Gokula Krishnan Santhanam
Defending Against Adversarial Attacks by Leveraging an Entire GAN
May 27, 2018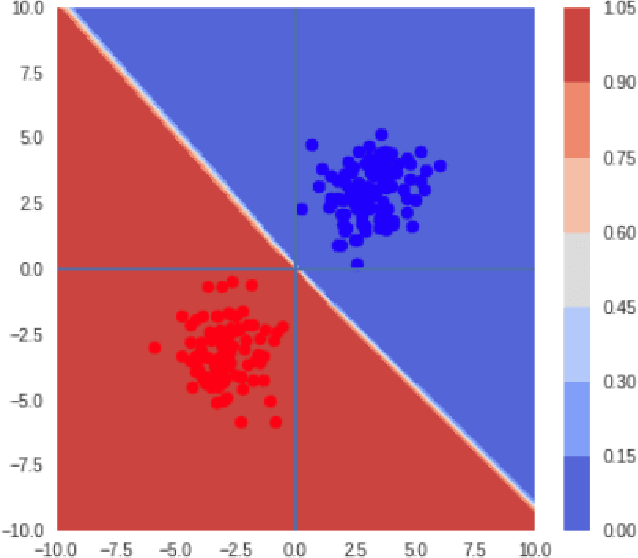
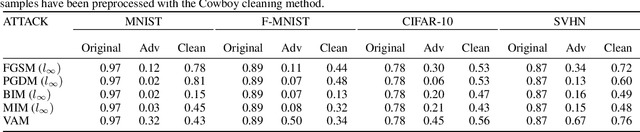
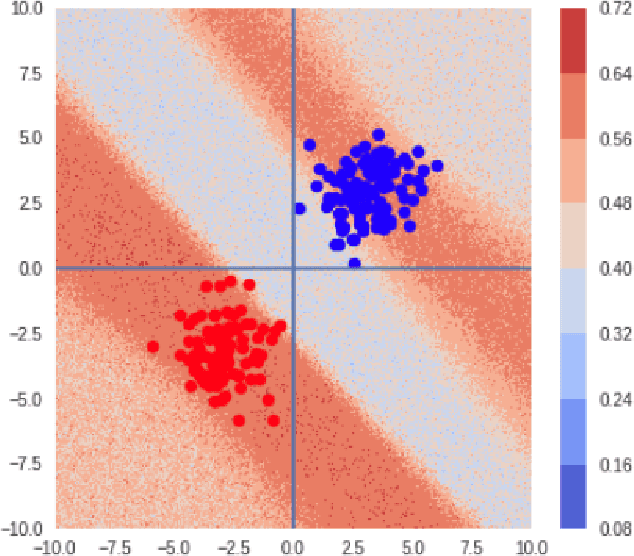
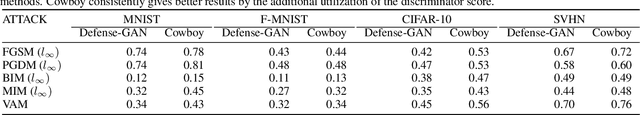
Abstract:Recent work has shown that state-of-the-art models are highly vulnerable to adversarial perturbations of the input. We propose cowboy, an approach to detecting and defending against adversarial attacks by using both the discriminator and generator of a GAN trained on the same dataset. We show that the discriminator consistently scores the adversarial samples lower than the real samples across multiple attacks and datasets. We provide empirical evidence that adversarial samples lie outside of the data manifold learned by the GAN. Based on this, we propose a cleaning method which uses both the discriminator and generator of the GAN to project the samples back onto the data manifold. This cleaning procedure is independent of the classifier and type of attack and thus can be deployed in existing systems.
Generative Adversarial Networks recover features in astrophysical images of galaxies beyond the deconvolution limit
Feb 01, 2017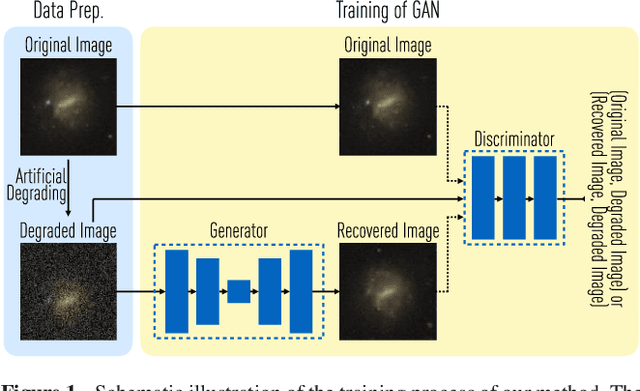
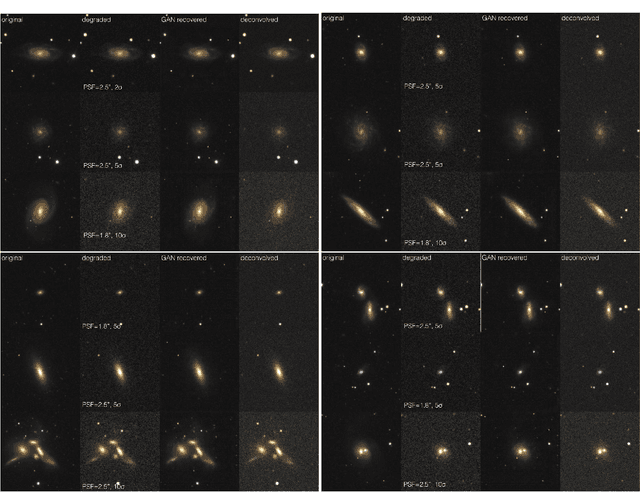
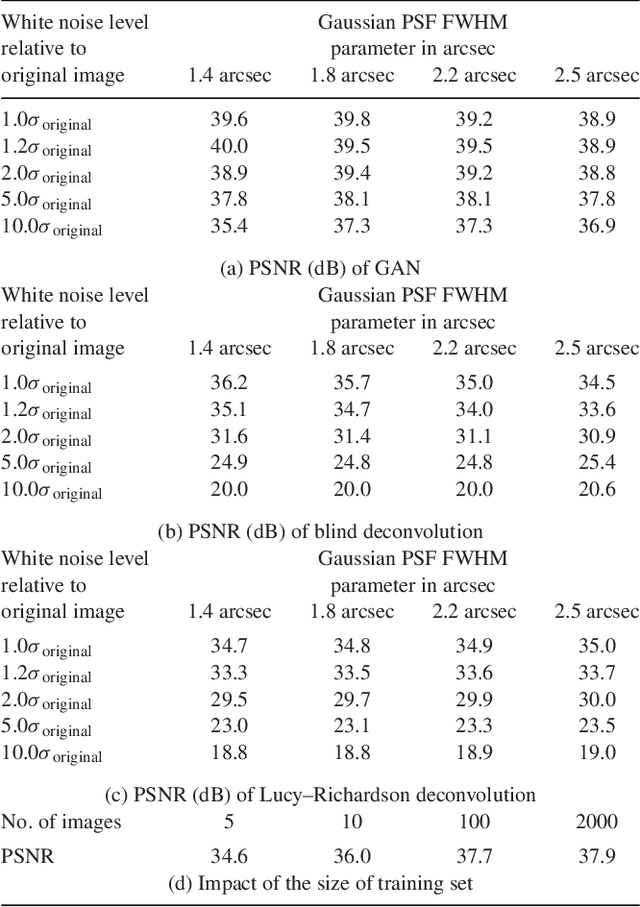
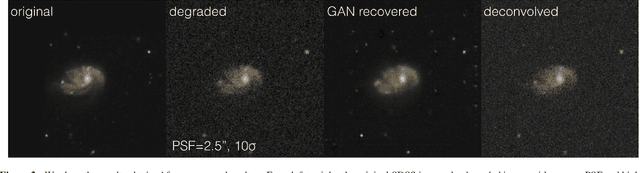

Abstract:Observations of astrophysical objects such as galaxies are limited by various sources of random and systematic noise from the sky background, the optical system of the telescope and the detector used to record the data. Conventional deconvolution techniques are limited in their ability to recover features in imaging data by the Shannon-Nyquist sampling theorem. Here we train a generative adversarial network (GAN) on a sample of $4,550$ images of nearby galaxies at $0.01<z<0.02$ from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey and conduct $10\times$ cross validation to evaluate the results. We present a method using a GAN trained on galaxy images that can recover features from artificially degraded images with worse seeing and higher noise than the original with a performance which far exceeds simple deconvolution. The ability to better recover detailed features such as galaxy morphology from low-signal-to-noise and low angular resolution imaging data significantly increases our ability to study existing data sets of astrophysical objects as well as future observations with observatories such as the Large Synoptic Sky Telescope (LSST) and the Hubble and James Webb space telescopes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge