Georgios Ch. Sirakoulis
Intelligent Client Selection for Federated Learning using Cellular Automata
Oct 18, 2023Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a promising solution for privacy-enhancement and latency minimization in various real-world applications, such as transportation, communications, and healthcare. FL endeavors to bring Machine Learning (ML) down to the edge by harnessing data from million of devices and IoT sensors, thus enabling rapid responses to dynamic environments and yielding highly personalized results. However, the increased amount of sensors across diverse applications poses challenges in terms of communication and resource allocation, hindering the participation of all devices in the federated process and prompting the need for effective FL client selection. To address this issue, we propose Cellular Automaton-based Client Selection (CA-CS), a novel client selection algorithm, which leverages Cellular Automata (CA) as models to effectively capture spatio-temporal changes in a fast-evolving environment. CA-CS considers the computational resources and communication capacity of each participating client, while also accounting for inter-client interactions between neighbors during the client selection process, enabling intelligent client selection for online FL processes on data streams that closely resemble real-world scenarios. In this paper, we present a thorough evaluation of the proposed CA-CS algorithm using MNIST and CIFAR-10 datasets, while making a direct comparison against a uniformly random client selection scheme. Our results demonstrate that CA-CS achieves comparable accuracy to the random selection approach, while effectively avoiding high-latency clients.
Protein Structured Reservoir computing for Spike-based Pattern Recognition
Aug 07, 2020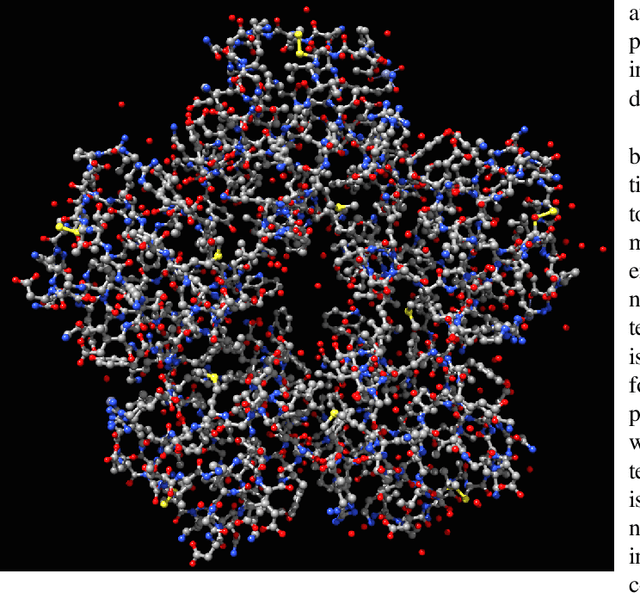
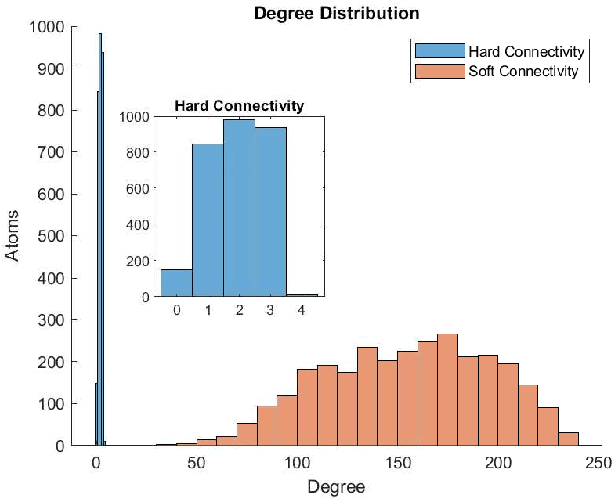
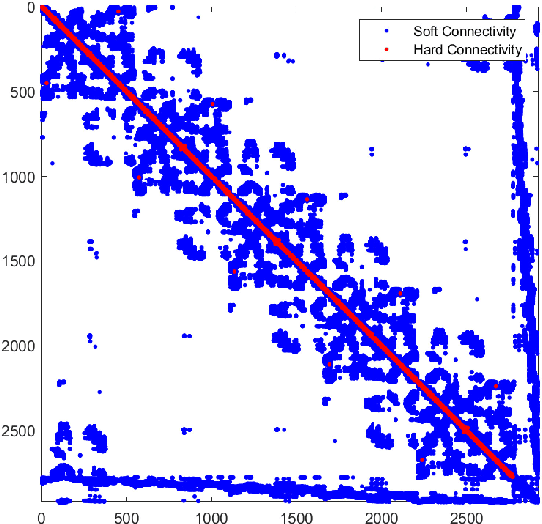

Abstract:Nowadays we witness a miniaturisation trend in the semiconductor industry backed up by groundbreaking discoveries and designs in nanoscale characterisation and fabrication. To facilitate the trend and produce ever smaller, faster and cheaper computing devices, the size of nanoelectronic devices is now reaching the scale of atoms or molecules - a technical goal undoubtedly demanding for novel devices. Following the trend, we explore an unconventional route of implementing a reservoir computing on a single protein molecule and introduce neuromorphic connectivity with a small-world networking property. We have chosen Izhikevich spiking neurons as elementary processors, corresponding to the atoms of verotoxin protein, and its molecule as a 'hardware' architecture of the communication networks connecting the processors. We apply on a single readout layer various training methods in a supervised fashion to investigate whether the molecular structured Reservoir Computing (RC) system is capable to deal with machine learning benchmarks. We start with the Remote Supervised Method, based on Spike-Timing-Dependent-Plasticity, and carry on with linear regression and scaled conjugate gradient back-propagation training methods. The RC network is evaluated as a proof-of-concept on the handwritten digit images from the MNIST dataset and demonstrates acceptable classification accuracy in comparison with other similar approaches.
Salt-n-pepper noise filtering using Cellular Automata
Aug 16, 2017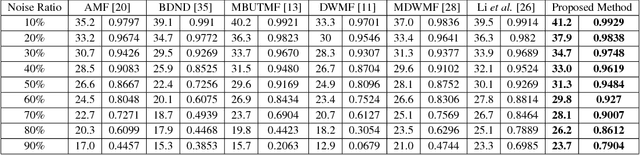
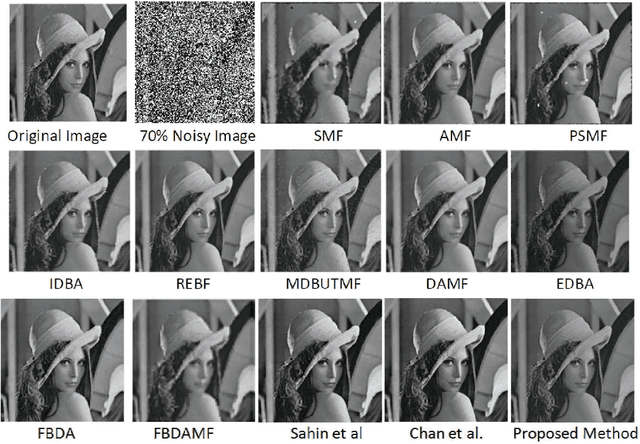
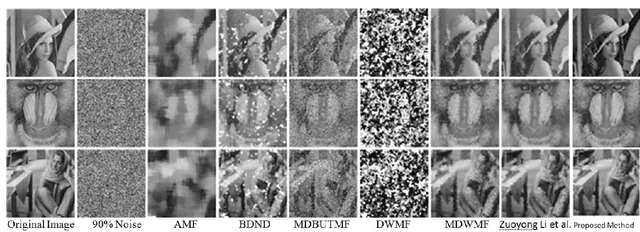
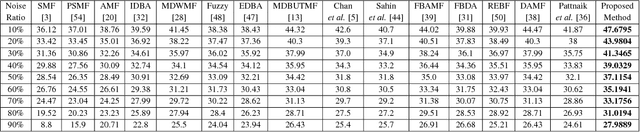

Abstract:Cellular Automata (CA) have been considered one of the most pronounced parallel computational tools in the recent era of nature and bio-inspired computing. Taking advantage of their local connectivity, the simplicity of their design and their inherent parallelism, CA can be effectively applied to many image processing tasks. In this paper, a CA approach for efficient salt-n-pepper noise filtering in grayscale images is presented. Using a 2D Moore neighborhood, the classified "noisy" cells are corrected by averaging the non-noisy neighboring cells. While keeping the computational burden really low, the proposed approach succeeds in removing high-noise levels from various images and yields promising qualitative and quantitative results, compared to state-of-the-art techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge