Modelling Major Disease Outbreaks in the 21st Century: A Causal Approach
Paper and Code
Sep 17, 2021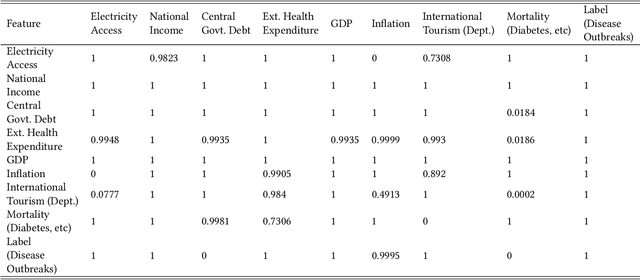
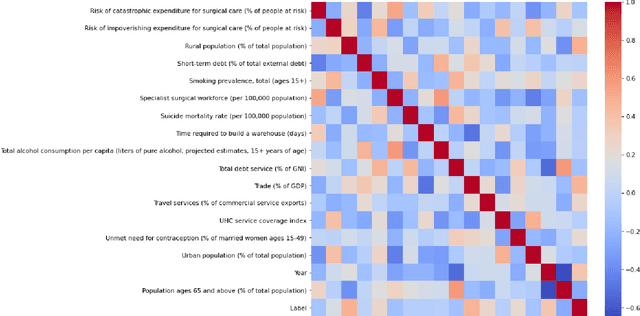
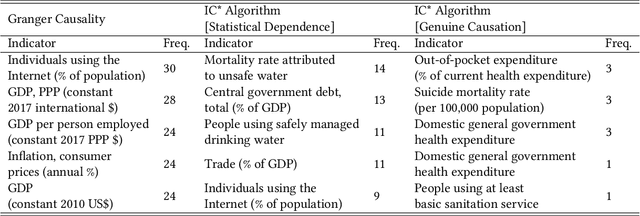
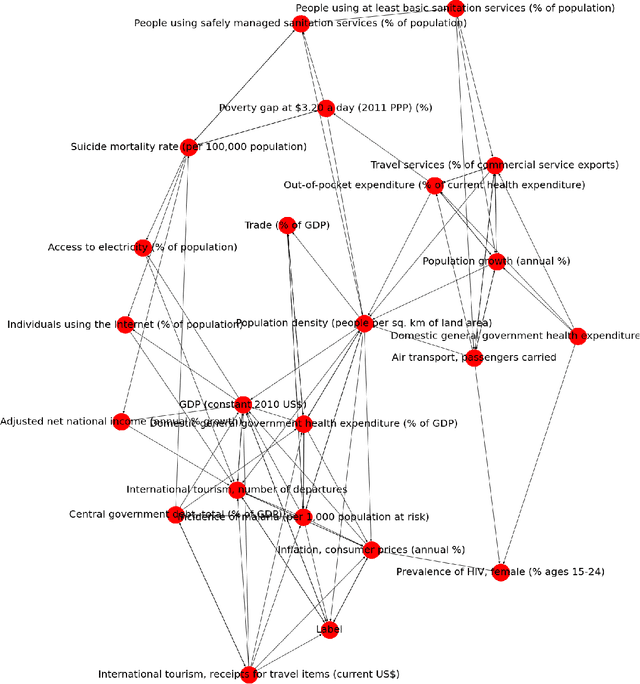
Epidemiologists aiming to model the dynamics of global events face a significant challenge in identifying the factors linked with anomalies such as disease outbreaks. In this paper, we present a novel method for identifying the most important development sectors sensitive to disease outbreaks by using global development indicators as markers. We use statistical methods to assess the causative linkages between these indicators and disease outbreaks, as well as to find the most often ranked indicators. We used data imputation techniques in addition to statistical analysis to convert raw real-world data sets into meaningful data for causal inference. The application of various algorithms for the detection of causal linkages between the indicators is the subject of this research. Despite the fact that disparities in governmental policies between countries account for differences in causal linkages, several indicators emerge as important determinants sensitive to disease outbreaks over the world in the 21st Century.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge