Ginger S. Watson
Improving mathematical questioning in teacher training
Dec 06, 2021
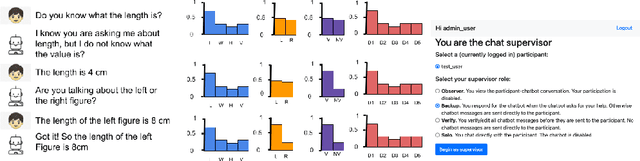
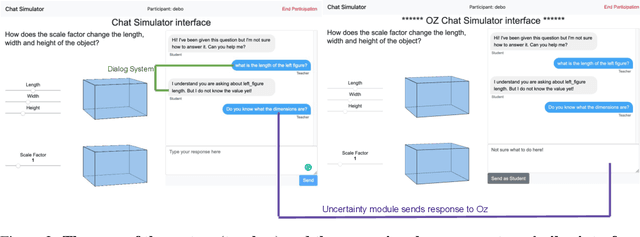
Abstract:High-fidelity, AI-based simulated classroom systems enable teachers to rehearse effective teaching strategies. However, dialogue-oriented open-ended conversations such as teaching a student about scale factors can be difficult to model. This paper builds a text-based interactive conversational agent to help teachers practice mathematical questioning skills based on the well-known Instructional Quality Assessment. We take a human-centered approach to designing our system, relying on advances in deep learning, uncertainty quantification, and natural language processing while acknowledging the limitations of conversational agents for specific pedagogical needs. Using experts' input directly during the simulation, we demonstrate how conversation success rate and high user satisfaction can be achieved.
Evaluation of mathematical questioning strategies using data collected through weak supervision
Dec 02, 2021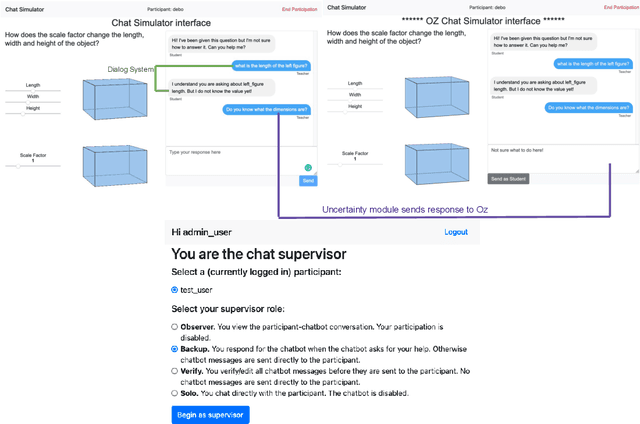
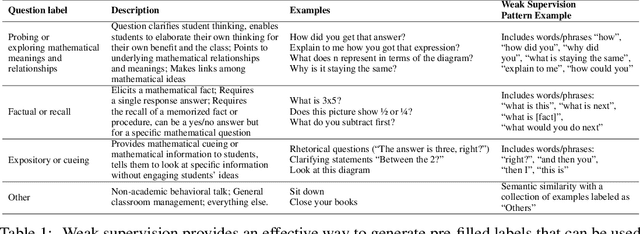
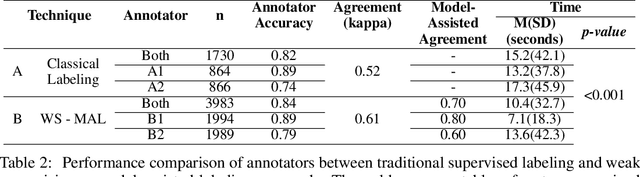

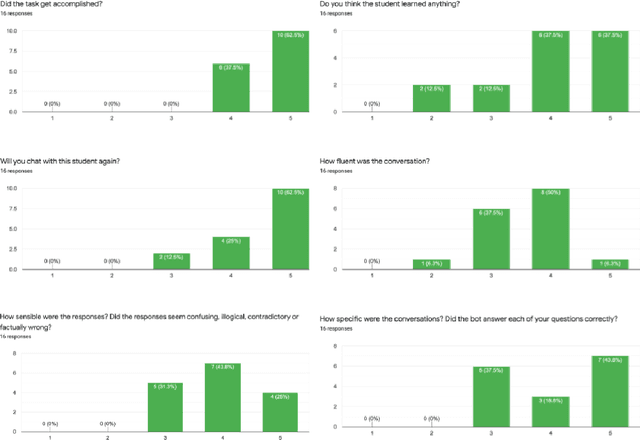
Abstract:A large body of research demonstrates how teachers' questioning strategies can improve student learning outcomes. However, developing new scenarios is challenging because of the lack of training data for a specific scenario and the costs associated with labeling. This paper presents a high-fidelity, AI-based classroom simulator to help teachers rehearse research-based mathematical questioning skills. Using a human-in-the-loop approach, we collected a high-quality training dataset for a mathematical questioning scenario. Using recent advances in uncertainty quantification, we evaluated our conversational agent for usability and analyzed the practicality of incorporating a human-in-the-loop approach for data collection and system evaluation for a mathematical questioning scenario.
Improving Classification through Weak Supervision in Context-specific Conversational Agent Development for Teacher Education
Oct 23, 2020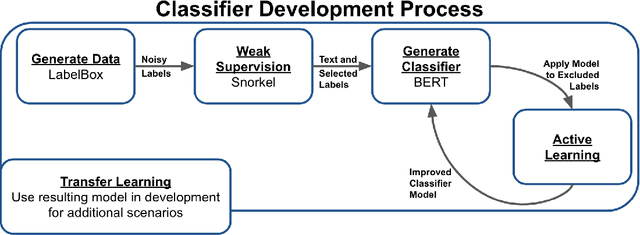

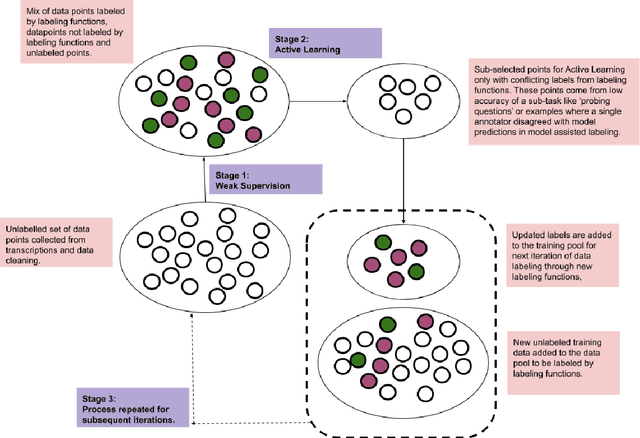
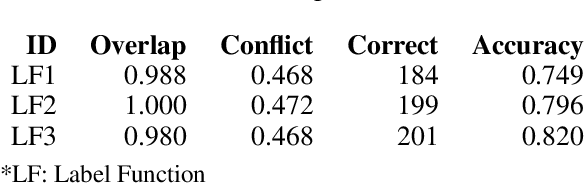
Abstract:Machine learning techniques applied to the Natural Language Processing (NLP) component of conversational agent development show promising results for improved accuracy and quality of feedback that a conversational agent can provide. The effort required to develop an educational scenario specific conversational agent is time consuming as it requires domain experts to label and annotate noisy data sources such as classroom videos. Previous approaches to modeling annotations have relied on labeling thousands of examples and calculating inter-annotator agreement and majority votes in order to model the necessary scenarios. This method, while proven successful, ignores individual annotator strengths in labeling a data point and under-utilizes examples that do not have a majority vote for labeling. We propose using a multi-task weak supervision method combined with active learning to address these concerns. This approach requires less labeling than traditional methods and shows significant improvements in precision, efficiency, and time-requirements than the majority vote method (Ratner 2019). We demonstrate the validity of this method on the Google Jigsaw data set and then propose a scenario to apply this method using the Instructional Quality Assessment(IQA) to define the categories for labeling. We propose using probabilistic modeling of annotator labeling to generate active learning examples to further label the data. Active learning is able to iteratively improve the training performance and accuracy of the original classification model. This approach combines state-of-the art labeling techniques of weak supervision and active learning to optimize results in the educational domain and could be further used to lessen the data requirements for expanded scenarios within the education domain through transfer learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge