Graciela Gonzalez
University of Pennsylvania
Social media mining for identification and exploration of health-related information from pregnant women
Feb 08, 2017
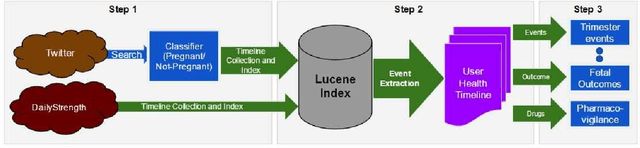
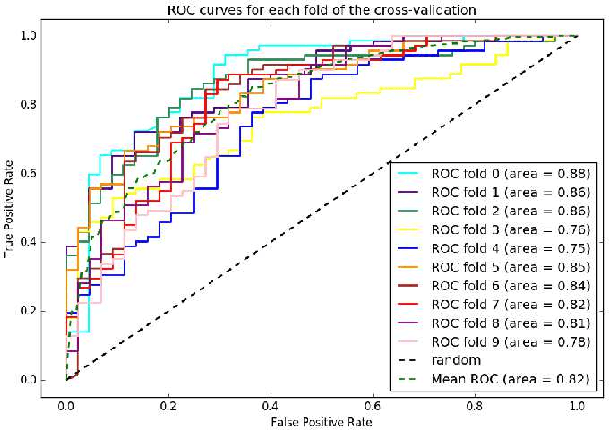
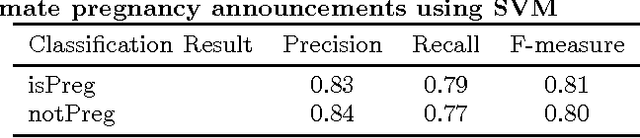
Abstract:Widespread use of social media has led to the generation of substantial amounts of information about individuals, including health-related information. Social media provides the opportunity to study health-related information about selected population groups who may be of interest for a particular study. In this paper, we explore the possibility of utilizing social media to perform targeted data collection and analysis from a particular population group -- pregnant women. We hypothesize that we can use social media to identify cohorts of pregnant women and follow them over time to analyze crucial health-related information. To identify potentially pregnant women, we employ simple rule-based searches that attempt to detect pregnancy announcements with moderate precision. To further filter out false positives and noise, we employ a supervised classifier using a small number of hand-annotated data. We then collect their posts over time to create longitudinal health timelines and attempt to divide the timelines into different pregnancy trimesters. Finally, we assess the usefulness of the timelines by performing a preliminary analysis to estimate drug intake patterns of our cohort at different trimesters. Our rule-based cohort identification technique collected 53,820 users over thirty months from Twitter. Our pregnancy announcement classification technique achieved an F-measure of 0.81 for the pregnancy class, resulting in 34,895 user timelines. Analysis of the timelines revealed that pertinent health-related information, such as drug-intake and adverse reactions can be mined from the data. Our approach to using user timelines in this fashion has produced very encouraging results and can be employed for other important tasks where cohorts, for which health-related information may not be available from other sources, are required to be followed over time to derive population-based estimates.
Mining the Web for Pharmacovigilance: the Case Study of Duloxetine and Venlafaxine
Oct 08, 2016
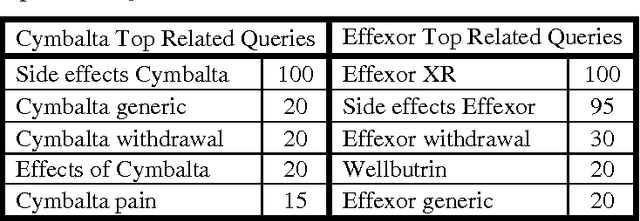
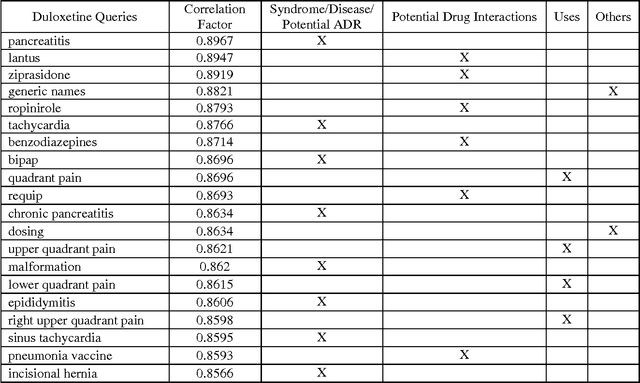
Abstract:Adverse reactions caused by drugs following their release into the market are among the leading causes of death in many countries. The rapid growth of electronically available health related information, and the ability to process large volumes of them automatically, using natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms, have opened new opportunities for pharmacovigilance. Survey found that more than 70% of US Internet users consult the Internet when they require medical information. In recent years, research in this area has addressed for Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) pharmacovigilance using social media, mainly Twitter and medical forums and websites. This paper will show the information which can be collected from a variety of Internet data sources and search engines, mainly Google Trends and Google Correlate. While considering the case study of two popular Major depressive Disorder (MDD) drugs, Duloxetine and Venlafaxine, we will provide a comparative analysis for their reactions using publicly-available alternative data sources.
BioSimplify: an open source sentence simplification engine to improve recall in automatic biomedical information extraction
Jul 28, 2011



Abstract:BioSimplify is an open source tool written in Java that introduces and facilitates the use of a novel model for sentence simplification tuned for automatic discourse analysis and information extraction (as opposed to sentence simplification for improving human readability). The model is based on a "shot-gun" approach that produces many different (simpler) versions of the original sentence by combining variants of its constituent elements. This tool is optimized for processing biomedical scientific literature such as the abstracts indexed in PubMed. We tested our tool on its impact to the task of PPI extraction and it improved the f-score of the PPI tool by around 7%, with an improvement in recall of around 20%. The BioSimplify tool and test corpus can be downloaded from https://biosimplify.sourceforge.net.
Towards Effective Sentence Simplification for Automatic Processing of Biomedical Text
Jan 24, 2010


Abstract:The complexity of sentences characteristic to biomedical articles poses a challenge to natural language parsers, which are typically trained on large-scale corpora of non-technical text. We propose a text simplification process, bioSimplify, that seeks to reduce the complexity of sentences in biomedical abstracts in order to improve the performance of syntactic parsers on the processed sentences. Syntactic parsing is typically one of the first steps in a text mining pipeline. Thus, any improvement in performance would have a ripple effect over all processing steps. We evaluated our method using a corpus of biomedical sentences annotated with syntactic links. Our empirical results show an improvement of 2.90% for the Charniak-McClosky parser and of 4.23% for the Link Grammar parser when processing simplified sentences rather than the original sentences in the corpus.
* 4 pages, In Proc. of the NAACL-HLT 2009, Boulder, USA, June
Sentence Simplification Aids Protein-Protein Interaction Extraction
Jan 24, 2010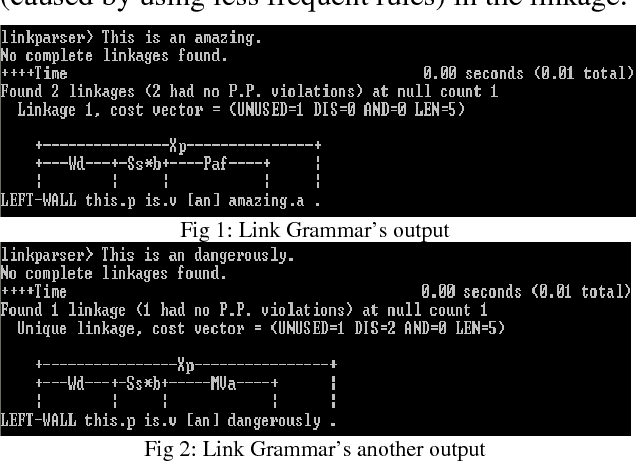
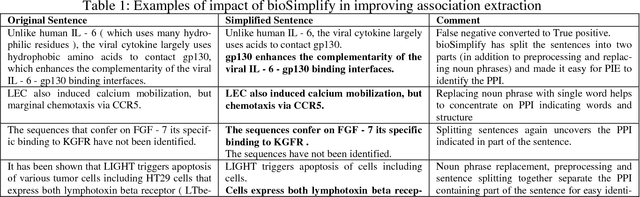
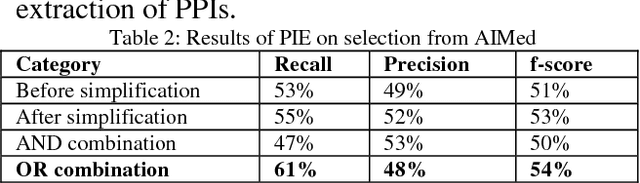

Abstract:Accurate systems for extracting Protein-Protein Interactions (PPIs) automatically from biomedical articles can help accelerate biomedical research. Biomedical Informatics researchers are collaborating to provide metaservices and advance the state-of-art in PPI extraction. One problem often neglected by current Natural Language Processing systems is the characteristic complexity of the sentences in biomedical literature. In this paper, we report on the impact that automatic simplification of sentences has on the performance of a state-of-art PPI extraction system, showing a substantial improvement in recall (8%) when the sentence simplification method is applied, without significant impact to precision.
* 6 pages, The 3rd International Symposium on Languages in Biology and Medicine, Jeju Island, South Korea, November 8-10, 2009
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge