Guy Kaplan
Follow the Flow: On Information Flow Across Textual Tokens in Text-to-Image Models
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Text-to-Image (T2I) models often suffer from issues such as semantic leakage, incorrect feature binding, and omissions of key concepts in the generated image. This work studies these phenomena by looking into the role of information flow between textual token representations. To this end, we generate images by applying the diffusion component on a subset of contextual token representations in a given prompt and observe several interesting phenomena. First, in many cases, a word or multiword expression is fully represented by one or two tokens, while other tokens are redundant. For example, in "San Francisco's Golden Gate Bridge", the token "gate" alone captures the full expression. We demonstrate the redundancy of these tokens by removing them after textual encoding and generating an image from the resulting representation. Surprisingly, we find that this process not only maintains image generation performance but also reduces errors by 21\% compared to standard generation. We then show that information can also flow between different expressions in a sentence, which often leads to semantic leakage. Based on this observation, we propose a simple, training-free method to mitigate semantic leakage: replacing the leaked item's representation after the textual encoding with its uncontextualized representation. Remarkably, this simple approach reduces semantic leakage by 85\%. Overall, our work provides a comprehensive analysis of information flow across textual tokens in T2I models, offering both novel insights and practical benefits.
From Tokens to Words: On the Inner Lexicon of LLMs
Oct 10, 2024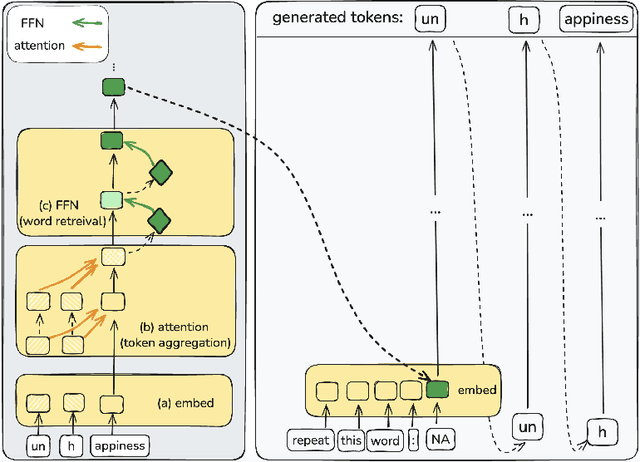
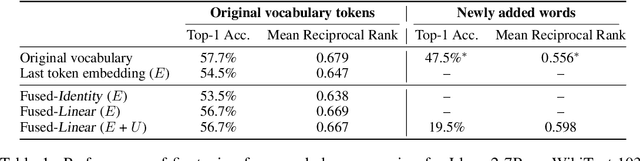
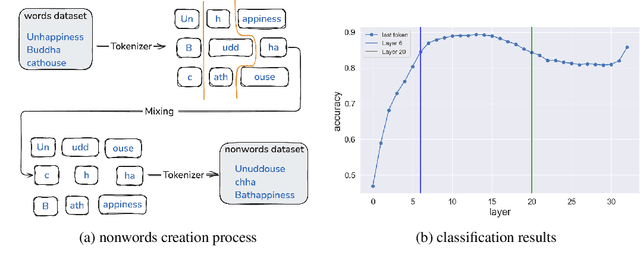
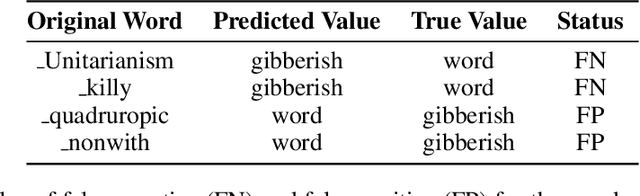
Abstract:Natural language is composed of words, but modern LLMs process sub-words as input. A natural question raised by this discrepancy is whether LLMs encode words internally, and if so how. We present evidence that LLMs engage in an intrinsic detokenization process, where sub-word sequences are combined into coherent word representations. Our experiments show that this process takes place primarily within the early and middle layers of the model. They also show that it is robust to non-morphemic splits, typos and perhaps importantly-to out-of-vocabulary words: when feeding the inner representation of such words to the model as input vectors, it can "understand" them despite never seeing them during training. Our findings suggest that LLMs maintain a latent vocabulary beyond the tokenizer's scope. These insights provide a practical, finetuning-free application for expanding the vocabulary of pre-trained models. By enabling the addition of new vocabulary words, we reduce input length and inference iterations, which reduces both space and model latency, with little to no loss in model accuracy.
State of What Art? A Call for Multi-Prompt LLM Evaluation
Dec 31, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have led to the development of various evaluation benchmarks. These benchmarks typically rely on a single instruction template for evaluating all LLMs on a specific task. In this paper, we comprehensively analyze the brittleness of results obtained via single-prompt evaluations across 6.5M instances, involving 20 different LLMs and 39 tasks from 3 benchmarks. To improve robustness of the analysis, we propose to evaluate LLMs with a set of diverse prompts instead. We discuss tailored evaluation metrics for specific use cases (e.g., LLM developers vs. developers interested in a specific downstream task), ensuring a more reliable and meaningful assessment of LLM capabilities. We then implement these criteria and conduct evaluations of multiple models, providing insights into the true strengths and limitations of current LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge