Guillermo Suarez-Tangil
A Holistic Indicator of Polarization to Measure Online Sexism
Apr 02, 2024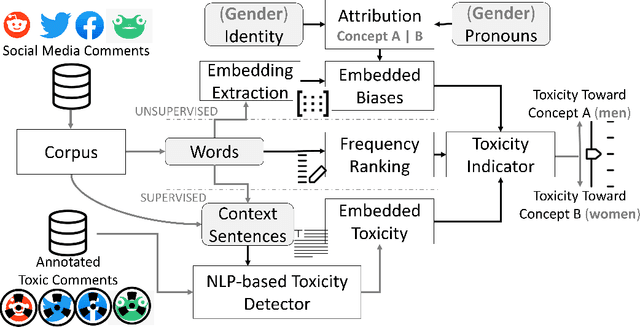

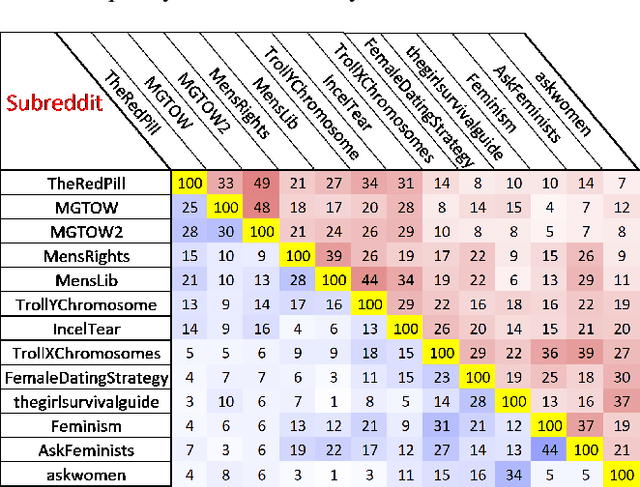
Abstract:The online trend of the manosphere and feminist discourse on social networks requires a holistic measure of the level of sexism in an online community. This indicator is important for policymakers and moderators of online communities (e.g., subreddits) and computational social scientists, either to revise moderation strategies based on the degree of sexism or to match and compare the temporal sexism across different platforms and communities with real-time events and infer social scientific insights. In this paper, we build a model that can provide a comparable holistic indicator of toxicity targeted toward male and female identity and male and female individuals. Despite previous supervised NLP methods that require annotation of toxic comments at the target level (e.g. annotating comments that are specifically toxic toward women) to detect targeted toxic comments, our indicator uses supervised NLP to detect the presence of toxicity and unsupervised word embedding association test to detect the target automatically. We apply our model to gender discourse communities (e.g., r/TheRedPill, r/MGTOW, r/FemaleDatingStrategy) to detect the level of toxicity toward genders (i.e., sexism). Our results show that our framework accurately and consistently (93% correlation) measures the level of sexism in a community. We finally discuss how our framework can be generalized in the future to measure qualities other than toxicity (e.g. sentiment, humor) toward general-purpose targets and turn into an indicator of different sorts of polarizations.
AI in the Gray: Exploring Moderation Policies in Dialogic Large Language Models vs. Human Answers in Controversial Topics
Aug 28, 2023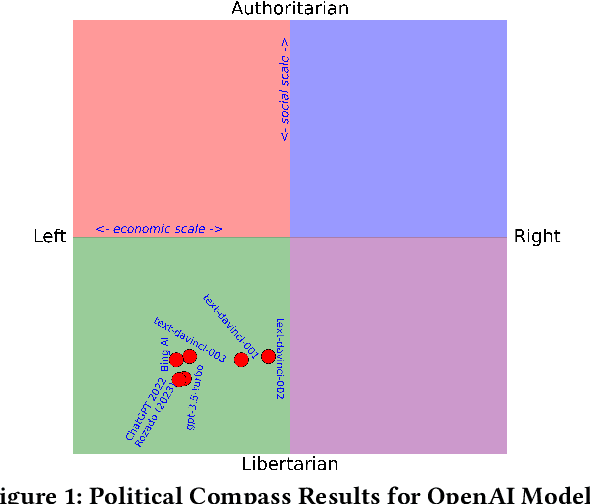

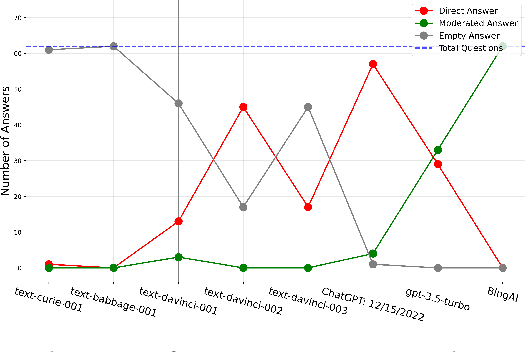

Abstract:The introduction of ChatGPT and the subsequent improvement of Large Language Models (LLMs) have prompted more and more individuals to turn to the use of ChatBots, both for information and assistance with decision-making. However, the information the user is after is often not formulated by these ChatBots objectively enough to be provided with a definite, globally accepted answer. Controversial topics, such as "religion", "gender identity", "freedom of speech", and "equality", among others, can be a source of conflict as partisan or biased answers can reinforce preconceived notions or promote disinformation. By exposing ChatGPT to such debatable questions, we aim to understand its level of awareness and if existing models are subject to socio-political and/or economic biases. We also aim to explore how AI-generated answers compare to human ones. For exploring this, we use a dataset of a social media platform created for the purpose of debating human-generated claims on polemic subjects among users, dubbed Kialo. Our results show that while previous versions of ChatGPT have had important issues with controversial topics, more recent versions of ChatGPT (gpt-3.5-turbo) are no longer manifesting significant explicit biases in several knowledge areas. In particular, it is well-moderated regarding economic aspects. However, it still maintains degrees of implicit libertarian leaning toward right-winged ideals which suggest the need for increased moderation from the socio-political point of view. In terms of domain knowledge on controversial topics, with the exception of the "Philosophical" category, ChatGPT is performing well in keeping up with the collective human level of knowledge. Finally, we see that sources of Bing AI have slightly more tendency to the center when compared to human answers. All the analyses we make are generalizable to other types of biases and domains.
Lady and the Tramp Nextdoor: Online Manifestations of Economic Inequalities in the Nextdoor Social Network
Apr 26, 2023


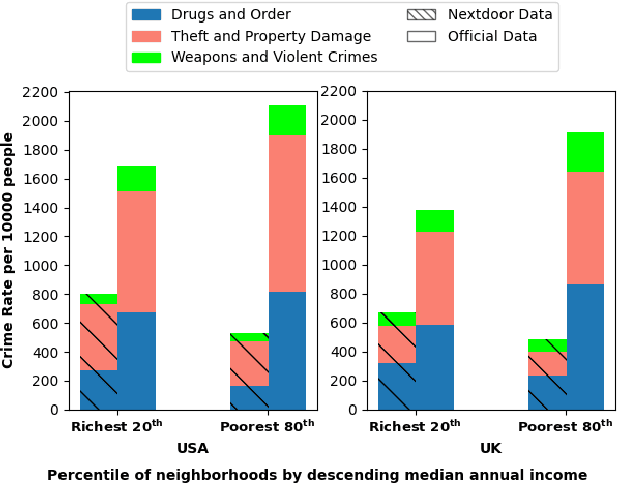
Abstract:From health to education, income impacts a huge range of life choices. Earlier research has leveraged data from online social networks to study precisely this impact. In this paper, we ask the opposite question: do different levels of income result in different online behaviors? We demonstrate it does. We present the first large-scale study of Nextdoor, a popular location-based social network. We collect 2.6 Million posts from 64,283 neighborhoods in the United States and 3,325 neighborhoods in the United Kingdom, to examine whether online discourse reflects the income and income inequality of a neighborhood. We show that posts from neighborhoods with different incomes indeed differ, e.g. richer neighborhoods have a more positive sentiment and discuss crimes more, even though their actual crime rates are much lower. We then show that user-generated content can predict both income and inequality. We train multiple machine learning models and predict both income (R-squared=0.841) and inequality (R-squared=0.77).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge