Grégoire Nieto
LJK
IntrinSeqNet: Learning to Estimate the Reflectance from Varying Illumination
Jun 13, 2019



Abstract:Intrinsic image decomposition describes an image based on its reflectance and shading components. In this paper we tackle the problem of estimating the diffuse reflectance from a sequence of images captured from a fixed viewpoint under various illuminations. To this end we propose a deep learning approach to avoid heuristics and strong assumptions on the reflectance prior. We compare two network architectures: one classic 'U' shaped Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) composed of Convolutional Gated Recurrent Units (CGRU). We train our networks on a new dataset specifically designed for the task of intrinsic decomposition from sequences. We test our networks on MIT and BigTime datasets and outperform state-of-the-art algorithms both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Rendu basé image avec contraintes sur les gradients
Dec 29, 2018



Abstract:Multi-view image-based rendering consists in generating a novel view of a scene from a set of source views. In general, this works by first doing a coarse 3D reconstruction of the scene, and then using this reconstruction to establish correspondences between source and target views, followed by blending the warped views to get the final image. Unfortunately, discontinuities in the blending weights, due to scene geometry or camera placement, result in artifacts in the target view. In this paper, we show how to avoid these artifacts by imposing additional constraints on the image gradients of the novel view. We propose a variational framework in which an energy functional is derived and optimized by iteratively solving a linear system. We demonstrate this method on several structured and unstructured multi-view datasets, and show that it numerically outperforms state-of-the-art methods, and eliminates artifacts that result from visibility discontinuities
Robust Point Light Source Estimation Using Differentiable Rendering
Dec 12, 2018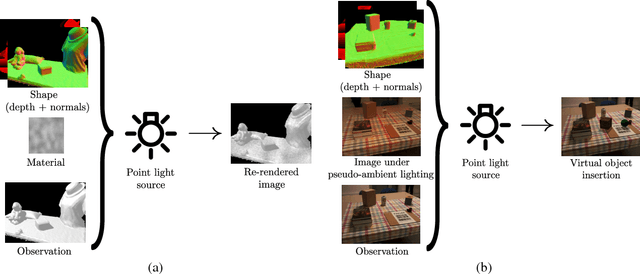

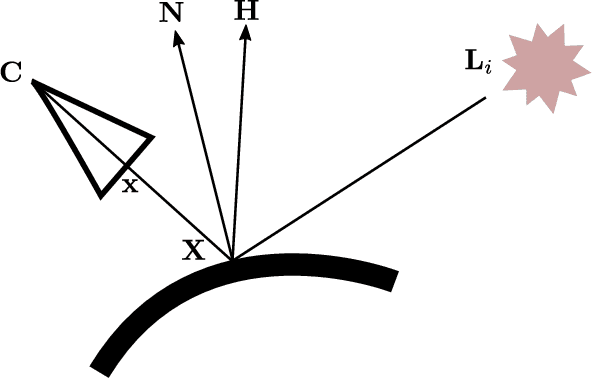

Abstract:Illumination estimation is often used in mixed reality to re-render a scene from another point of view, to change the color/texture of an object, or to insert a virtual object consistently lit into a real video or photograph. Specifically, the estimation of a point light source is required for the shadows cast by the inserted object to be consistent with the real scene. We tackle the problem of illumination retrieval given an RGBD image of the scene as an inverse problem: we aim to find the illumination that minimizes the photometric error between the rendered image and the observation. In particular we propose a novel differentiable renderer based on the Blinn-Phong model with cast shadows. We compare our differentiable renderer to state-of-the-art methods and demonstrate its robustness to an incorrect reflectance estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge