Gaëtan Serré
CB
Stein Boltzmann Sampling: A Variational Approach for Global Optimization
Feb 20, 2024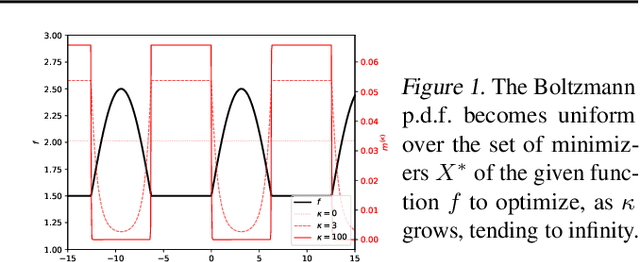
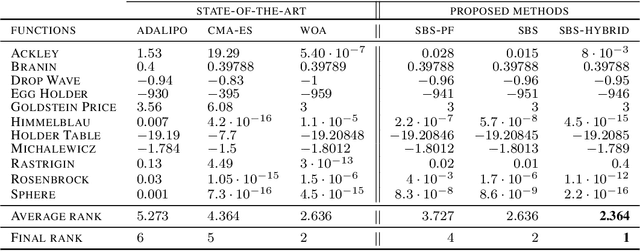
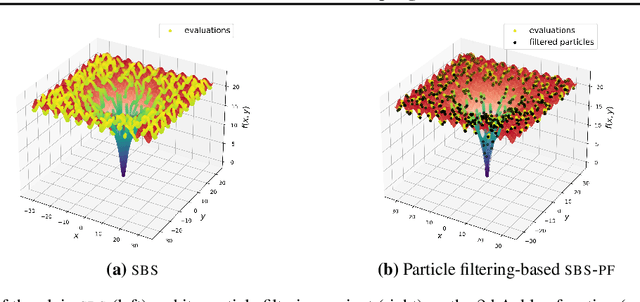
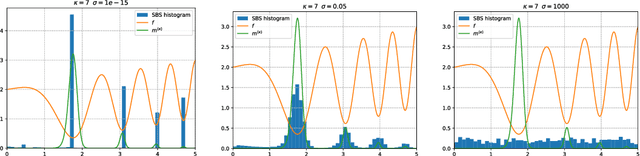
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a new flow-based method for global optimization of Lipschitz functions, called Stein Boltzmann Sampling (SBS). Our method samples from the Boltzmann distribution that becomes asymptotically uniform over the set of the minimizers of the function to be optimized. Candidate solutions are sampled via the \emph{Stein Variational Gradient Descent} algorithm. We prove the asymptotic convergence of our method, introduce two SBS variants, and provide a detailed comparison with several state-of-the-art global optimization algorithms on various benchmark functions. The design of our method, the theoretical results, and our experiments, suggest that SBS is particularly well-suited to be used as a continuation of efficient global optimization methods as it can produce better solutions while making a good use of the budget.
Reinforcement learning for Energies of the future and carbon neutrality: a Challenge Design
Jul 21, 2022
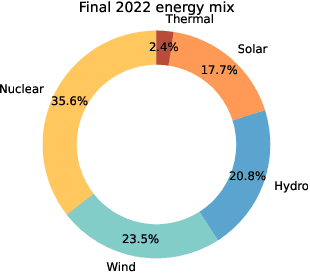

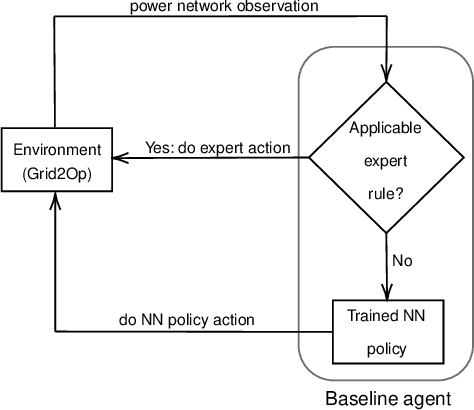
Abstract:Current rapid changes in climate increase the urgency to change energy production and consumption management, to reduce carbon and other green-house gas production. In this context, the French electricity network management company RTE (R{\'e}seau de Transport d'{\'E}lectricit{\'e}) has recently published the results of an extensive study outlining various scenarios for tomorrow's French power management. We propose a challenge that will test the viability of such a scenario. The goal is to control electricity transportation in power networks, while pursuing multiple objectives: balancing production and consumption, minimizing energetic losses, and keeping people and equipment safe and particularly avoiding catastrophic failures. While the importance of the application provides a goal in itself, this challenge also aims to push the state-of-the-art in a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) called Reinforcement Learning (RL), which offers new possibilities to tackle control problems. In particular, various aspects of the combination of Deep Learning and RL called Deep Reinforcement Learning remain to be harnessed in this application domain. This challenge belongs to a series started in 2019 under the name "Learning to run a power network" (L2RPN). In this new edition, we introduce new more realistic scenarios proposed by RTE to reach carbon neutrality by 2050, retiring fossil fuel electricity production, increasing proportions of renewable and nuclear energy and introducing batteries. Furthermore, we provide a baseline using state-of-the-art reinforcement learning algorithm to stimulate the future participants.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge