Giorgio Terracina
Extended High Utility Pattern Mining: An Answer Set Programming Based Framework and Applications
Mar 23, 2023Abstract:Detecting sets of relevant patterns from a given dataset is an important challenge in data mining. The relevance of a pattern, also called utility in the literature, is a subjective measure and can be actually assessed from very different points of view. Rule-based languages like Answer Set Programming (ASP) seem well suited for specifying user-provided criteria to assess pattern utility in a form of constraints; moreover, declarativity of ASP allows for a very easy switch between several criteria in order to analyze the dataset from different points of view. In this paper, we make steps toward extending the notion of High Utility Pattern Mining (HUPM); in particular we introduce a new framework that allows for new classes of utility criteria not considered in the previous literature. We also show how recent extensions of ASP with external functions can support a fast and effective encoding and testing of the new framework. To demonstrate the potential of the proposed framework, we exploit it as a building block for the definition of an innovative method for predicting ICU admission for COVID-19 patients. Finally, an extensive experimental activity demonstrates both from a quantitative and a qualitative point of view the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Under consideration in Theory and Practice of Logic Programming (TPLP)
A Logic-Based Framework Leveraging Neural Networks for Studying the Evolution of Neurological Disorders
Oct 21, 2019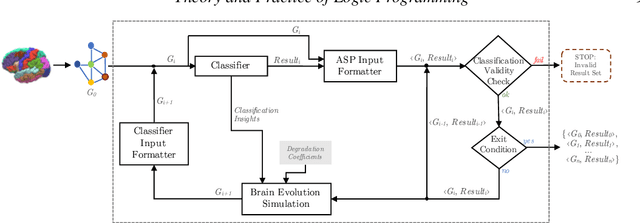
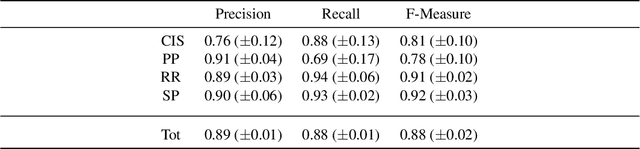
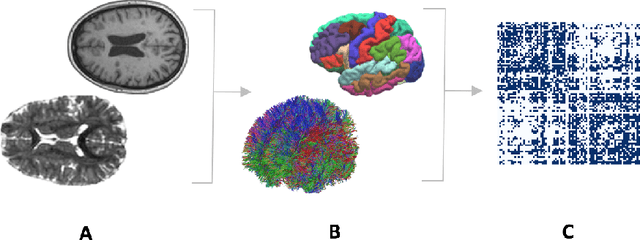
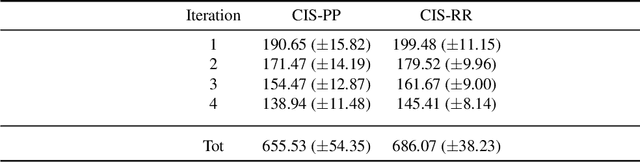
Abstract:Deductive formalisms have been strongly developed in recent years; among them, Answer Set Programming (ASP) gained some momentum, and has been lately fruitfully employed in many real-world scenarios. Nonetheless, in spite of a large number of success stories in relevant application areas, and even in industrial contexts, deductive reasoning cannot be considered the ultimate, comprehensive solution to AI; indeed, in several contexts, other approaches result to be more useful. Typical Bioinformatics tasks, for instance classification, are currently carried out mostly by Machine Learning (ML) based solutions. In this paper, we focus on the relatively new problem of analyzing the evolution of neurological disorders. In this context, ML approaches already demonstrated to be a viable solution for classification tasks; here, we show how ASP can play a relevant role in the brain evolution simulation task. In particular, we propose a general and extensible framework to support physicians and researchers at understanding the complex mechanisms underlying neurological disorders. The framework relies on a combined use of ML and ASP, and is general enough to be applied in several other application scenarios, which are outlined in the paper.
Taming Primary Key Violations to Query Large Inconsistent Data
Jul 22, 2015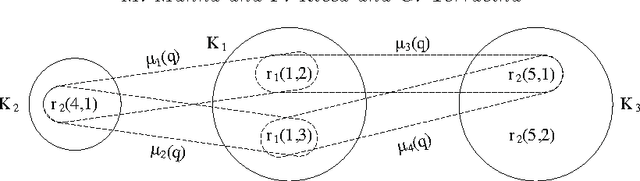
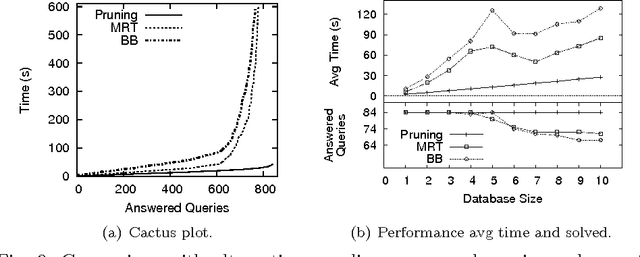
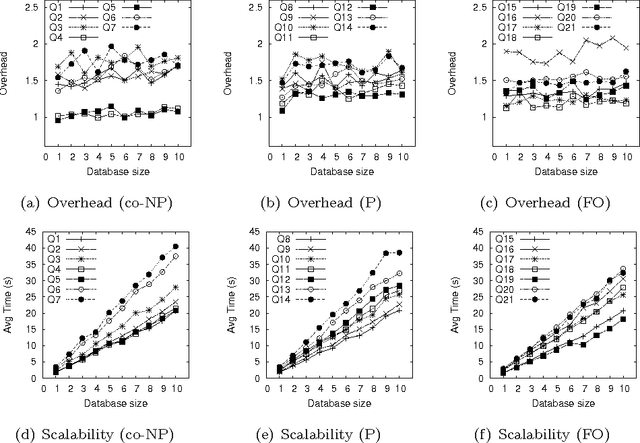
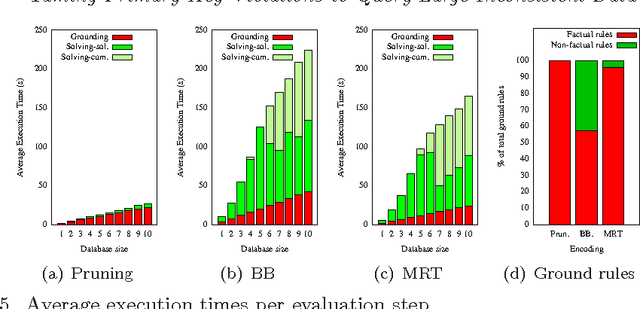
Abstract:Consistent query answering over a database that violates primary key constraints is a classical hard problem in database research that has been traditionally dealt with logic programming. However, the applicability of existing logic-based solutions is restricted to data sets of moderate size. This paper presents a novel decomposition and pruning strategy that reduces, in polynomial time, the problem of computing the consistent answer to a conjunctive query over a database subject to primary key constraints to a collection of smaller problems of the same sort that can be solved independently. The new strategy is naturally modeled and implemented using Answer Set Programming (ASP). An experiment run on benchmarks from the database world prove the effectiveness and efficiency of our ASP-based approach also on large data sets. To appear in Theory and Practice of Logic Programming (TPLP), Proceedings of ICLP 2015.
Consistent Query Answering via ASP from Different Perspectives: Theory and Practice
Oct 07, 2011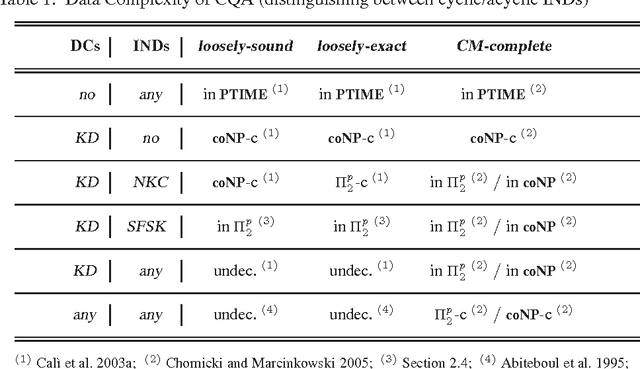
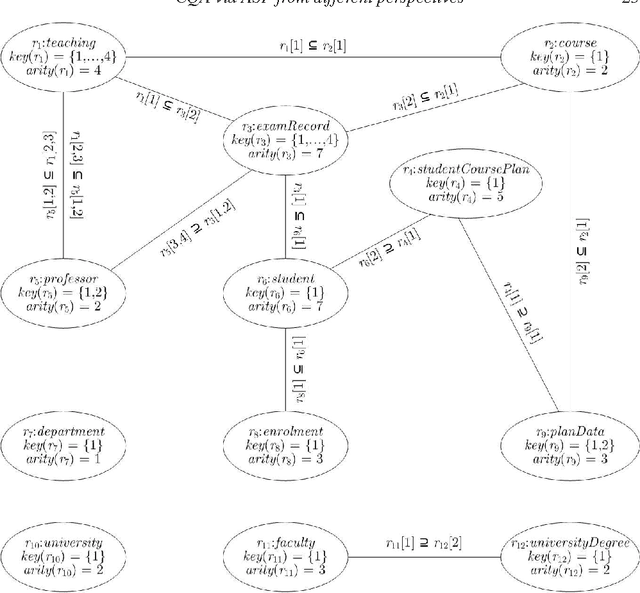
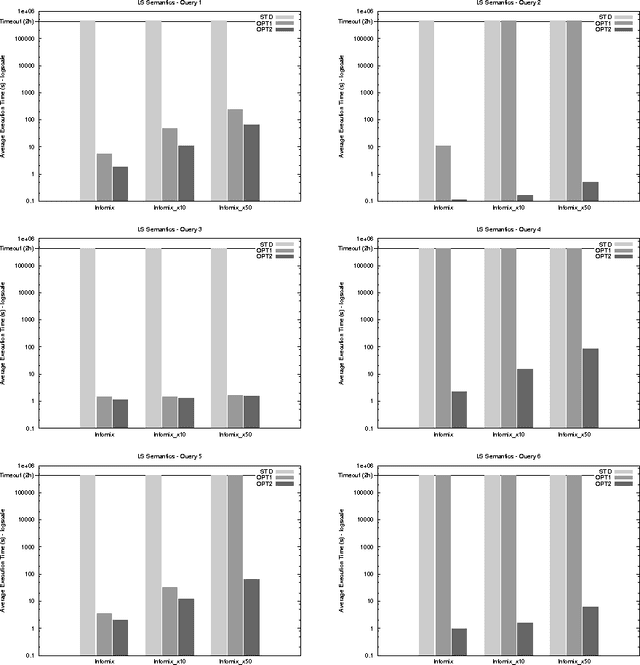
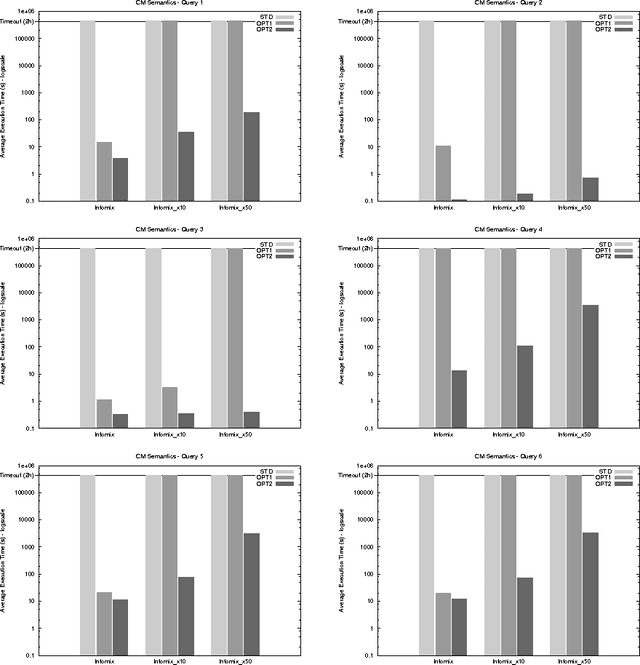
Abstract:A data integration system provides transparent access to different data sources by suitably combining their data, and providing the user with a unified view of them, called global schema. However, source data are generally not under the control of the data integration process, thus integrated data may violate global integrity constraints even in presence of locally-consistent data sources. In this scenario, it may be anyway interesting to retrieve as much consistent information as possible. The process of answering user queries under global constraint violations is called consistent query answering (CQA). Several notions of CQA have been proposed, e.g., depending on whether integrated information is assumed to be sound, complete, exact or a variant of them. This paper provides a contribution in this setting: it uniforms solutions coming from different perspectives under a common ASP-based core, and provides query-driven optimizations designed for isolating and eliminating inefficiencies of the general approach for computing consistent answers. Moreover, the paper introduces some new theoretical results enriching existing knowledge on decidability and complexity of the considered problems. The effectiveness of the approach is evidenced by experimental results. To appear in Theory and Practice of Logic Programming (TPLP).
Experimenting with recursive queries in database and logic programming systems
Apr 24, 2007

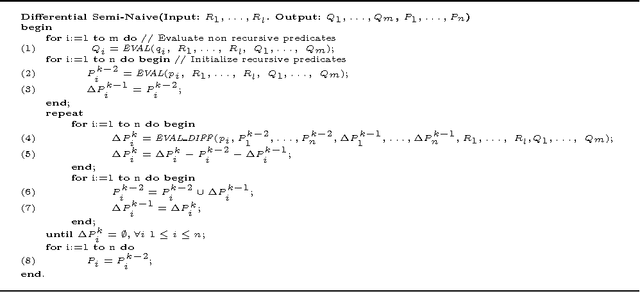

Abstract:This paper considers the problem of reasoning on massive amounts of (possibly distributed) data. Presently, existing proposals show some limitations: {\em (i)} the quantity of data that can be handled contemporarily is limited, due to the fact that reasoning is generally carried out in main-memory; {\em (ii)} the interaction with external (and independent) DBMSs is not trivial and, in several cases, not allowed at all; {\em (iii)} the efficiency of present implementations is still not sufficient for their utilization in complex reasoning tasks involving massive amounts of data. This paper provides a contribution in this setting; it presents a new system, called DLV$^{DB}$, which aims to solve these problems. Moreover, the paper reports the results of a thorough experimental analysis we have carried out for comparing our system with several state-of-the-art systems (both logic and databases) on some classical deductive problems; the other tested systems are: LDL++, XSB, Smodels and three top-level commercial DBMSs. DLV$^{DB}$ significantly outperforms even the commercial Database Systems on recursive queries. To appear in Theory and Practice of Logic Programming (TPLP)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge