Guillaume Gadek
HYBRINFOX at CheckThat! 2024 -- Task 2: Enriching BERT Models with the Expert System VAGO for Subjectivity Detection
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents the HYBRINFOX method used to solve Task 2 of Subjectivity detection of the CLEF 2024 CheckThat! competition. The specificity of the method is to use a hybrid system, combining a RoBERTa model, fine-tuned for subjectivity detection, a frozen sentence-BERT (sBERT) model to capture semantics, and several scores calculated by the English version of the expert system VAGO, developed independently of this task to measure vagueness and subjectivity in texts based on the lexicon. In English, the HYBRINFOX method ranked 1st with a macro F1 score of 0.7442 on the evaluation data. For the other languages, the method used a translation step into English, producing more mixed results (ranking 1st in Multilingual and 2nd in Italian over the baseline, but under the baseline in Bulgarian, German, and Arabic). We explain the principles of our hybrid approach, and outline ways in which the method could be improved for other languages besides English.
HYBRINFOX at CheckThat! 2024 -- Task 1: Enhancing Language Models with Structured Information for Check-Worthiness Estimation
Jul 04, 2024


Abstract:This paper summarizes the experiments and results of the HYBRINFOX team for the CheckThat! 2024 - Task 1 competition. We propose an approach enriching Language Models such as RoBERTa with embeddings produced by triples (subject ; predicate ; object) extracted from the text sentences. Our analysis of the developmental data shows that this method improves the performance of Language Models alone. On the evaluation data, its best performance was in English, where it achieved an F1 score of 71.1 and ranked 12th out of 27 candidates. On the other languages (Dutch and Arabic), it obtained more mixed results. Future research tracks are identified toward adapting this processing pipeline to more recent Large Language Models.
A Multi-Label Dataset of French Fake News: Human and Machine Insights
Apr 11, 2024
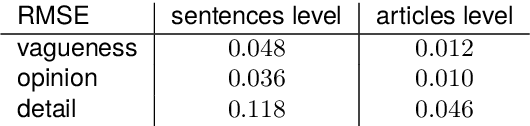
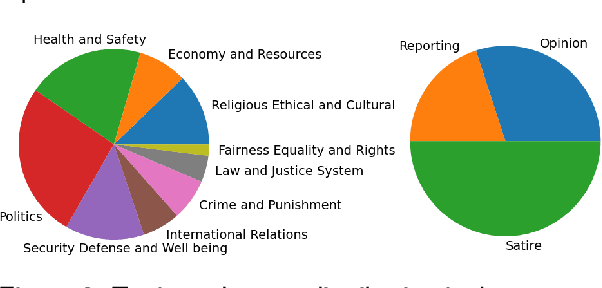
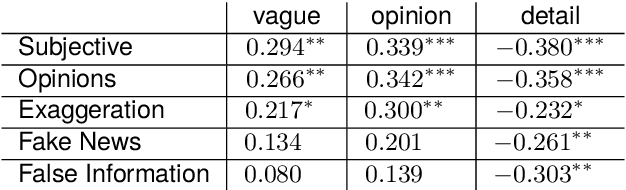
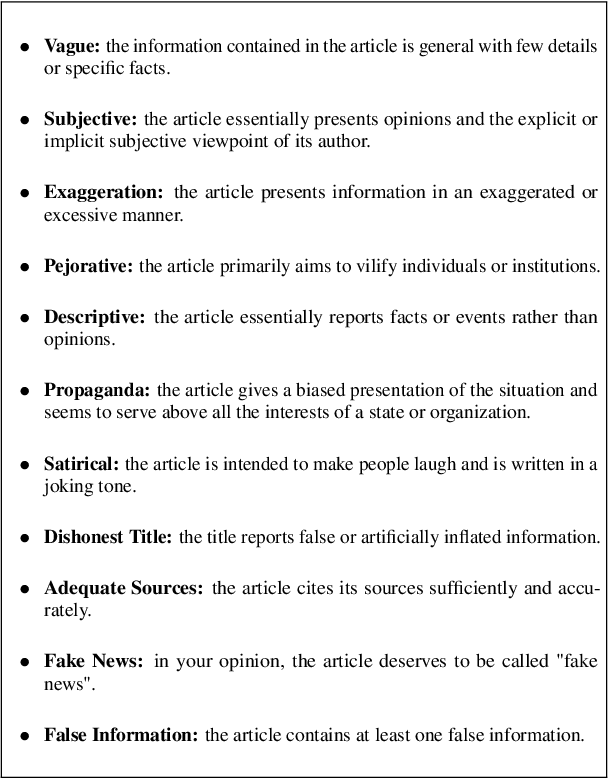
Abstract:We present a corpus of 100 documents, OBSINFOX, selected from 17 sources of French press considered unreliable by expert agencies, annotated using 11 labels by 8 annotators. By collecting more labels than usual, by more annotators than is typically done, we can identify features that humans consider as characteristic of fake news, and compare them to the predictions of automated classifiers. We present a topic and genre analysis using Gate Cloud, indicative of the prevalence of satire-like text in the corpus. We then use the subjectivity analyzer VAGO, and a neural version of it, to clarify the link between ascriptions of the label Subjective and ascriptions of the label Fake News. The annotated dataset is available online at the following url: https://github.com/obs-info/obsinfox Keywords: Fake News, Multi-Labels, Subjectivity, Vagueness, Detail, Opinion, Exaggeration, French Press
Exposing propaganda: an analysis of stylistic cues comparing human annotations and machine classification
Feb 07, 2024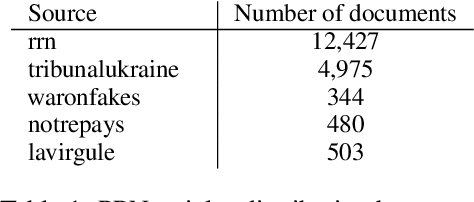
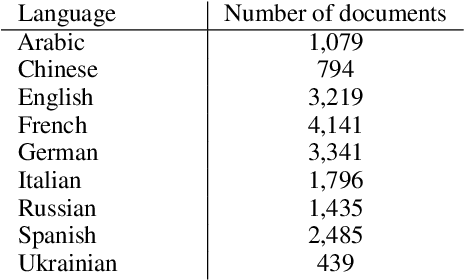
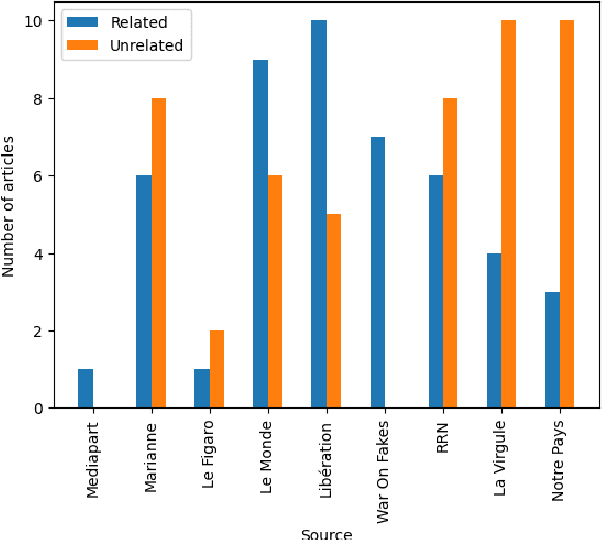
Abstract:This paper investigates the language of propaganda and its stylistic features. It presents the PPN dataset, standing for Propagandist Pseudo-News, a multisource, multilingual, multimodal dataset composed of news articles extracted from websites identified as propaganda sources by expert agencies. A limited sample from this set was randomly mixed with papers from the regular French press, and their URL masked, to conduct an annotation-experiment by humans, using 11 distinct labels. The results show that human annotators were able to reliably discriminate between the two types of press across each of the labels. We propose different NLP techniques to identify the cues used by the annotators, and to compare them with machine classification. They include the analyzer VAGO to measure discourse vagueness and subjectivity, a TF-IDF to serve as a baseline, and four different classifiers: two RoBERTa-based models, CATS using syntax, and one XGBoost combining syntactic and semantic features.
Combining Vagueness Detection with Deep Learning to Identify Fake News
Oct 31, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we combine two independent detection methods for identifying fake news: the algorithm VAGO uses semantic rules combined with NLP techniques to measure vagueness and subjectivity in texts, while the classifier FAKE-CLF relies on Convolutional Neural Network classification and supervised deep learning to classify texts as biased or legitimate. We compare the results of the two methods on four corpora. We find a positive correlation between the vagueness and subjectivity measures obtained by VAGO, and the classification of text as biased by FAKE-CLF. The comparison yields mutual benefits: VAGO helps explain the results of FAKE-CLF. Conversely FAKE-CLF helps us corroborate and expand VAGO's database. The use of two complementary techniques (rule-based vs data-driven) proves a fruitful approach for the challenging problem of identifying fake news.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge