Haozhan Sun
Development and Application of a Monte Carlo Tree Search Algorithm for Simulating Da Vinci Code Game Strategies
Mar 15, 2024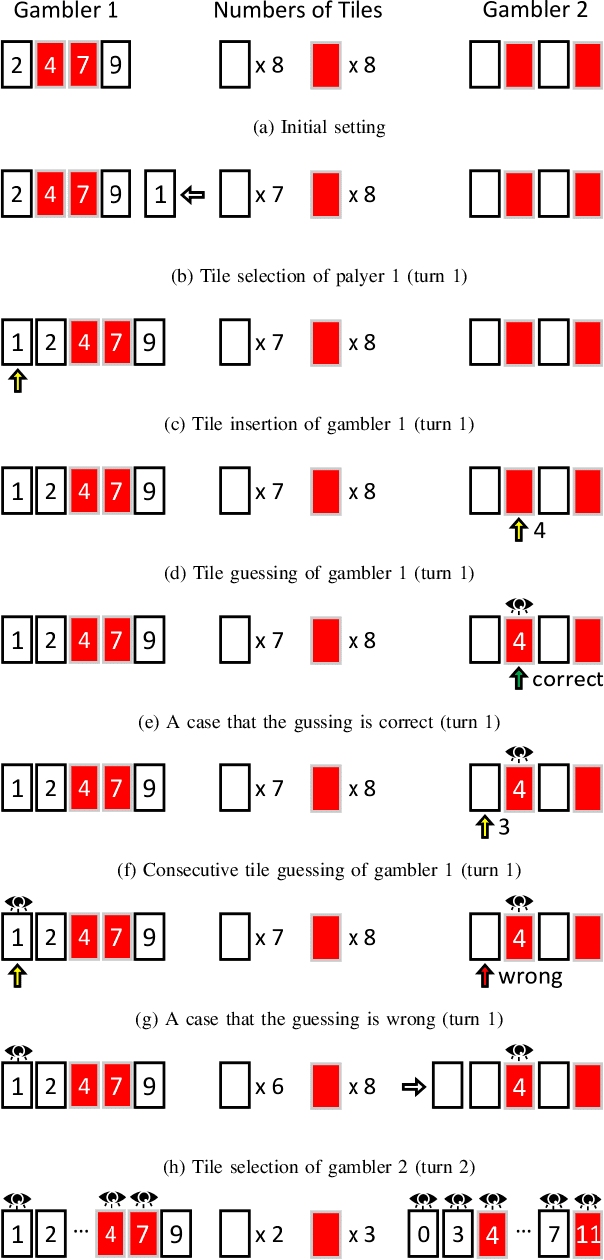
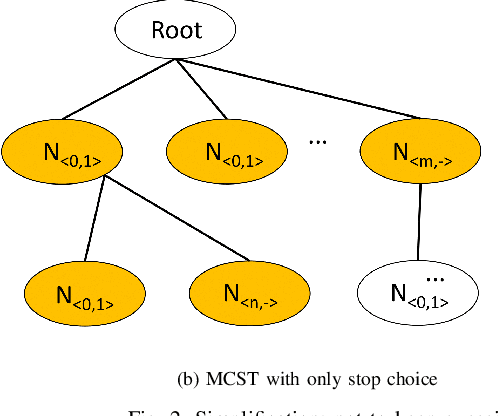
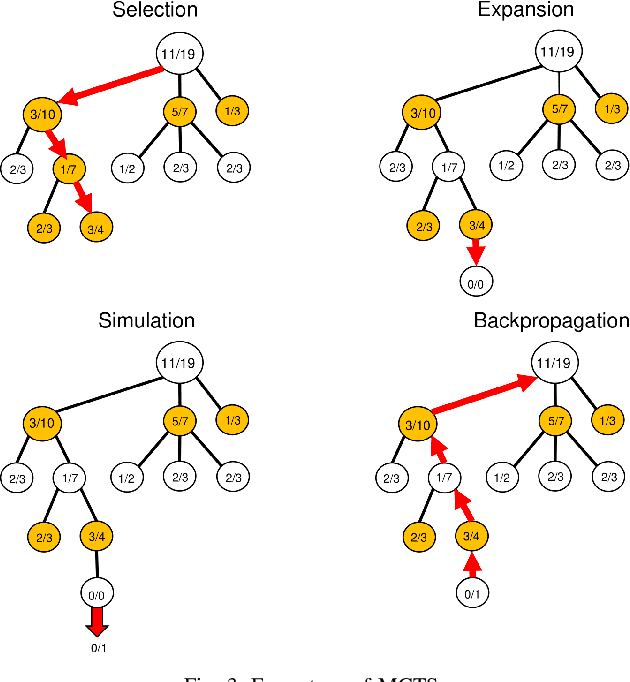
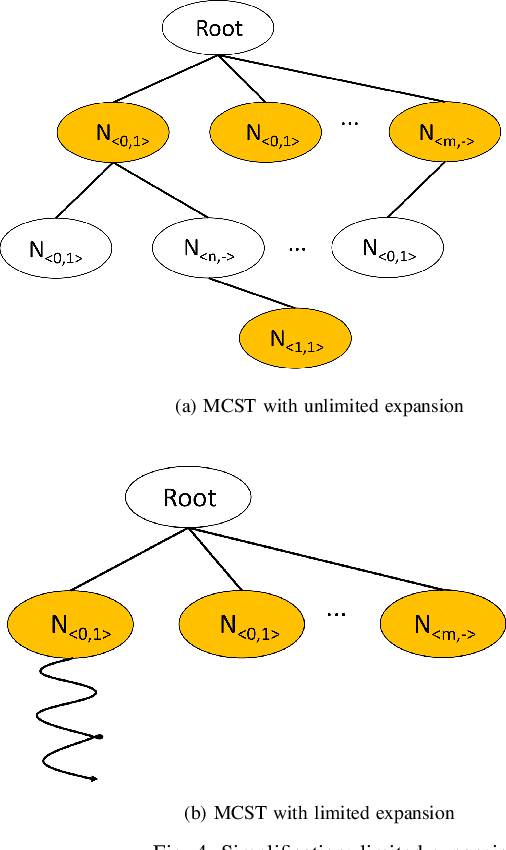
Abstract:In this study, we explore the efficiency of the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), a prominent decision-making algorithm renowned for its effectiveness in complex decision environments, contingent upon the volume of simulations conducted. Notwithstanding its broad applicability, the algorithm's performance can be adversely impacted in certain scenarios, particularly within the domain of game strategy development. This research posits that the inherent branch divergence within the Da Vinci Code board game significantly impedes parallelism when executed on Graphics Processing Units (GPUs). To investigate this hypothesis, we implemented and meticulously evaluated two variants of the MCTS algorithm, specifically designed to assess the impact of branch divergence on computational performance. Our comparative analysis reveals a linear improvement in performance with the CPU-based implementation, in stark contrast to the GPU implementation, which exhibits a non-linear enhancement pattern and discernible performance troughs. These findings contribute to a deeper understanding of the MCTS algorithm's behavior in divergent branch scenarios, highlighting critical considerations for optimizing game strategy algorithms on parallel computing architectures.
Analyzing the Granularity and Cost of Annotation in Clinical Sequence Labeling
Aug 23, 2021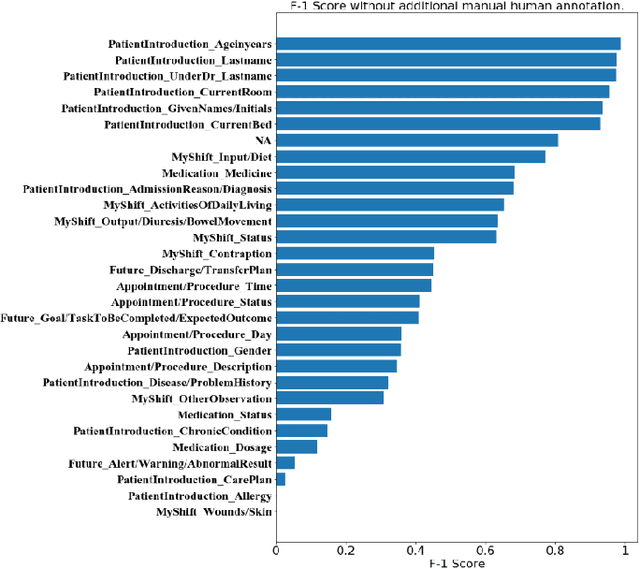
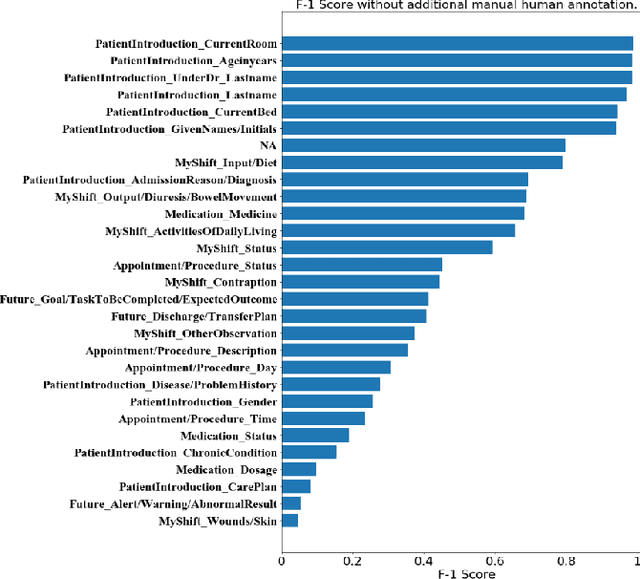
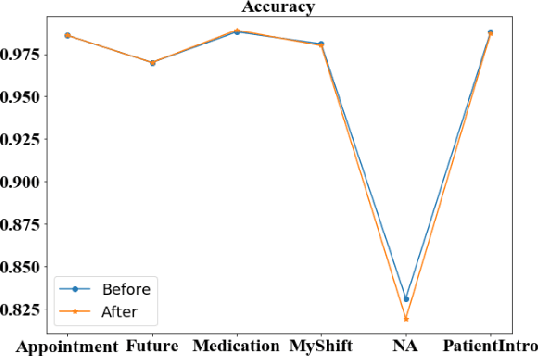
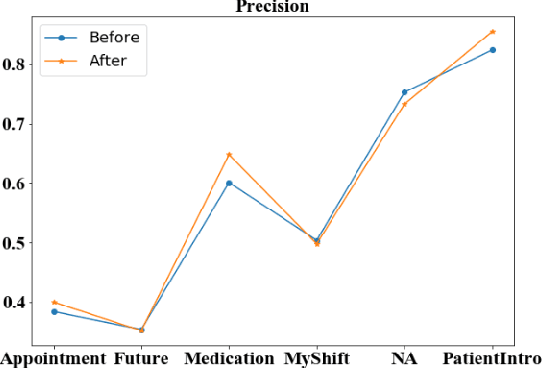
Abstract:Well-annotated datasets, as shown in recent top studies, are becoming more important for researchers than ever before in supervised machine learning (ML). However, the dataset annotation process and its related human labor costs remain overlooked. In this work, we analyze the relationship between the annotation granularity and ML performance in sequence labeling, using clinical records from nursing shift-change handover. We first study a model derived from textual language features alone, without additional information based on nursing knowledge. We find that this sequence tagger performs well in most categories under this granularity. Then, we further include the additional manual annotations by a nurse, and find the sequence tagging performance remaining nearly the same. Finally, we give a guideline and reference to the community arguing it is not necessary and even not recommended to annotate in detailed granularity because of a low Return on Investment. Therefore we recommend emphasizing other features, like textual knowledge, for researchers and practitioners as a cost-effective source for increasing the sequence labeling performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge