Guang Wu
Enhanced Photovoltaic Power Forecasting: An iTransformer and LSTM-Based Model Integrating Temporal and Covariate Interactions
Dec 03, 2024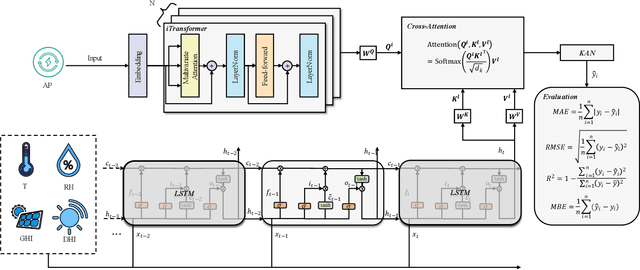
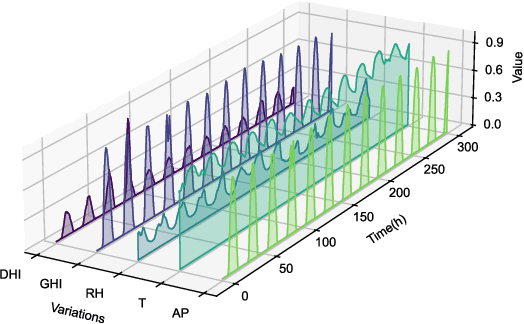
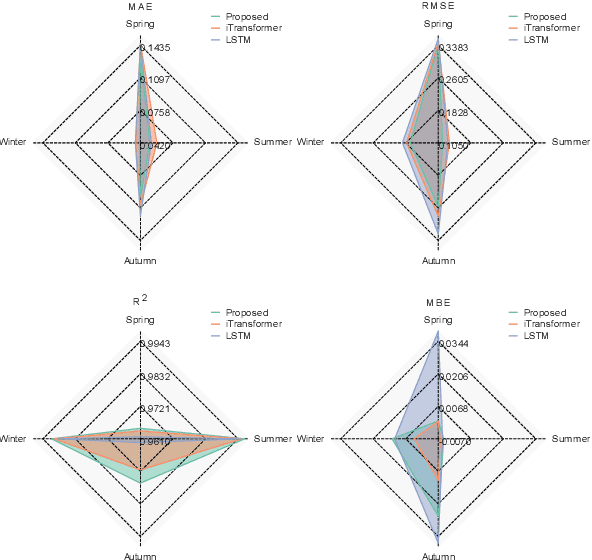

Abstract:Accurate photovoltaic (PV) power forecasting is critical for integrating renewable energy sources into the grid, optimizing real-time energy management, and ensuring energy reliability amidst increasing demand. However, existing models often struggle with effectively capturing the complex relationships between target variables and covariates, as well as the interactions between temporal dynamics and multivariate data, leading to suboptimal forecasting accuracy. To address these challenges, we propose a novel model architecture that leverages the iTransformer for feature extraction from target variables and employs long short-term memory (LSTM) to extract features from covariates. A cross-attention mechanism is integrated to fuse the outputs of both models, followed by a Kolmogorov-Arnold network (KAN) mapping for enhanced representation. The effectiveness of the proposed model is validated using publicly available datasets from Australia, with experiments conducted across four seasons. Results demonstrate that the proposed model effectively capture seasonal variations in PV power generation and improve forecasting accuracy.
Human Respiration Detection Under Interference: Challenges and Solutions
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Recent research has highlighted the detection of human respiration rate using commodity WiFi devices. Nevertheless, these devices encounter challenges in accurately discerning human respiration amidst the prevailing human motion interference encountered in daily life. To tackle this predicament, this paper introduces a passive sensing and communication system designed specifically for respiration detection in the presence of robust human motion interference. Operating within the 60.48GHz band, the proposed system aims to detect human respiration even when confronted with substantial human motion interference within close proximity. Subsequently, a neural network is trained using the collected data by us to enable human respiration detection. The experimental results demonstrate a consistently high accuracy rate over 90\% of the human respiration detection under interference, given an adequate sensing duration. Finally, an empirical model is derived analytically to achieve the respiratory rate counting in 10 seconds.
f-VAEs: Improve VAEs with Conditional Flows
Sep 16, 2018Abstract:In this paper, we integrate VAEs and flow-based generative models successfully and get f-VAEs. Compared with VAEs, f-VAEs generate more vivid images, solved the blurred-image problem of VAEs. Compared with flow-based models such as Glow, f-VAE is more lightweight and converges faster, achieving the same performance under smaller-size architecture.
Topological design of an asymmetric 3-translational parallel mechanism with zero coupling degree and motion decoupling
May 23, 2018
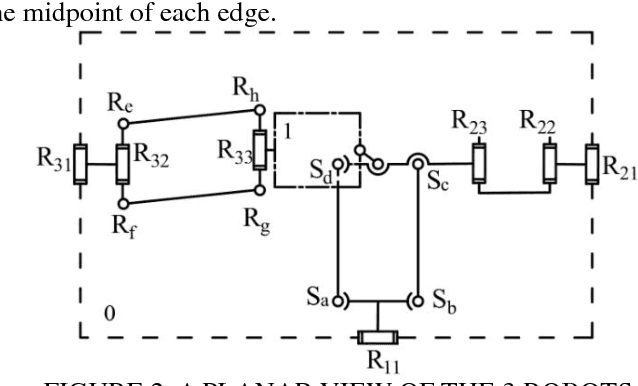


Abstract:In this paper a new asymmetric 3-translational (3T) parallel manipulator, i.e., RPa(3R) 2R+RPa, with zero coupling degree and decoupled motion is firstly proposed according to topology design theory of parallel mechanism (PM) based on position and orientation characteristics (POC) equations. The main topological characteristics such as POC, degree of freedom and coupling degree are calculated. Then, the analytical formula for the direct and inverse kinematic are directly derived since coupling degree of the PM is zero. The study of singular configurations is simple because of the independence of the kinematic chains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge