Harsimrat Kaeley
Support for Stock Trend Prediction Using Transformers and Sentiment Analysis
May 18, 2023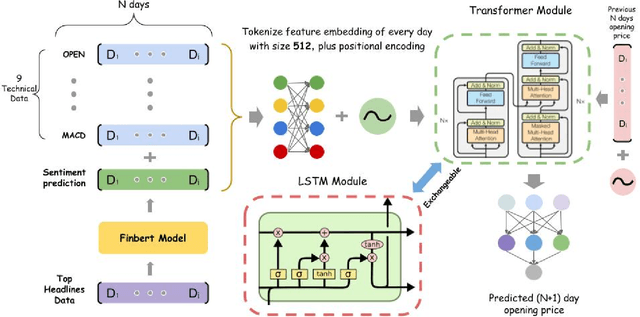
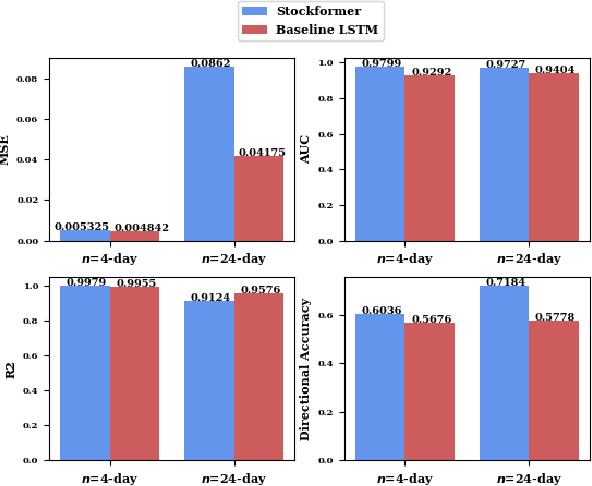
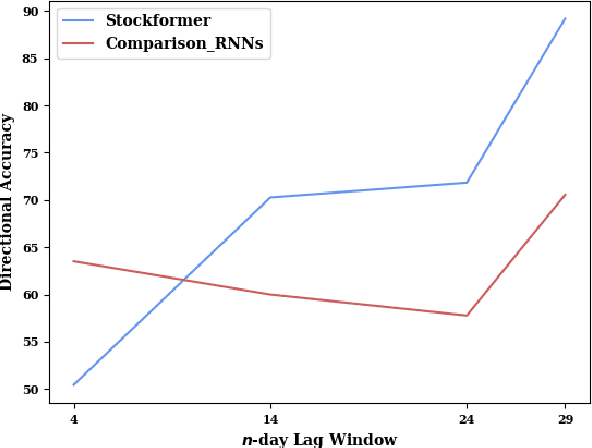
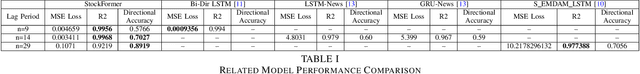
Abstract:Stock trend analysis has been an influential time-series prediction topic due to its lucrative and inherently chaotic nature. Many models looking to accurately predict the trend of stocks have been based on Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). However, due to the limitations of RNNs, such as gradient vanish and long-term dependencies being lost as sequence length increases, in this paper we develop a Transformer based model that uses technical stock data and sentiment analysis to conduct accurate stock trend prediction over long time windows. This paper also introduces a novel dataset containing daily technical stock data and top news headline data spanning almost three years. Stock prediction based solely on technical data can suffer from lag caused by the inability of stock indicators to effectively factor in breaking market news. The use of sentiment analysis on top headlines can help account for unforeseen shifts in market conditions caused by news coverage. We measure the performance of our model against RNNs over sequence lengths spanning 5 business days to 30 business days to mimic different length trading strategies. This reveals an improvement in directional accuracy over RNNs as sequence length is increased, with the largest improvement being close to 18.63% at 30 business days.
roadscene2vec: A Tool for Extracting and Embedding Road Scene-Graphs
Sep 02, 2021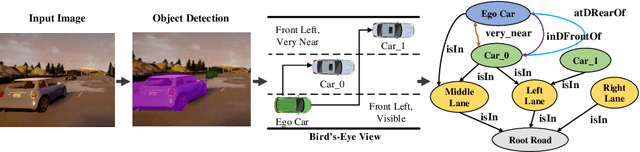
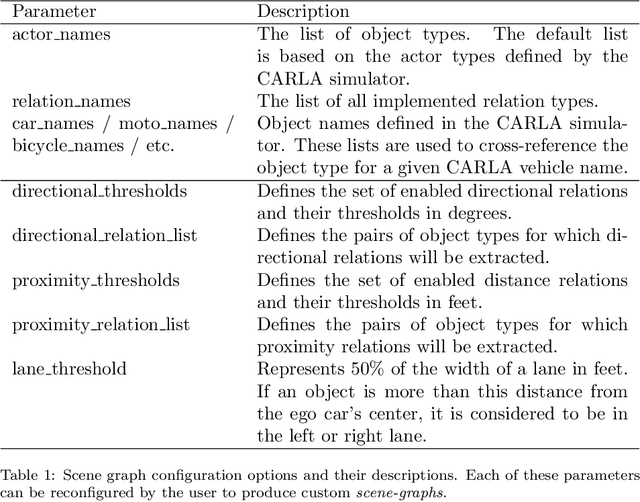
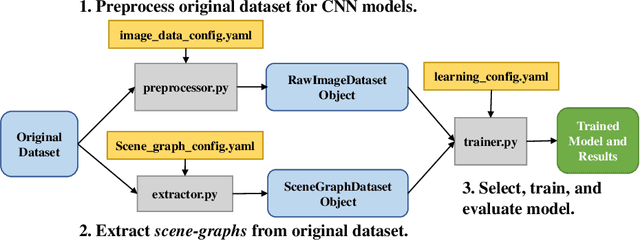
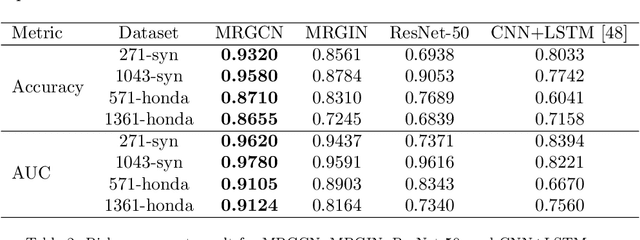
Abstract:Recently, road scene-graph representations used in conjunction with graph learning techniques have been shown to outperform state-of-the-art deep learning techniques in tasks including action classification, risk assessment, and collision prediction. To enable the exploration of applications of road scene-graph representations, we introduce roadscene2vec: an open-source tool for extracting and embedding road scene-graphs. The goal of roadscene2vec is to enable research into the applications and capabilities of road scene-graphs by providing tools for generating scene-graphs, graph learning models to generate spatio-temporal scene-graph embeddings, and tools for visualizing and analyzing scene-graph-based methodologies. The capabilities of roadscene2vec include (i) customized scene-graph generation from either video clips or data from the CARLA simulator, (ii) multiple configurable spatio-temporal graph embedding models and baseline CNN-based models, (iii) built-in functionality for using graph and sequence embeddings for risk assessment and collision prediction applications, (iv) tools for evaluating transfer learning, and (v) utilities for visualizing scene-graphs and analyzing the explainability of graph learning models. We demonstrate the utility of roadscene2vec for these use cases with experimental results and qualitative evaluations for both graph learning models and CNN-based models. roadscene2vec is available at https://github.com/AICPS/roadscene2vec.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge