G. Charbel N. Kindji
IRISA, MALT
Datum-wise Transformer for Synthetic Tabular Data Detection in the Wild
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:The growing power of generative models raises major concerns about the authenticity of published content. To address this problem, several synthetic content detection methods have been proposed for uniformly structured media such as image or text. However, little work has been done on the detection of synthetic tabular data, despite its importance in industry and government. This form of data is complex to handle due to the diversity of its structures: the number and types of the columns may vary wildly from one table to another. We tackle the tough problem of detecting synthetic tabular data ''in the wild'', i.e. when the model is deployed on table structures it has never seen before. We introduce a novel datum-wise transformer architecture and show that it outperforms existing models. Furthermore, we investigate the application of domain adaptation techniques to enhance the effectiveness of our model, thereby providing a more robust data-forgery detection solution.
Synthetic Tabular Data Detection In the Wild
Mar 03, 2025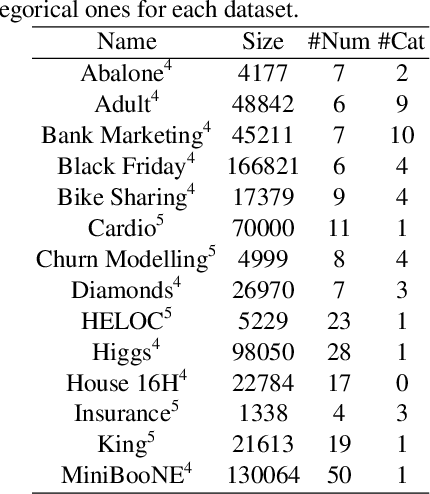
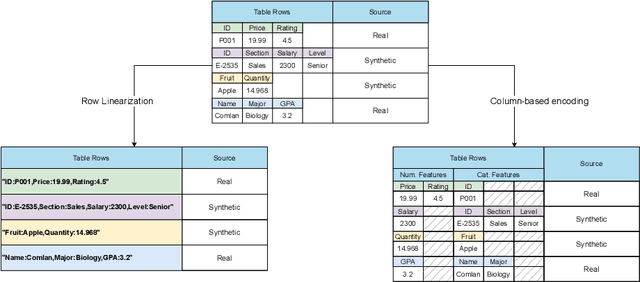
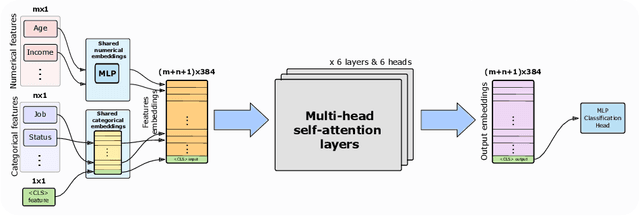
Abstract:Detecting synthetic tabular data is essential to prevent the distribution of false or manipulated datasets that could compromise data-driven decision-making. This study explores whether synthetic tabular data can be reliably identified across different tables. This challenge is unique to tabular data, where structures (such as number of columns, data types, and formats) can vary widely from one table to another. We propose four table-agnostic detectors combined with simple preprocessing schemes that we evaluate on six evaluation protocols, with different levels of ''wildness''. Our results show that cross-table learning on a restricted set of tables is possible even with naive preprocessing schemes. They confirm however that cross-table transfer (i.e. deployment on a table that has not been seen before) is challenging. This suggests that sophisticated encoding schemes are required to handle this problem.
Cross-table Synthetic Tabular Data Detection
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Detecting synthetic tabular data is essential to prevent the distribution of false or manipulated datasets that could compromise data-driven decision-making. This study explores whether synthetic tabular data can be reliably identified ''in the wild''-meaning across different generators, domains, and table formats. This challenge is unique to tabular data, where structures (such as number of columns, data types, and formats) can vary widely from one table to another. We propose three cross-table baseline detectors and four distinct evaluation protocols, each corresponding to a different level of ''wildness''. Our very preliminary results confirm that cross-table adaptation is a challenging task.
Under the Hood of Tabular Data Generation Models: the Strong Impact of Hyperparameter Tuning
Jun 18, 2024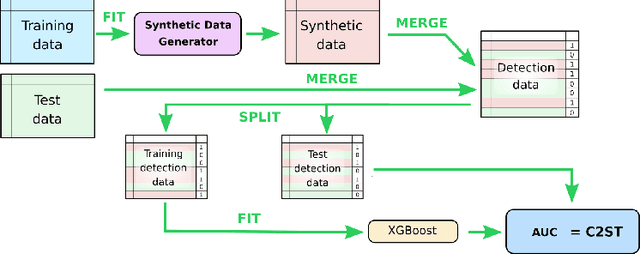
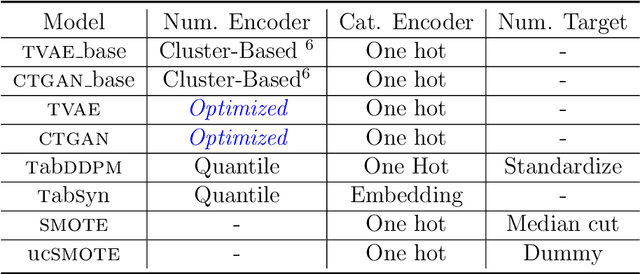
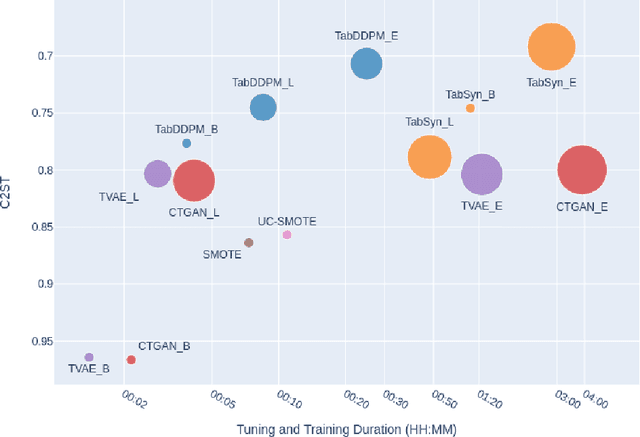
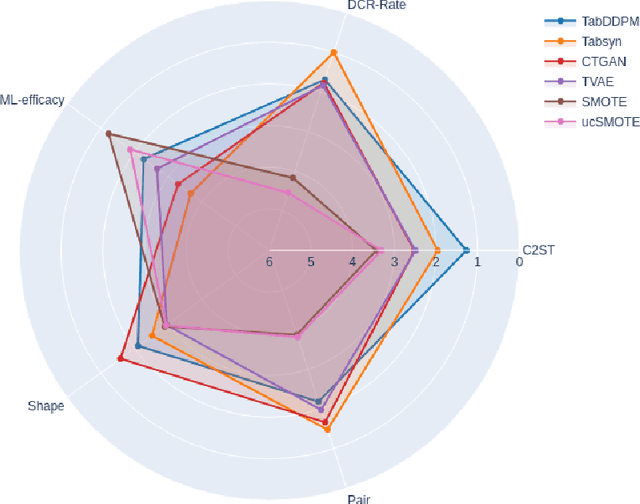
Abstract:We investigate the impact of dataset-specific hyperparameter, feature encoding, and architecture tuning on five recent model families for tabular data generation through an extensive benchmark on 16 datasets. This study addresses the practical need for a unified evaluation of models that fully considers hyperparameter optimization. Additionally, we propose a reduced search space for each model that allows for quick optimization, achieving nearly equivalent performance at a significantly lower cost.Our benchmark demonstrates that, for most models, large-scale dataset-specific tuning substantially improves performance compared to the original configurations. Furthermore, we confirm that diffusion-based models generally outperform other models on tabular data. However, this advantage is not significant when the entire tuning and training process is restricted to the same GPU budget for all models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge