estimation in the presence of runtime domain corruption on benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge