Fujun Gao
Achieving Covert Communication With A Probabilistic Jamming Strategy
Aug 29, 2023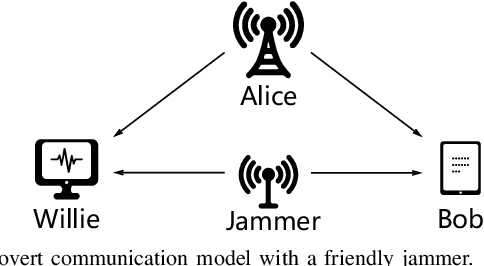
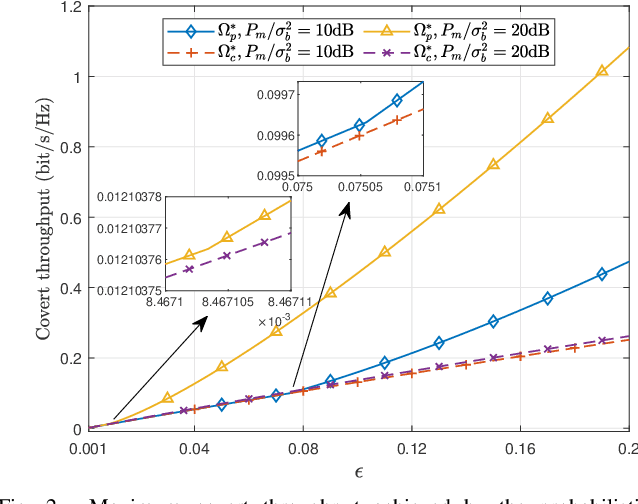
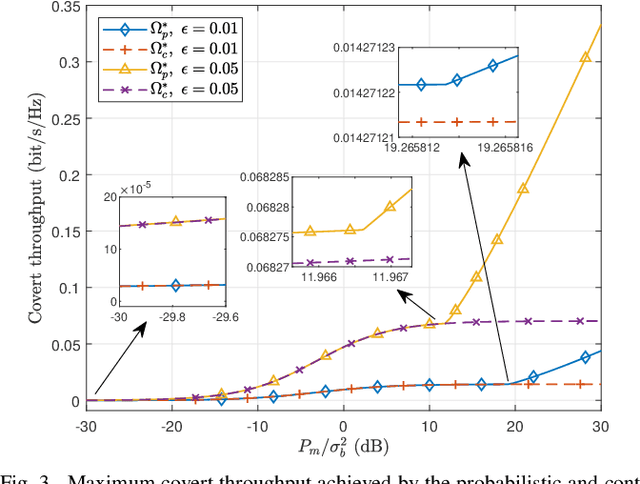
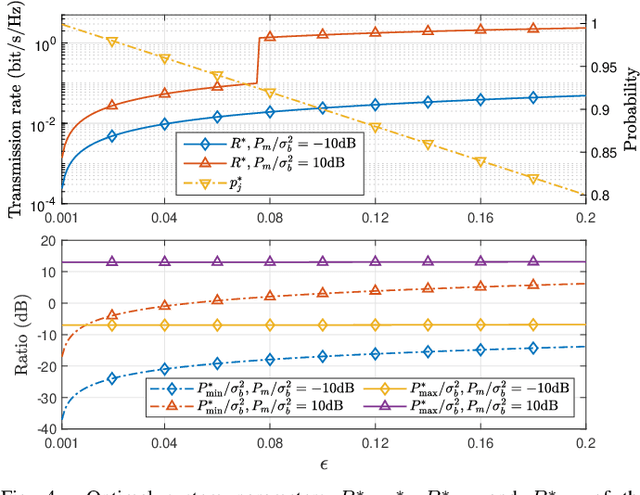
Abstract:In this work, we consider a covert communication scenario, where a transmitter Alice communicates to a receiver Bob with the aid of a probabilistic and uninformed jammer against an adversary warden's detection. The transmission status and power of the jammer are random and follow some priori probabilities. We first analyze the warden's detection performance as a function of the jammer's transmission probability, transmit power distribution, and Alice's transmit power. We then maximize the covert throughput from Alice to Bob subject to a covertness constraint, by designing the covert communication strategies from three different perspectives: Alice's perspective, the jammer's perspective, and the global perspective. Our analysis reveals that the minimum jamming power should not always be zero in the probabilistic jamming strategy, which is different from that in the continuous jamming strategy presented in the literature. In addition, we prove that the minimum jamming power should be the same as Alice's covert transmit power, depending on the covertness and average jamming power constraints. Furthermore, our results show that the probabilistic jamming can outperform the continuous jamming in terms of achieving a higher covert throughput under the same covertness and average jamming power constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge