Gaozhen Nie
AI Models Still Lag Behind Traditional Numerical Models in Predicting Sudden-Turning Typhoons
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Given the interpretability, accuracy, and stability of numerical weather prediction (NWP) models, current operational weather forecasting relies heavily on the NWP approach. In the past two years, the rapid development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has provided an alternative solution for medium-range (1-10 days) weather forecasting. Bi et al. (2023) (hereafter Bi23) introduced the first AI-based weather prediction (AIWP) model in China, named Pangu-Weather, which offers fast prediction without compromising accuracy. In their work, Bi23 made notable claims regarding its effectiveness in extreme weather predictions. However, this claim lacks persuasiveness because the extreme nature of the two tropical cyclones (TCs) examples presented in Bi23, namely Typhoon Kong-rey and Typhoon Yutu, stems primarily from their intensities rather than their moving paths. Their claim may mislead into another meaning which is that Pangu-Weather works well in predicting unusual typhoon paths, which was not explicitly analyzed. Here, we reassess Pangu-Weather's ability to predict extreme TC trajectories from 2020-2024. Results reveal that while Pangu-Weather overall outperforms NWP models in predicting tropical cyclone (TC) tracks, it falls short in accurately predicting the rarely observed sudden-turning tracks, such as Typhoon Khanun in 2023. We argue that current AIWP models still lag behind traditional NWP models in predicting such rare extreme events in medium-range forecasts.
Weather2K: A Multivariate Spatio-Temporal Benchmark Dataset for Meteorological Forecasting Based on Real-Time Observation Data from Ground Weather Stations
Feb 21, 2023
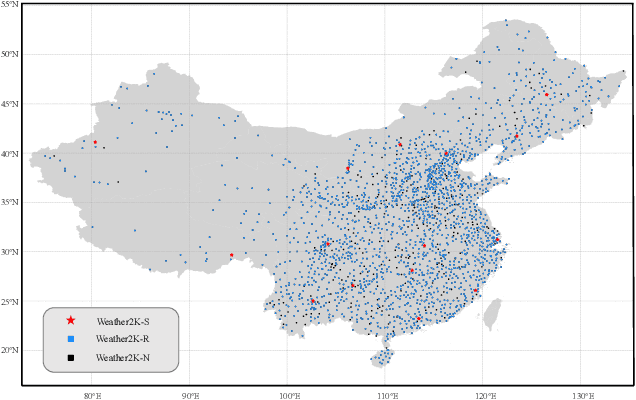

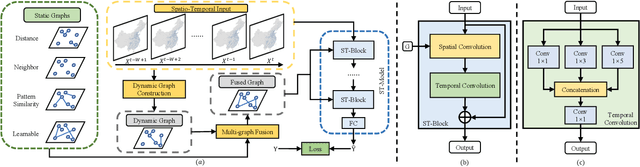
Abstract:Weather forecasting is one of the cornerstones of meteorological work. In this paper, we present a new benchmark dataset named Weather2K, which aims to make up for the deficiencies of existing weather forecasting datasets in terms of real-time, reliability, and diversity, as well as the key bottleneck of data quality. To be specific, our Weather2K is featured from the following aspects: 1) Reliable and real-time data. The data is hourly collected from 2,130 ground weather stations covering an area of 6 million square kilometers. 2) Multivariate meteorological variables. 20 meteorological factors and 3 constants for position information are provided with a length of 40,896 time steps. 3) Applicable to diverse tasks. We conduct a set of baseline tests on time series forecasting and spatio-temporal forecasting. To the best of our knowledge, our Weather2K is the first attempt to tackle weather forecasting task by taking full advantage of the strengths of observation data from ground weather stations. Based on Weather2K, we further propose Meteorological Factors based Multi-Graph Convolution Network (MFMGCN), which can effectively construct the intrinsic correlation among geographic locations based on meteorological factors. Sufficient experiments show that MFMGCN improves both the forecasting performance and temporal robustness. We hope our Weather2K can significantly motivate researchers to develop efficient and accurate algorithms to advance the task of weather forecasting. The dataset can be available at https://github.com/bycnfz/weather2k/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge