Harsh Sakhrani
Artificial Intuition: Efficient Classification of Scientific Abstracts
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:It is desirable to coarsely classify short scientific texts, such as grant or publication abstracts, for strategic insight or research portfolio management. These texts efficiently transmit dense information to experts possessing a rich body of knowledge to aid interpretation. Yet this task is remarkably difficult to automate because of brevity and the absence of context. To address this gap, we have developed a novel approach to generate and appropriately assign coarse domain-specific labels. We show that a Large Language Model (LLM) can provide metadata essential to the task, in a process akin to the augmentation of supplemental knowledge representing human intuition, and propose a workflow. As a pilot study, we use a corpus of award abstracts from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). We develop new assessment tools in concert with established performance metrics.
Coral: An Approach for Conversational Agents in Mental Health Applications
Nov 16, 2021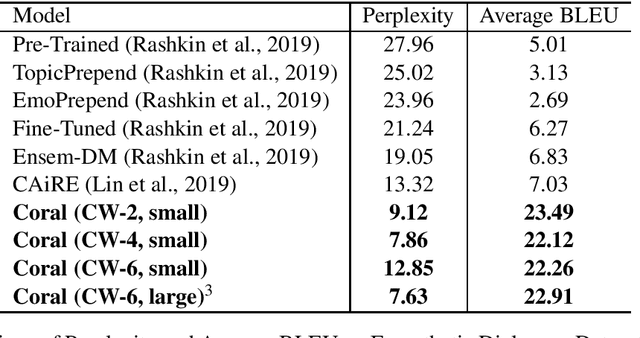
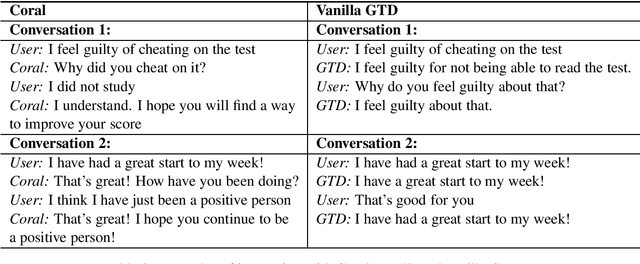
Abstract:It may be difficult for some individuals to open up and share their thoughts and feelings in front of a mental health expert. For those who are more at ease with a virtual agent, conversational agents can serve as an intermediate step in the right direction. The conversational agent must therefore be empathetic and able to conduct free-flowing conversations. To this effect, we present an approach for creating a generative empathetic open-domain chatbot that can be used for mental health applications. We leverage large scale pre-training and empathetic conversational data to make the responses more empathetic in nature and a multi-turn dialogue arrangement to maintain context. Our models achieve state-of-the-art results on the Empathetic Dialogues test set.
Investigating the Relationship Between World Development Indicators and the Occurrence of Disease Outbreaks in the 21st Century: A Case Study
Sep 20, 2021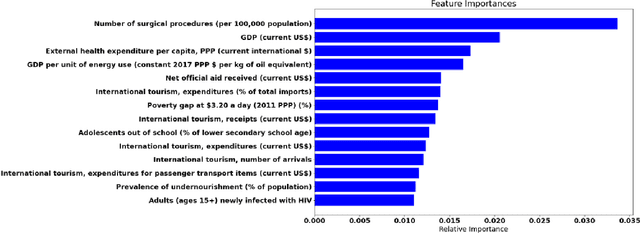


Abstract:The timely identification of socio-economic sectors vulnerable to a disease outbreak presents an important challenge to the civic authorities and healthcare workers interested in outbreak mitigation measures. This problem was traditionally solved by studying the aberrances in small-scale healthcare data. In this paper, we leverage data driven models to determine the relationship between the trends of World Development Indicators and occurrence of disease outbreaks using worldwide historical data from 2000-2019, and treat it as a classic supervised classification problem. CART based feature selection was employed in an unorthodox fashion to determine the covariates getting affected by the disease outbreak, thus giving the most vulnerable sectors. The result involves a comprehensive analysis of different classification algorithms and is indicative of the relationship between the disease outbreak occurrence and the magnitudes of various development indicators.
Modelling Major Disease Outbreaks in the 21st Century: A Causal Approach
Sep 17, 2021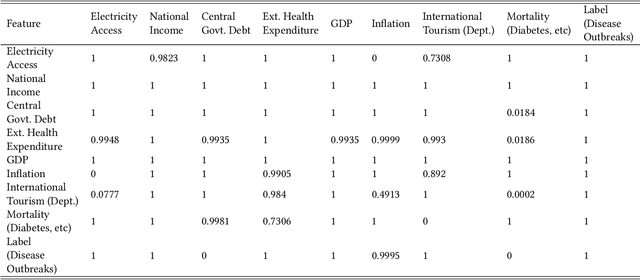
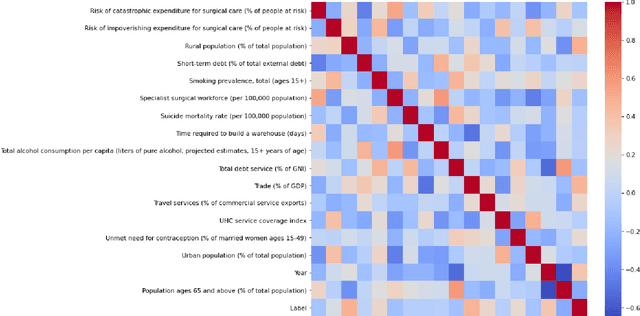
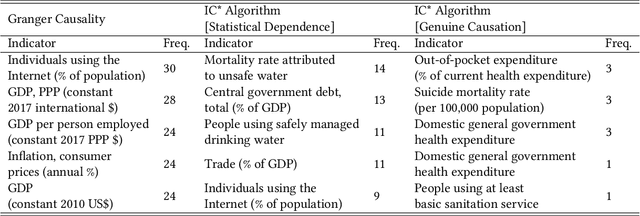
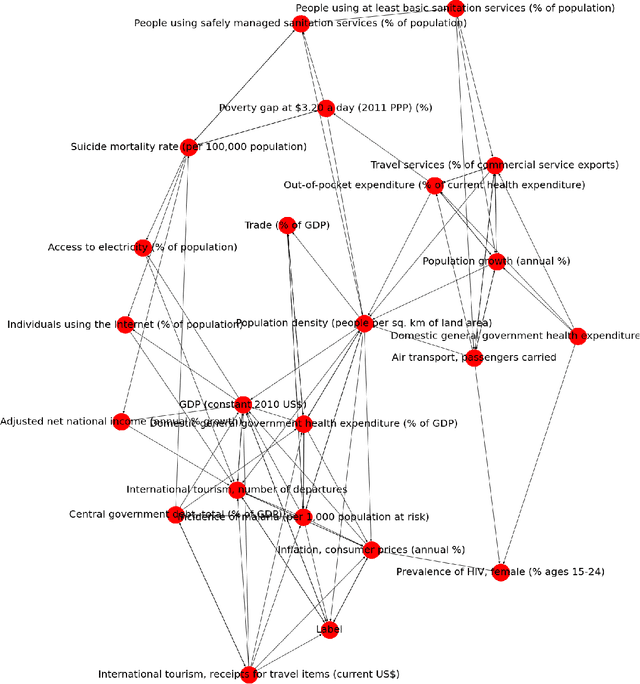
Abstract:Epidemiologists aiming to model the dynamics of global events face a significant challenge in identifying the factors linked with anomalies such as disease outbreaks. In this paper, we present a novel method for identifying the most important development sectors sensitive to disease outbreaks by using global development indicators as markers. We use statistical methods to assess the causative linkages between these indicators and disease outbreaks, as well as to find the most often ranked indicators. We used data imputation techniques in addition to statistical analysis to convert raw real-world data sets into meaningful data for causal inference. The application of various algorithms for the detection of causal linkages between the indicators is the subject of this research. Despite the fact that disparities in governmental policies between countries account for differences in causal linkages, several indicators emerge as important determinants sensitive to disease outbreaks over the world in the 21st Century.
Contextualized Embeddings based Convolutional Neural Networks for Duplicate Question Identification
Sep 06, 2021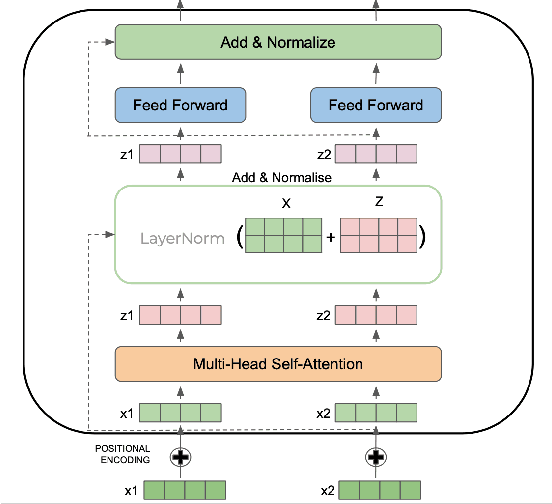

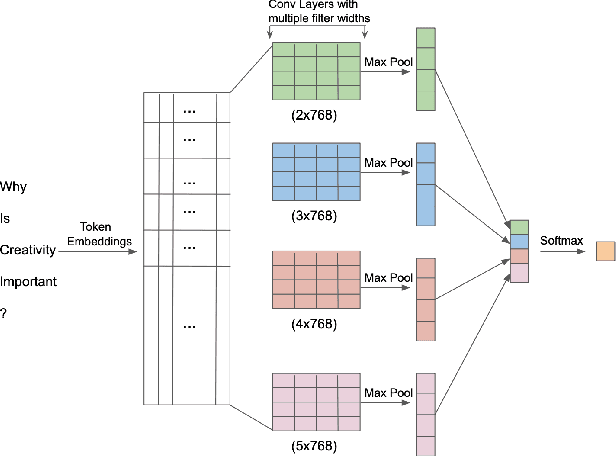
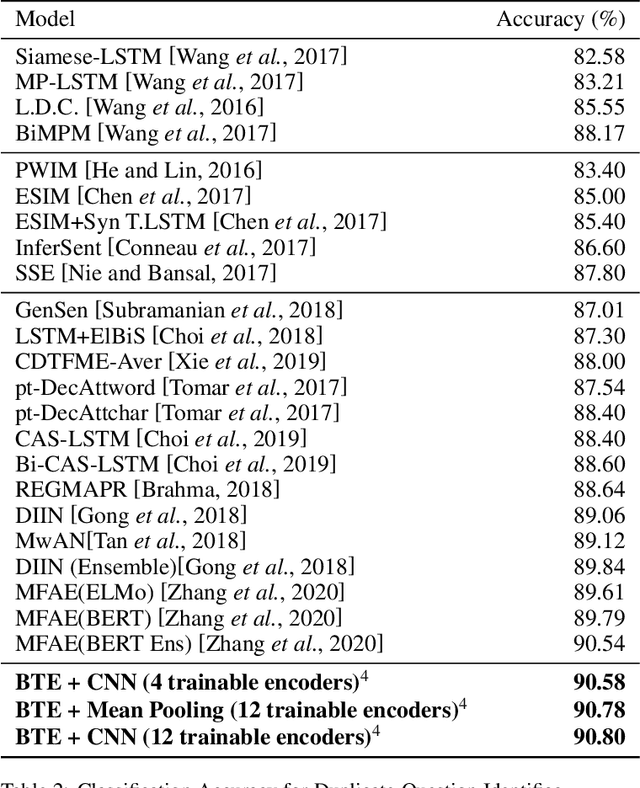
Abstract:Question Paraphrase Identification (QPI) is a critical task for large-scale Question-Answering forums. The purpose of QPI is to determine whether a given pair of questions are semantically identical or not. Previous approaches for this task have yielded promising results, but have often relied on complex recurrence mechanisms that are expensive and time-consuming in nature. In this paper, we propose a novel architecture combining a Bidirectional Transformer Encoder with Convolutional Neural Networks for the QPI task. We produce the predictions from the proposed architecture using two different inference setups: Siamese and Matched Aggregation. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Quora Question Pairs dataset. We empirically prove that the addition of convolution layers to the model architecture improves the results in both inference setups. We also investigate the impact of partial and complete fine-tuning and analyze the trade-off between computational power and accuracy in the process. Based on the obtained results, we conclude that the Matched-Aggregation setup consistently outperforms the Siamese setup. Our work provides insights into what architecture combinations and setups are likely to produce better results for the QPI task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge