Han Mei
DPF-Net: Physical Imaging Model Embedded Data-Driven Underwater Image Enhancement
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:Due to the complex interplay of light absorption and scattering in the underwater environment, underwater images experience significant degradation. This research presents a two-stage underwater image enhancement network called the Data-Driven and Physical Parameters Fusion Network (DPF-Net), which harnesses the robustness of physical imaging models alongside the generality and efficiency of data-driven methods. We first train a physical parameter estimate module using synthetic datasets to guarantee the trustworthiness of the physical parameters, rather than solely learning the fitting relationship between raw and reference images by the application of the imaging equation, as is common in prior studies. This module is subsequently trained in conjunction with an enhancement network, where the estimated physical parameters are integrated into a data-driven model within the embedding space. To maintain the uniformity of the restoration process amid underwater imaging degradation, we propose a physics-based degradation consistency loss. Additionally, we suggest an innovative weak reference loss term utilizing the entire dataset, which alleviates our model's reliance on the quality of individual reference images. Our proposed DPF-Net demonstrates superior performance compared to other benchmark methods across multiple test sets, achieving state-of-the-art results. The source code and pre-trained models are available on the project home page: https://github.com/OUCVisionGroup/DPF-Net.
Depth-Assisted Network for Indiscernible Marine Object Counting with Adaptive Motion-Differentiated Feature Encoding
Mar 11, 2025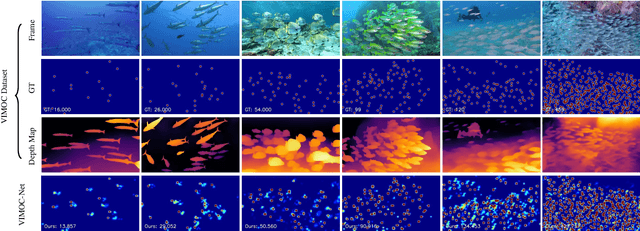
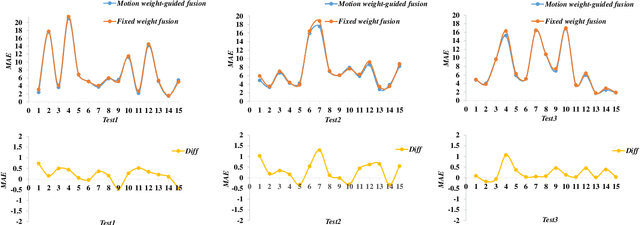
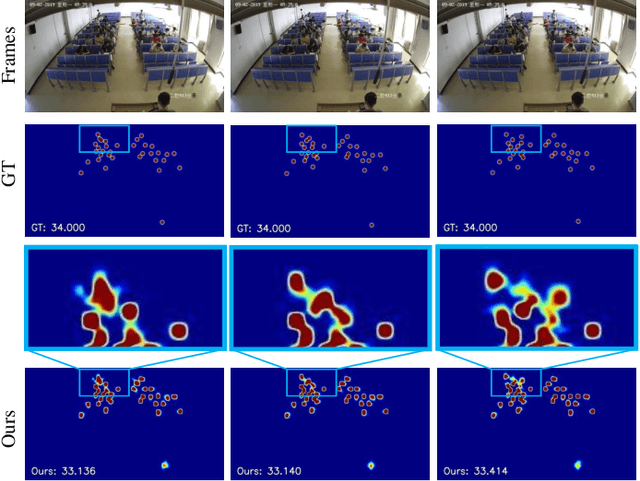
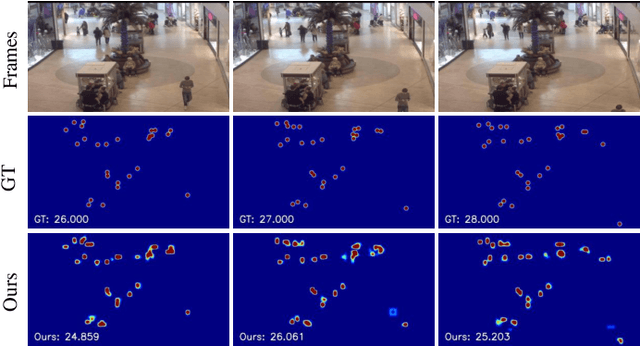
Abstract:Indiscernible marine object counting encounters numerous challenges, including limited visibility in underwater scenes, mutual occlusion and overlap among objects, and the dynamic similarity in appearance, color, and texture between the background and foreground. These factors significantly complicate the counting process. To address the scarcity of video-based indiscernible object counting datasets, we have developed a novel dataset comprising 50 videos, from which approximately 800 frames have been extracted and annotated with around 40,800 point-wise object labels. This dataset accurately represents real underwater environments where indiscernible marine objects are intricately integrated with their surroundings, thereby comprehensively illustrating the aforementioned challenges in object counting. To address these challenges, we propose a depth-assisted network with adaptive motion-differentiated feature encoding. The network consists of a backbone encoding module and three branches: a depth-assisting branch, a density estimation branch, and a motion weight generation branch. Depth-aware features extracted by the depth-assisting branch are enhanced via a depth-enhanced encoder to improve object representation. Meanwhile, weights from the motion weight generation branch refine multi-scale perception features in the adaptive flow estimation module. Experimental results demonstrate that our method not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on the proposed dataset but also yields competitive results on three additional video-based crowd counting datasets. The pre-trained model, code, and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/OUCVisionGroup/VIMOC-Net.
WaterMono: Teacher-Guided Anomaly Masking and Enhancement Boosting for Robust Underwater Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation
Jun 19, 2024



Abstract:Depth information serves as a crucial prerequisite for various visual tasks, whether on land or underwater. Recently, self-supervised methods have achieved remarkable performance on several terrestrial benchmarks despite the absence of depth annotations. However, in more challenging underwater scenarios, they encounter numerous brand-new obstacles such as the influence of marine life and degradation of underwater images, which break the assumption of a static scene and bring low-quality images, respectively. Besides, the camera angles of underwater images are more diverse. Fortunately, we have discovered that knowledge distillation presents a promising approach for tackling these challenges. In this paper, we propose WaterMono, a novel framework for depth estimation coupled with image enhancement. It incorporates the following key measures: (1) We present a Teacher-Guided Anomaly Mask to identify dynamic regions within the images; (2) We employ depth information combined with the Underwater Image Formation Model to generate enhanced images, which in turn contribute to the depth estimation task; and (3) We utilize a rotated distillation strategy to enhance the model's rotational robustness. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method for both depth estimation and image enhancement. The source code and pre-trained models are available on the project home page: https://github.com/OUCVisionGroup/WaterMono.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge