Geevarghese George
Developing Predictive and Robust Radiomics Models for Chemotherapy Response in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Objectives: High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) is typically diagnosed at an advanced stage with extensive peritoneal metastases, making treatment challenging. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) is often used to reduce tumor burden before surgery, but about 40% of patients show limited response. Radiomics, combined with machine learning (ML), offers a promising non-invasive method for predicting NACT response by analyzing computed tomography (CT) imaging data. This study aimed to improve response prediction in HGSOC patients undergoing NACT by integration different feature selection methods. Materials and methods: A framework for selecting robust radiomics features was introduced by employing an automated randomisation algorithm to mimic inter-observer variability, ensuring a balance between feature robustness and prediction accuracy. Four response metrics were used: chemotherapy response score (CRS), RECIST, volume reduction (VolR), and diameter reduction (DiaR). Lesions in different anatomical sites were studied. Pre- and post-NACT CT scans were used for feature extraction and model training on one cohort, and an independent cohort was used for external testing. Results: The best prediction performance was achieved using all lesions combined for VolR prediction, with an AUC of 0.83. Omental lesions provided the best results for CRS prediction (AUC 0.77), while pelvic lesions performed best for DiaR (AUC 0.76). Conclusion: The integration of robustness into the feature selection processes ensures the development of reliable models and thus facilitates the implementation of the radiomics models in clinical applications for HGSOC patients. Future work should explore further applications of radiomics in ovarian cancer, particularly in real-time clinical settings.
Breast MRI radiomics and machine learning radiomics-based predictions of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy -- how are they affected by variations in tumour delineation?
Sep 03, 2023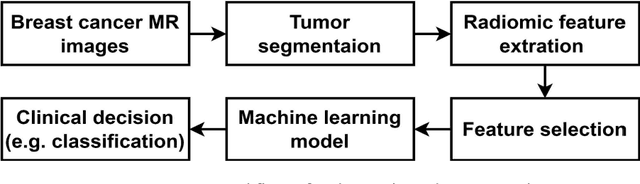
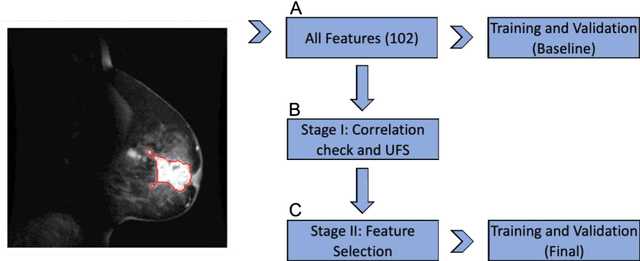
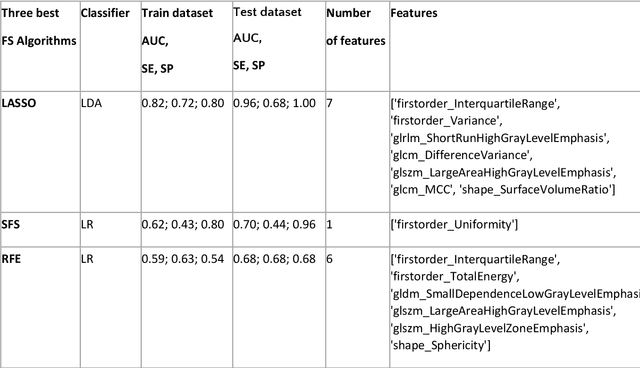
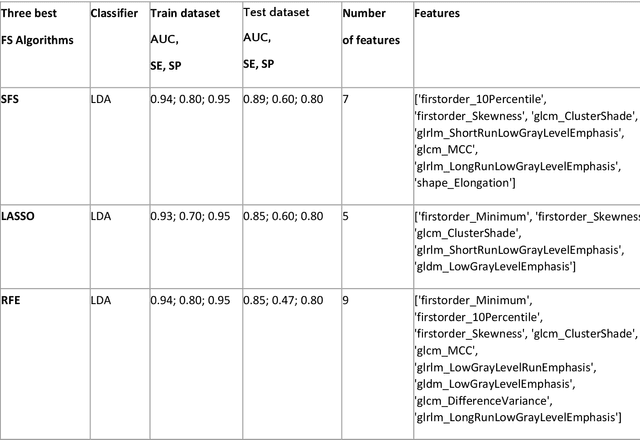
Abstract:Manual delineation of volumes of interest (VOIs) by experts is considered the gold-standard method in radiomics analysis. However, it suffers from inter- and intra-operator variability. A quantitative assessment of the impact of variations in these delineations on the performance of the radiomics predictors is required to develop robust radiomics based prediction models. In this study, we developed radiomics models for the prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with two different breast cancer subtypes based on contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging acquired prior to treatment (baseline MRI scans). Different mathematical operations such as erosion, smoothing, dilation, randomization, and ellipse fitting were applied to the original VOIs delineated by experts to simulate variations of segmentation masks. The effects of such VOI modifications on various steps of the radiomics workflow, including feature extraction, feature selection, and prediction performance, were evaluated. Using manual tumor VOIs and radiomics features extracted from baseline MRI scans, an AUC of up to 0.96 and 0.89 was achieved for human epidermal growth receptor 2 positive and triple-negative breast cancer, respectively. For smoothing and erosion, VOIs yielded the highest number of robust features and the best prediction performance, while ellipse fitting and dilation lead to the lowest robustness and prediction performance for both breast cancer subtypes. At most 28% of the selected features were similar to manual VOIs when different VOI delineation data were used. Differences in VOI delineation affects different steps of radiomics analysis, and their quantification is therefore important for development of standardized radiomics research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge