Georgios Sidiropoulos
Improving the Robustness of Dense Retrievers Against Typos via Multi-Positive Contrastive Learning
Mar 16, 2024Abstract:Dense retrieval has become the new paradigm in passage retrieval. Despite its effectiveness on typo-free queries, it is not robust when dealing with queries that contain typos. Current works on improving the typo-robustness of dense retrievers combine (i) data augmentation to obtain the typoed queries during training time with (ii) additional robustifying subtasks that aim to align the original, typo-free queries with their typoed variants. Even though multiple typoed variants are available as positive samples per query, some methods assume a single positive sample and a set of negative ones per anchor and tackle the robustifying subtask with contrastive learning; therefore, making insufficient use of the multiple positives (typoed queries). In contrast, in this work, we argue that all available positives can be used at the same time and employ contrastive learning that supports multiple positives (multi-positive). Experimental results on two datasets show that our proposed approach of leveraging all positives simultaneously and employing multi-positive contrastive learning on the robustifying subtask yields improvements in robustness against using contrastive learning with a single positive.
Natural Language Processing of Aviation Occurrence Reports for Safety Management
Jan 13, 2023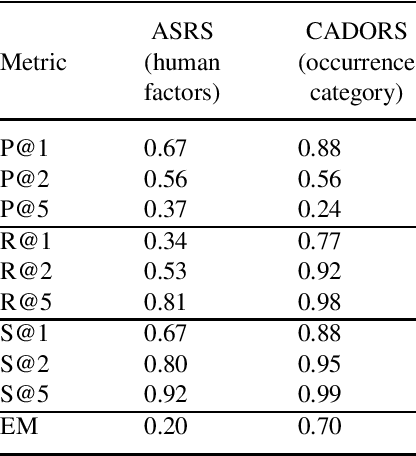
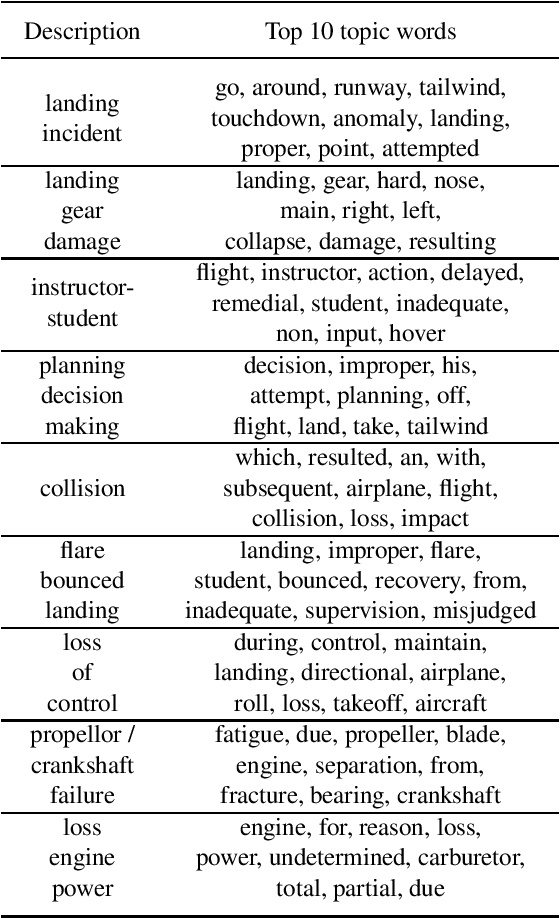
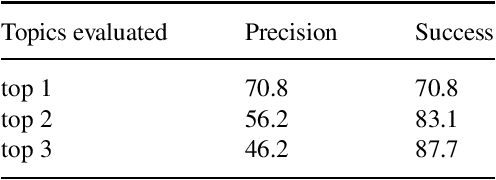
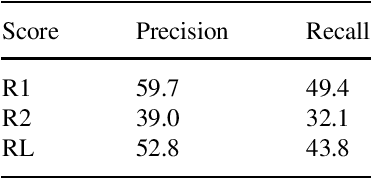
Abstract:Occurrence reporting is a commonly used method in safety management systems to obtain insight in the prevalence of hazards and accident scenarios. In support of safety data analysis, reports are often categorized according to a taxonomy. However, the processing of the reports can require significant effort from safety analysts and a common problem is interrater variability in labeling processes. Also, in some cases, reports are not processed according to a taxonomy, or the taxonomy does not fully cover the contents of the documents. This paper explores various Natural Language Processing (NLP) methods to support the analysis of aviation safety occurrence reports. In particular, the problems studied are the automatic labeling of reports using a classification model, extracting the latent topics in a collection of texts using a topic model and the automatic generation of probable cause texts. Experimental results showed that (i) under the right conditions the labeling of occurrence reports can be effectively automated with a transformer-based classifier, (ii) topic modeling can be useful for finding the topics present in a collection of reports, and (iii) using a summarization model can be a promising direction for generating probable cause texts.
On the Impact of Speech Recognition Errors in Passage Retrieval for Spoken Question Answering
Sep 26, 2022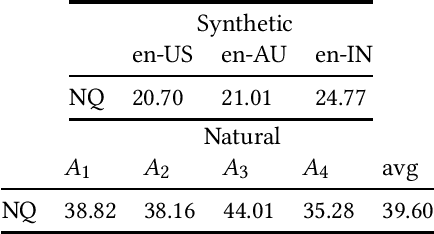
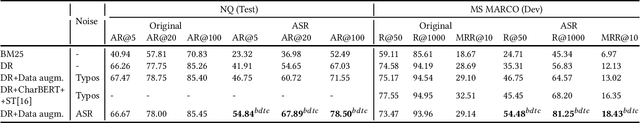
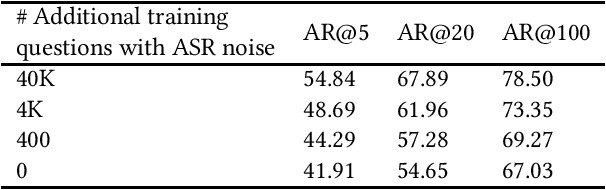
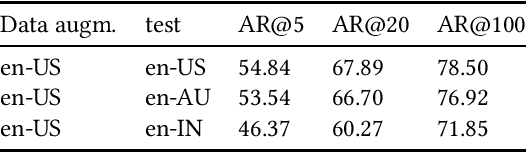
Abstract:Interacting with a speech interface to query a Question Answering (QA) system is becoming increasingly popular. Typically, QA systems rely on passage retrieval to select candidate contexts and reading comprehension to extract the final answer. While there has been some attention to improving the reading comprehension part of QA systems against errors that automatic speech recognition (ASR) models introduce, the passage retrieval part remains unexplored. However, such errors can affect the performance of passage retrieval, leading to inferior end-to-end performance. To address this gap, we augment two existing large-scale passage ranking and open domain QA datasets with synthetic ASR noise and study the robustness of lexical and dense retrievers against questions with ASR noise. Furthermore, we study the generalizability of data augmentation techniques across different domains; with each domain being a different language dialect or accent. Finally, we create a new dataset with questions voiced by human users and use their transcriptions to show that the retrieval performance can further degrade when dealing with natural ASR noise instead of synthetic ASR noise.
Analysing the Robustness of Dual Encoders for Dense Retrieval Against Misspellings
May 04, 2022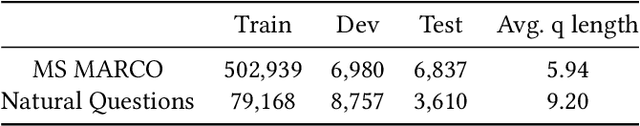
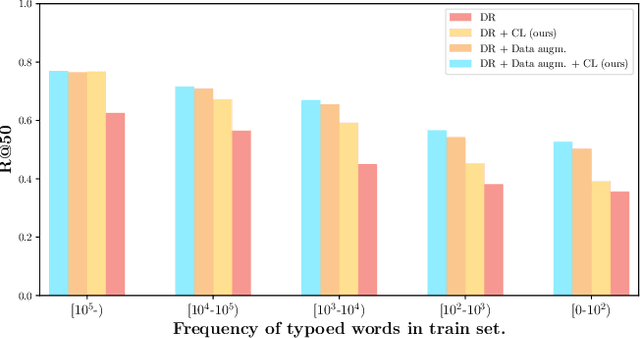
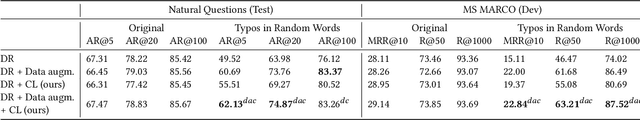
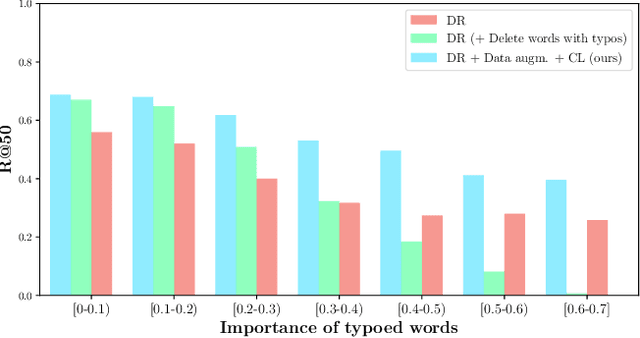
Abstract:Dense retrieval is becoming one of the standard approaches for document and passage ranking. The dual-encoder architecture is widely adopted for scoring question-passage pairs due to its efficiency and high performance. Typically, dense retrieval models are evaluated on clean and curated datasets. However, when deployed in real-life applications, these models encounter noisy user-generated text. That said, the performance of state-of-the-art dense retrievers can substantially deteriorate when exposed to noisy text. In this work, we study the robustness of dense retrievers against typos in the user question. We observe a significant drop in the performance of the dual-encoder model when encountering typos and explore ways to improve its robustness by combining data augmentation with contrastive learning. Our experiments on two large-scale passage ranking and open-domain question answering datasets show that our proposed approach outperforms competing approaches. Additionally, we perform a thorough analysis on robustness. Finally, we provide insights on how different typos affect the robustness of embeddings differently and how our method alleviates the effect of some typos but not of others.
Analysing Dense Passage Retrieval for Multi-hop Question Answering
Jun 15, 2021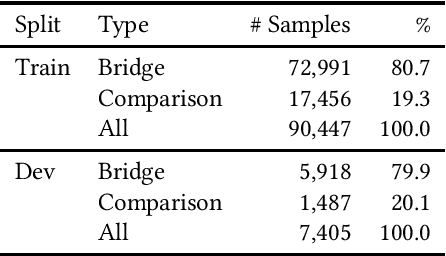
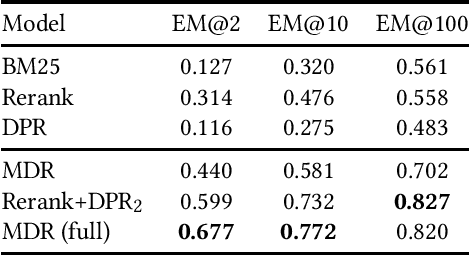
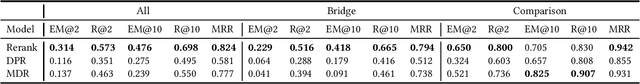
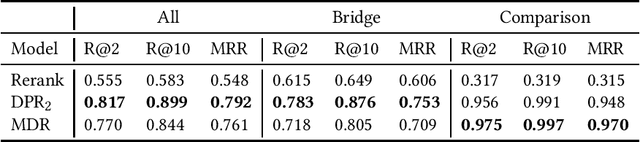
Abstract:We analyse the performance of passage retrieval models in the presence of complex (multi-hop) questions to provide a better understanding of how retrieval systems behave when multiple hops of reasoning are needed. In simple open-domain question answering (QA), dense passage retrieval has become one of the standard approaches for retrieving the relevant passages to infer an answer. Recently, dense passage retrieval also achieved state-of-the-art results in multi-hop QA, where aggregating information from multiple documents and reasoning over them is required. However, so far, the dense retrieval models are not evaluated properly concerning the multi-hop nature of the problem: models are typically evaluated by the end result of the retrieval pipeline, which leaves unclear where their success lies. In this work, we provide an in-depth evaluation of such models not only unveiling the reasons behind their success but also their limitations. Moreover, we introduce a hybrid (lexical and dense) retrieval approach that is highly competitive with the state-of-the-art dense retrieval model, while requiring substantially less computational resources. Furthermore, we also perform qualitative analysis to better understand the challenges behind passage retrieval for multi-hop QA.
Knowledge Graph Simple Question Answering for Unseen Domains
May 25, 2020
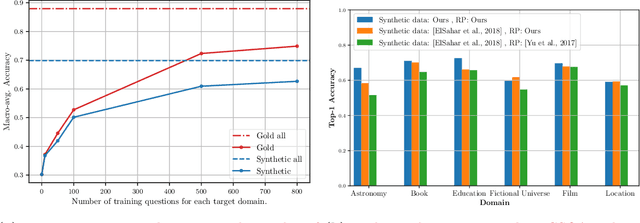
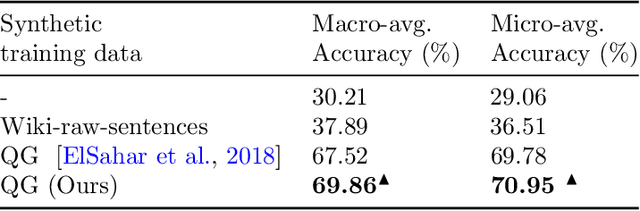
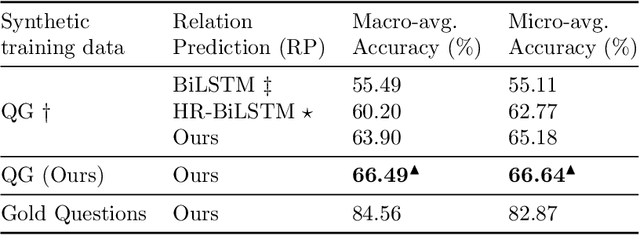
Abstract:Knowledge graph simple question answering (KGSQA), in its standard form, does not take into account that human-curated question answering training data only cover a small subset of the relations that exist in a Knowledge Graph (KG), or even worse, that new domains covering unseen and rather different to existing domains relations are added to the KG. In this work, we study KGSQA in a previously unstudied setting where new, unseen domains are added during test time. In this setting, question-answer pairs of the new domain do not appear during training, thus making the task more challenging. We propose a data-centric domain adaptation framework that consists of a KGSQA system that is applicable to new domains, and a sequence to sequence question generation method that automatically generates question-answer pairs for the new domain. Since the effectiveness of question generation for KGSQA can be restricted by the limited lexical variety of the generated questions, we use distant supervision to extract a set of keywords that express each relation of the unseen domain and incorporate those in the question generation method. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework significantly improves over zero-shot baselines and is robust across domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge