Guannan Liu
Code Vulnerability Repair with Large Language Model using Context-Aware Prompt Tuning
Sep 27, 2024
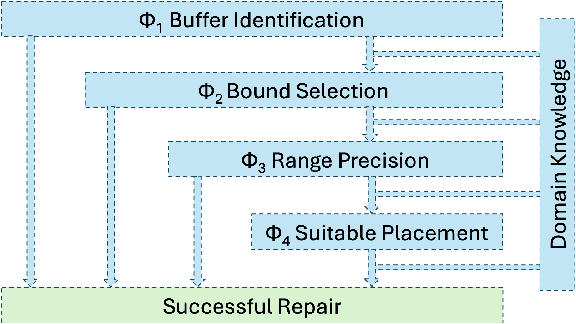
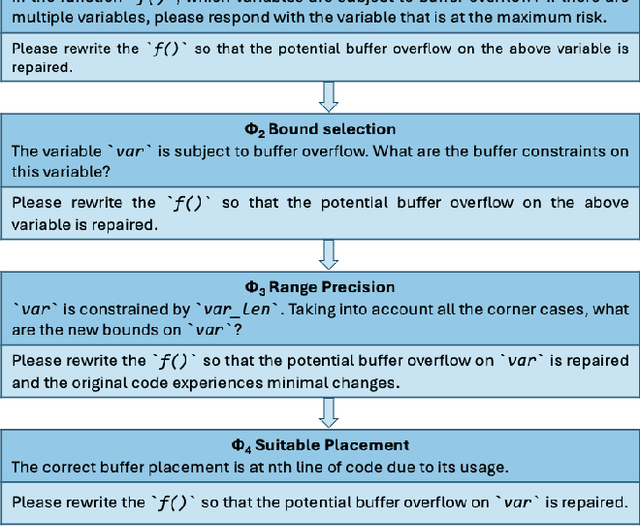
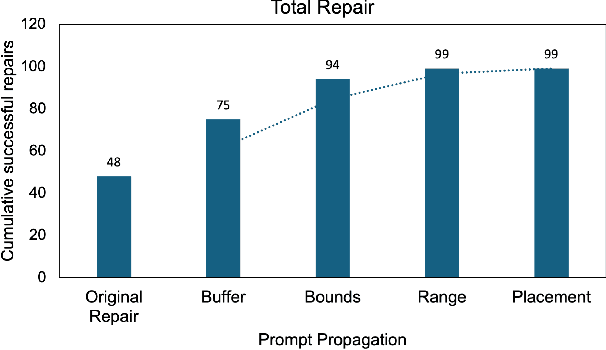
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown significant challenges in detecting and repairing vulnerable code, particularly when dealing with vulnerabilities involving multiple aspects, such as variables, code flows, and code structures. In this study, we utilize GitHub Copilot as the LLM and focus on buffer overflow vulnerabilities. Our experiments reveal a notable gap in Copilot's abilities when dealing with buffer overflow vulnerabilities, with a 76% vulnerability detection rate but only a 15% vulnerability repair rate. To address this issue, we propose context-aware prompt tuning techniques designed to enhance LLM performance in repairing buffer overflow. By injecting a sequence of domain knowledge about the vulnerability, including various security and code contexts, we demonstrate that Copilot's successful repair rate increases to 63%, representing more than four times the improvement compared to repairs without domain knowledge.
Modeling Reference-dependent Choices with Graph Neural Networks
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:While the classic Prospect Theory has highlighted the reference-dependent and comparative nature of consumers' product evaluation processes, few models have successfully integrated this theoretical hypothesis into data-driven preference quantification, particularly in the realm of recommender systems development. To bridge this gap, we propose a new research problem of modeling reference-dependent preferences from a data-driven perspective, and design a novel deep learning-based framework named Attributed Reference-dependent Choice Model for Recommendation (ArcRec) to tackle the inherent challenges associated with this problem. ArcRec features in building a reference network from aggregated historical purchase records for instantiating theoretical reference points, which is then decomposed into product attribute specific sub-networks and represented through Graph Neural Networks. In this way, the reference points of a consumer can be encoded at the attribute-level individually from her past experiences but also reflect the crowd influences. ArcRec also makes novel contributions to quantifying consumers' reference-dependent preferences using a deep neural network-based utility function that integrates both interest-inspired and price-inspired preferences, with their complex interaction effects captured by an attribute-aware price sensitivity mechanism. Most importantly, ArcRec introduces a novel Attribute-level Willingness-To-Pay measure to the reference-dependent utility function, which captures a consumer's heterogeneous salience of product attributes via observing her attribute-level price tolerance to a product. Empirical evaluations on both synthetic and real-world online shopping datasets demonstrate ArcRec's superior performances over fourteen state-of-the-art baselines.
Multi-Aspect Temporal Network Embedding: A Mixture of Hawkes Process View
May 18, 2021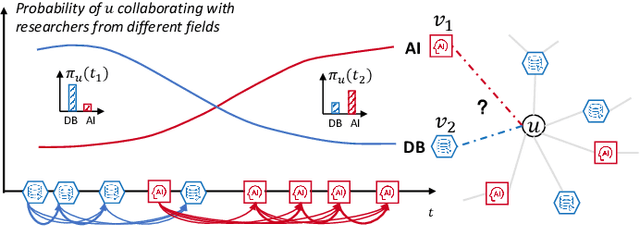
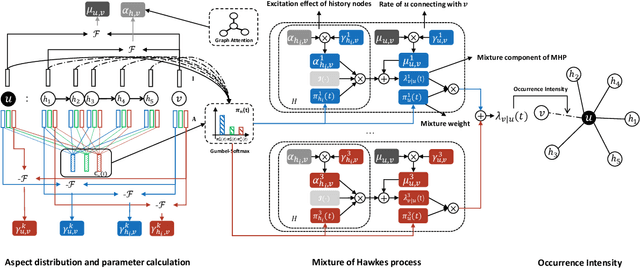
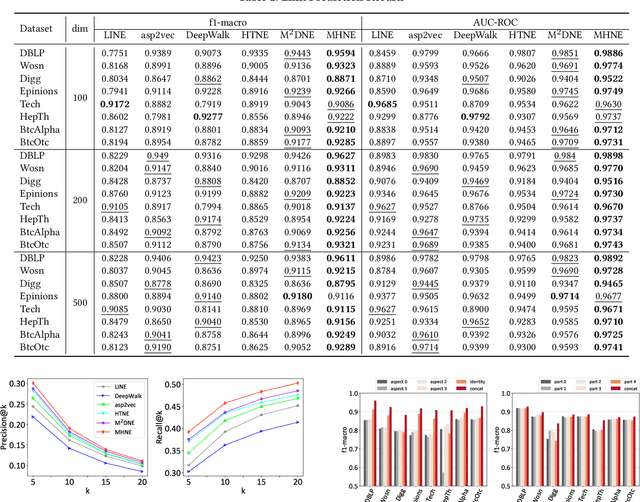
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the tremendous research interests in network embedding. Extant works have taken the neighborhood formation as the critical information to reveal the inherent dynamics of network structures, and suggested encoding temporal edge formation sequences to capture the historical influences of neighbors. In this paper, however, we argue that the edge formation can be attributed to a variety of driving factors including the temporal influence, which is better referred to as multiple aspects. As a matter of fact, different node aspects can drive the formation of distinctive neighbors, giving birth to the multi-aspect embedding that relates to but goes beyond a temporal scope. Along this vein, we propose a Mixture of Hawkes-based Temporal Network Embeddings (MHNE) model to capture the aspect-driven neighborhood formation of networks. In MHNE, we encode the multi-aspect embeddings into the mixture of Hawkes processes to gain the advantages in modeling the excitation effects and the latent aspects. Specifically, a graph attention mechanism is used to assign different weights to account for the excitation effects of history events, while a Gumbel-Softmax is plugged in to derive the distribution over the aspects. Extensive experiments on 8 different temporal networks have demonstrated the great performance of the multi-aspect embeddings obtained by MHNE in comparison with the state-of-the-art methods.
Social Media Would Not Lie: Prediction of the 2016 Taiwan Election via Online Heterogeneous Data
Apr 04, 2018
Abstract:The prevalence of online media has attracted researchers from various domains to explore human behavior and make interesting predictions. In this research, we leverage heterogeneous social media data collected from various online platforms to predict Taiwan's 2016 presidential election. In contrast to most existing research, we take a "signal" view of heterogeneous information and adopt the Kalman filter to fuse multiple signals into daily vote predictions for the candidates. We also consider events that influenced the election in a quantitative manner based on the so-called event study model that originated in the field of financial research. We obtained the following interesting findings. First, public opinions in online media dominate traditional polls in Taiwan election prediction in terms of both predictive power and timeliness. But offline polls can still function on alleviating the sample bias of online opinions. Second, although online signals converge as election day approaches, the simple Facebook "Like" is consistently the strongest indicator of the election result. Third, most influential events have a strong connection to cross-strait relations, and the Chou Tzu-yu flag incident followed by the apology video one day before the election increased the vote share of Tsai Ing-Wen by 3.66%. This research justifies the predictive power of online media in politics and the advantages of information fusion. The combined use of the Kalman filter and the event study method contributes to the data-driven political analytics paradigm for both prediction and attribution purposes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge