George Legrady
Equivalence: An analysis of artists' roles with Image Generative AI from Conceptual Art perspective through an interactive installation design practice
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:Over the past year, the emergence of advanced text-to-image Generative AI models has significantly impacted the art world, challenging traditional notions of creativity and the role of artists. This study explores how artists interact with these technologies, using a 5P model (Purpose, People, Process, Product, and Press) based on Rhodes' creativity framework to compare the artistic processes behind Conceptual Art and Image Generative AI. To exemplify this framework, a practical case study titled "Equivalence", a multi-screen interactive installation that converts users' speech input into continuously evolving paintings developed based on Stable Diffusion and NLP algorithms, was developed. Through comprehensive analysis and the case study, this work aims to broaden our understanding of artists' roles and foster a deeper appreciation for the creative aspects inherent in artwork created with Image Generative AI.
Combating the "Sameness" in AI Art: Reflections on the Interactive AI Installation Fencing Hallucination
Nov 28, 2023Abstract:The article summarizes three types of "sameness" issues in Artificial Intelligence(AI) art, each occurring at different stages of development in AI image creation tools. Through the Fencing Hallucination project, the article reflects on the design of AI art production in alleviating the sense of uniformity, maintaining the uniqueness of images from an AI image synthesizer, and enhancing the connection between the artworks and the audience. This paper endeavors to stimulate the creation of distinctive AI art by recounting the efforts and insights derived from the Fencing Hallucination project, all dedicated to addressing the issue of "sameness".
Visual Diagnostics for Deep Reinforcement Learning Policy Development
Sep 26, 2018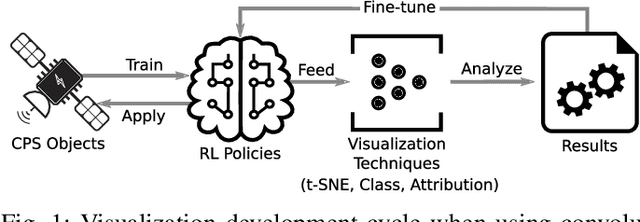

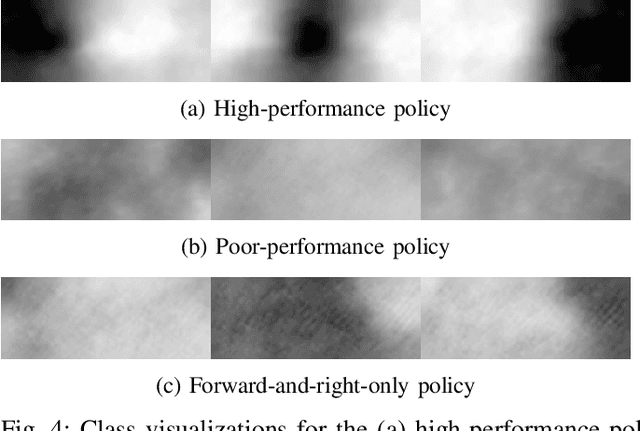
Abstract:Modern vision-based reinforcement learning techniques often use convolutional neural networks (CNN) as universal function approximators to choose which action to take for a given visual input. Until recently, CNNs have been treated like black-box functions, but this mindset is especially dangerous when used for control in safety-critical settings. In this paper, we present our extensions of CNN visualization algorithms to the domain of vision-based reinforcement learning. We use a simulated drone environment as an example scenario. These visualization algorithms are an important tool for behavior introspection and provide insight into the qualities and flaws of trained policies when interacting with the physical world. A video may be seen at https://sites.google.com/view/drlvisual .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge