Dimitrios Tourtounis
Salt-n-pepper noise filtering using Cellular Automata
Aug 16, 2017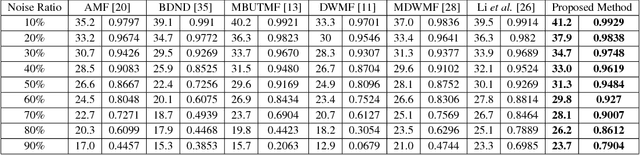
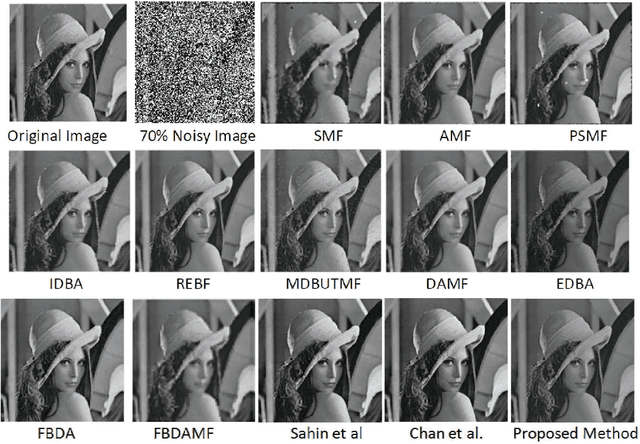
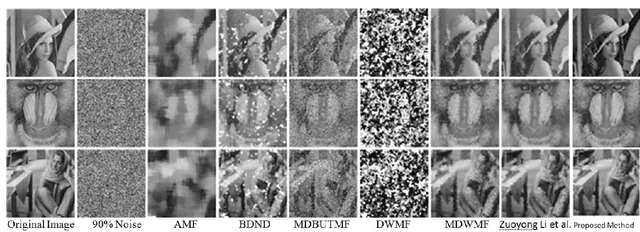
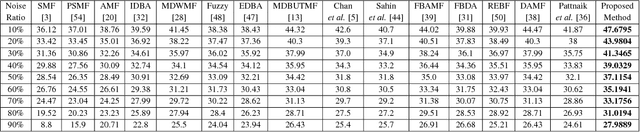

Abstract:Cellular Automata (CA) have been considered one of the most pronounced parallel computational tools in the recent era of nature and bio-inspired computing. Taking advantage of their local connectivity, the simplicity of their design and their inherent parallelism, CA can be effectively applied to many image processing tasks. In this paper, a CA approach for efficient salt-n-pepper noise filtering in grayscale images is presented. Using a 2D Moore neighborhood, the classified "noisy" cells are corrected by averaging the non-noisy neighboring cells. While keeping the computational burden really low, the proposed approach succeeds in removing high-noise levels from various images and yields promising qualitative and quantitative results, compared to state-of-the-art techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge