Pramod Bharadwaj Chandrashekar
Arizona State University
Social media mining for identification and exploration of health-related information from pregnant women
Feb 08, 2017
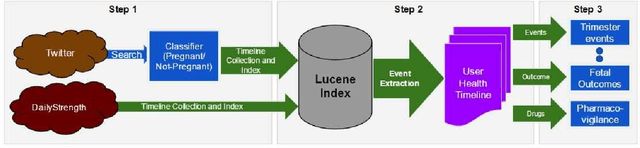
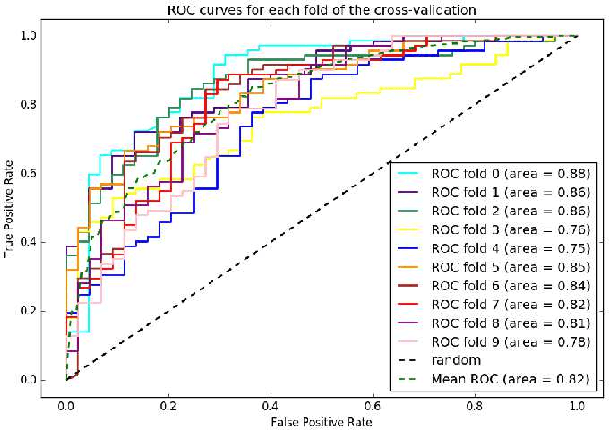
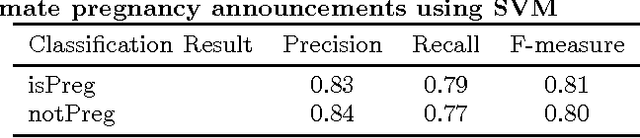
Abstract:Widespread use of social media has led to the generation of substantial amounts of information about individuals, including health-related information. Social media provides the opportunity to study health-related information about selected population groups who may be of interest for a particular study. In this paper, we explore the possibility of utilizing social media to perform targeted data collection and analysis from a particular population group -- pregnant women. We hypothesize that we can use social media to identify cohorts of pregnant women and follow them over time to analyze crucial health-related information. To identify potentially pregnant women, we employ simple rule-based searches that attempt to detect pregnancy announcements with moderate precision. To further filter out false positives and noise, we employ a supervised classifier using a small number of hand-annotated data. We then collect their posts over time to create longitudinal health timelines and attempt to divide the timelines into different pregnancy trimesters. Finally, we assess the usefulness of the timelines by performing a preliminary analysis to estimate drug intake patterns of our cohort at different trimesters. Our rule-based cohort identification technique collected 53,820 users over thirty months from Twitter. Our pregnancy announcement classification technique achieved an F-measure of 0.81 for the pregnancy class, resulting in 34,895 user timelines. Analysis of the timelines revealed that pertinent health-related information, such as drug-intake and adverse reactions can be mined from the data. Our approach to using user timelines in this fashion has produced very encouraging results and can be employed for other important tasks where cohorts, for which health-related information may not be available from other sources, are required to be followed over time to derive population-based estimates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge