Analysing the Robustness of Dual Encoders for Dense Retrieval Against Misspellings
Paper and Code
May 04, 2022
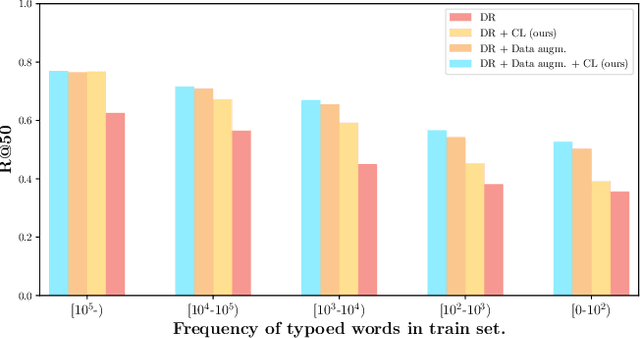
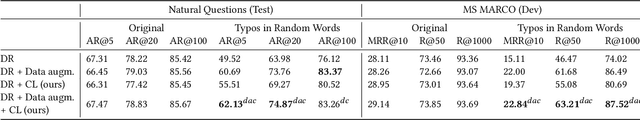
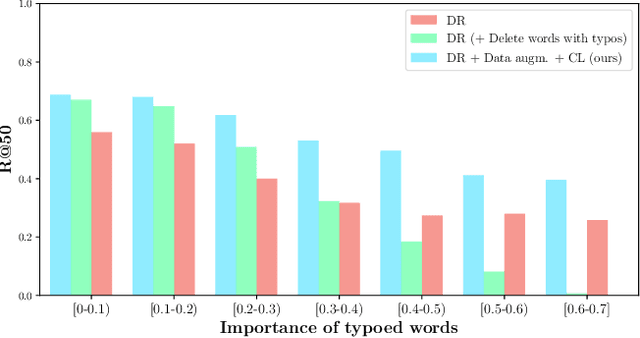
Dense retrieval is becoming one of the standard approaches for document and passage ranking. The dual-encoder architecture is widely adopted for scoring question-passage pairs due to its efficiency and high performance. Typically, dense retrieval models are evaluated on clean and curated datasets. However, when deployed in real-life applications, these models encounter noisy user-generated text. That said, the performance of state-of-the-art dense retrievers can substantially deteriorate when exposed to noisy text. In this work, we study the robustness of dense retrievers against typos in the user question. We observe a significant drop in the performance of the dual-encoder model when encountering typos and explore ways to improve its robustness by combining data augmentation with contrastive learning. Our experiments on two large-scale passage ranking and open-domain question answering datasets show that our proposed approach outperforms competing approaches. Additionally, we perform a thorough analysis on robustness. Finally, we provide insights on how different typos affect the robustness of embeddings differently and how our method alleviates the effect of some typos but not of others.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge