Habibullah Habibullah
Source-Free Cross-Domain Continual Learning
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Although existing cross-domain continual learning approaches successfully address many streaming tasks having domain shifts, they call for a fully labeled source domain hindering their feasibility in the privacy constrained environments. This paper goes one step ahead with the problem of source-free cross-domain continual learning where the use of source-domain samples are completely prohibited. We propose the idea of rehearsal-free frequency-aware dynamic prompt collaborations (REFEREE) to cope with the absence of labeled source-domain samples in realm of cross-domain continual learning. REFEREE is built upon a synergy between a source-pre-trained model and a large-scale vision-language model, thus overcoming the problem of sub-optimal generalizations when relying only on a source pre-trained model. The domain shift problem between the source domain and the target domain is handled by a frequency-aware prompting technique encouraging low-frequency components while suppressing high-frequency components. This strategy generates frequency-aware augmented samples, robust against noisy pseudo labels. The noisy pseudo-label problem is further addressed with the uncertainty-aware weighting strategy where the mean and covariance matrix are weighted by prediction uncertainties, thus mitigating the adverse effects of the noisy pseudo label. Besides, the issue of catastrophic forgetting (CF) is overcome by kernel linear discriminant analysis (KLDA) where the backbone network is frozen while the classification is performed using the linear discriminant analysis approach guided by the random kernel method. Our rigorous numerical studies confirm the advantage of our approach where it beats prior arts having access to source domain samples with significant margins.
Black-Box Time-Series Domain Adaptation via Cross-Prompt Foundation Models
Oct 01, 2025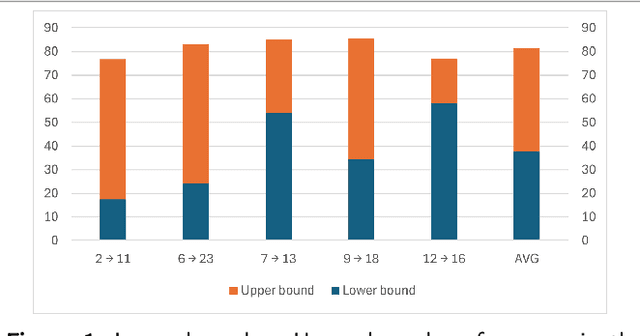
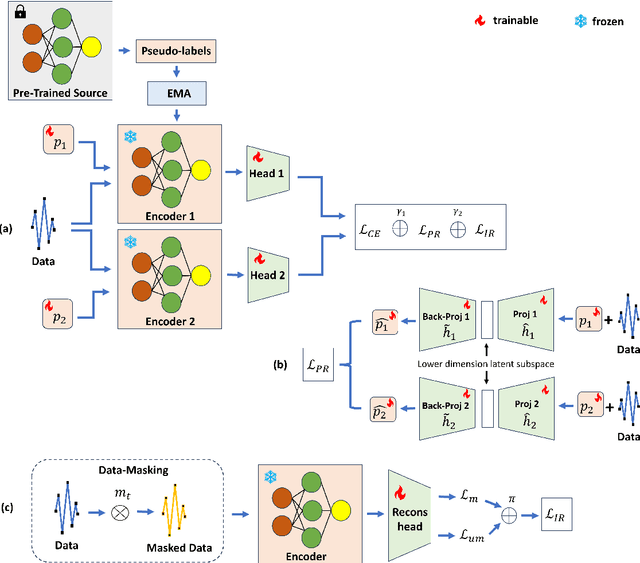
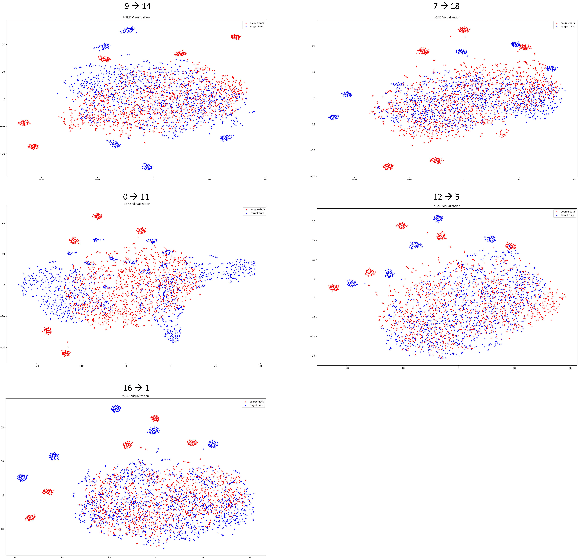
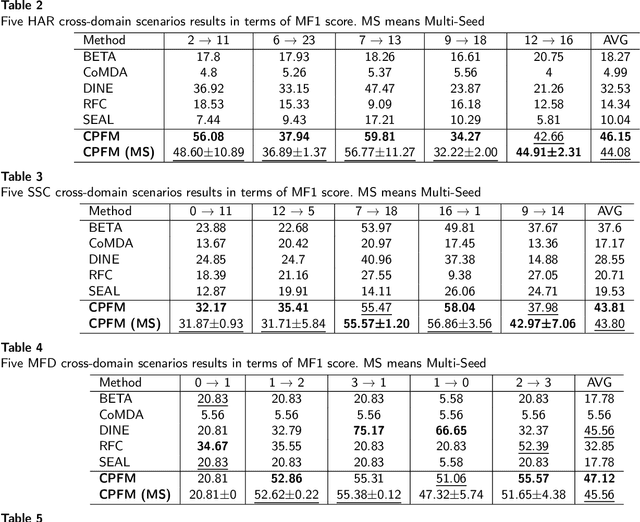
Abstract:The black-box domain adaptation (BBDA) topic is developed to address the privacy and security issues where only an application programming interface (API) of the source model is available for domain adaptations. Although the BBDA topic has attracted growing research attentions, existing works mostly target the vision applications and are not directly applicable to the time-series applications possessing unique spatio-temporal characteristics. In addition, none of existing approaches have explored the strength of foundation model for black box time-series domain adaptation (BBTSDA). This paper proposes a concept of Cross-Prompt Foundation Model (CPFM) for the BBTSDA problems. CPFM is constructed under a dual branch network structure where each branch is equipped with a unique prompt to capture different characteristics of data distributions. In the domain adaptation phase, the reconstruction learning phase in the prompt and input levels is developed. All of which are built upon a time-series foundation model to overcome the spatio-temporal dynamic. Our rigorous experiments substantiate the advantage of CPFM achieving improved results with noticeable margins from its competitors in three time-series datasets of different application domains.
PROL : Rehearsal Free Continual Learning in Streaming Data via Prompt Online Learning
Jul 16, 2025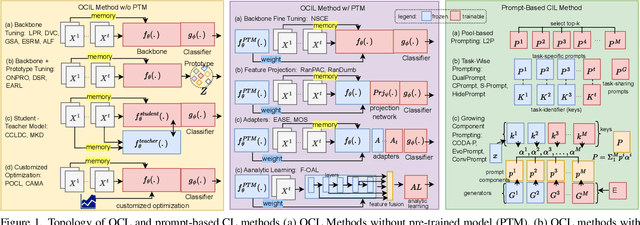
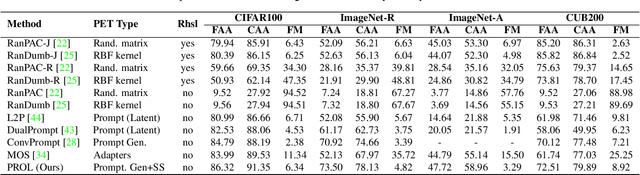
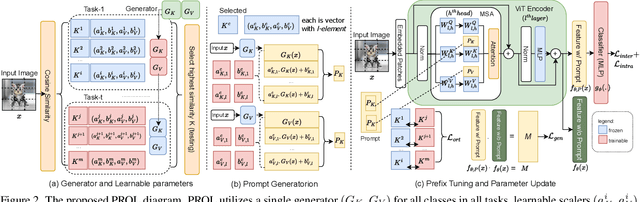
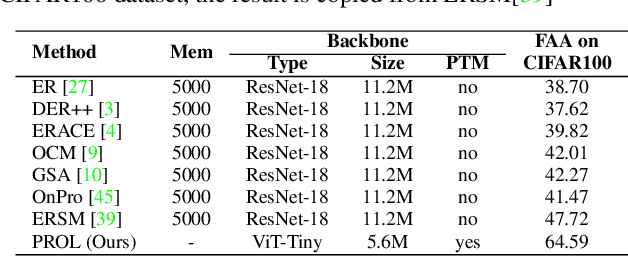
Abstract:The data privacy constraint in online continual learning (OCL), where the data can be seen only once, complicates the catastrophic forgetting problem in streaming data. A common approach applied by the current SOTAs in OCL is with the use of memory saving exemplars or features from previous classes to be replayed in the current task. On the other hand, the prompt-based approach performs excellently in continual learning but with the cost of a growing number of trainable parameters. The first approach may not be applicable in practice due to data openness policy, while the second approach has the issue of throughput associated with the streaming data. In this study, we propose a novel prompt-based method for online continual learning that includes 4 main components: (1) single light-weight prompt generator as a general knowledge, (2) trainable scaler-and-shifter as specific knowledge, (3) pre-trained model (PTM) generalization preserving, and (4) hard-soft updates mechanism. Our proposed method achieves significantly higher performance than the current SOTAs in CIFAR100, ImageNet-R, ImageNet-A, and CUB dataset. Our complexity analysis shows that our method requires a relatively smaller number of parameters and achieves moderate training time, inference time, and throughput. For further study, the source code of our method is available at https://github.com/anwarmaxsum/PROL.
Time and Frequency Synergy for Source-Free Time-Series Domain Adaptations
Oct 23, 2024



Abstract:The issue of source-free time-series domain adaptations still gains scarce research attentions. On the other hand, existing approaches rely solely on time-domain features ignoring frequency components providing complementary information. This paper proposes Time Frequency Domain Adaptation (TFDA), a method to cope with the source-free time-series domain adaptation problems. TFDA is developed with a dual branch network structure fully utilizing both time and frequency features in delivering final predictions. It induces pseudo-labels based on a neighborhood concept where predictions of a sample group are aggregated to generate reliable pseudo labels. The concept of contrastive learning is carried out in both time and frequency domains with pseudo label information and a negative pair exclusion strategy to make valid neighborhood assumptions. In addition, the time-frequency consistency technique is proposed using the self-distillation strategy while the uncertainty reduction strategy is implemented to alleviate uncertainties due to the domain shift problem. Last but not least, the curriculum learning strategy is integrated to combat noisy pseudo labels. Our experiments demonstrate the advantage of our approach over prior arts with noticeable margins in benchmark problems.
PIP: Prototypes-Injected Prompt for Federated Class Incremental Learning
Jul 30, 2024



Abstract:Federated Class Incremental Learning (FCIL) is a new direction in continual learning (CL) for addressing catastrophic forgetting and non-IID data distribution simultaneously. Existing FCIL methods call for high communication costs and exemplars from previous classes. We propose a novel rehearsal-free method for FCIL named prototypes-injected prompt (PIP) that involves 3 main ideas: a) prototype injection on prompt learning, b) prototype augmentation, and c) weighted Gaussian aggregation on the server side. Our experiment result shows that the proposed method outperforms the current state of the arts (SOTAs) with a significant improvement (up to 33%) in CIFAR100, MiniImageNet and TinyImageNet datasets. Our extensive analysis demonstrates the robustness of PIP in different task sizes, and the advantage of requiring smaller participating local clients, and smaller global rounds. For further study, source codes of PIP, baseline, and experimental logs are shared publicly in https://github.com/anwarmaxsum/PIP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge