Frederico G. Guimarães
Online path planning for kinematic-constrained UAVs in a dynamic environment based on a Differential Evolution algorithm
Oct 24, 2024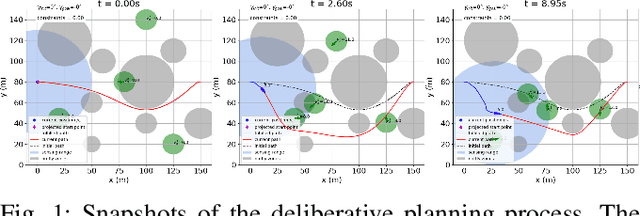
Abstract:This research presents an online path planner for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) that can handle dynamic obstacles and UAV motion constraints, including maximum curvature and desired orientations. Our proposed planner uses a NURBS path representation and a Differential Evolution algorithm, incorporating concepts from the Velocity Obstacle approach in a constraint function. Initial results show that our approach is feasible and provides a foundation for future extensions to three-dimensional (3D) environments.
The Cone epsilon-Dominance: An Approach for Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization
Jul 14, 2020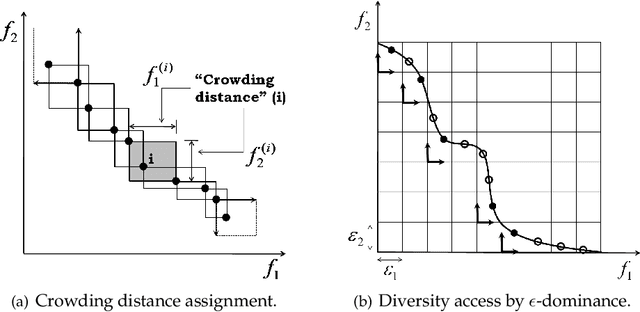
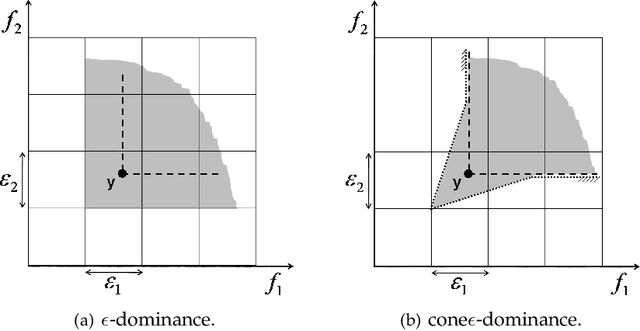
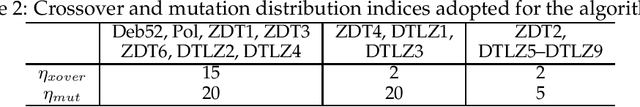
Abstract:We propose the cone epsilon-dominance approach to improve convergence and diversity in multiobjective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs). A cone-eps-MOEA is presented and compared with MOEAs based on the standard Pareto relation (NSGA-II, NSGA-II*, SPEA2, and a clustered NSGA-II) and on the epsilon-dominance (eps-MOEA). The comparison is performed both in terms of computational complexity and on four performance indicators selected to quantify the quality of the final results obtained by each algorithm: the convergence, diversity, hypervolume, and coverage of many sets metrics. Sixteen well-known benchmark problems are considered in the experimental section, including the ZDT and the DTLZ families. To evaluate the possible differences amongst the algorithms, a carefully designed experiment is performed for the four performance metrics. The results obtained suggest that the cone-eps-MOEA is capable of presenting an efficient and balanced performance over all the performance metrics considered. These results strongly support the conclusion that the cone-eps-MOEA is a competitive approach for obtaining an efficient balance between convergence and diversity to the Pareto front, and as such represents a useful tool for the solution of multiobjective optimization problems.
COVID-ABS: An Agent-Based Model of COVID-19 Epidemic to Simulate Health and Economic Effects of Social Distancing Interventions
Jun 09, 2020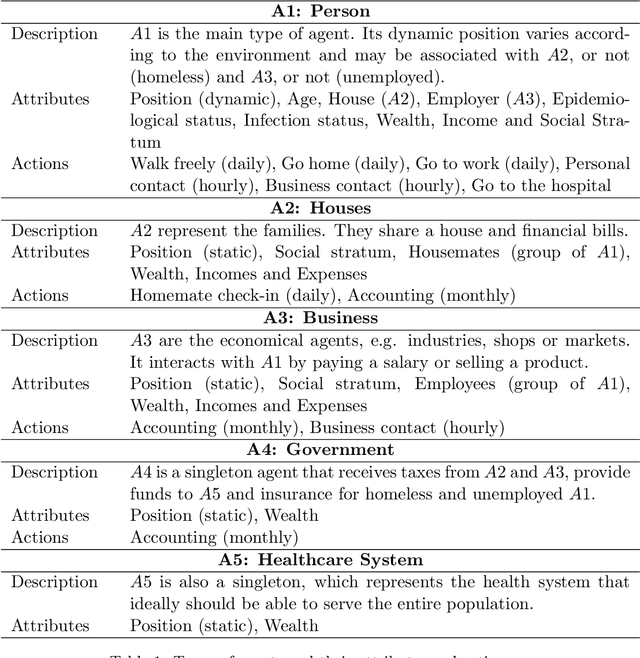
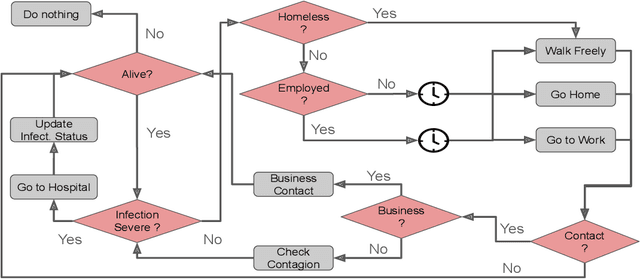
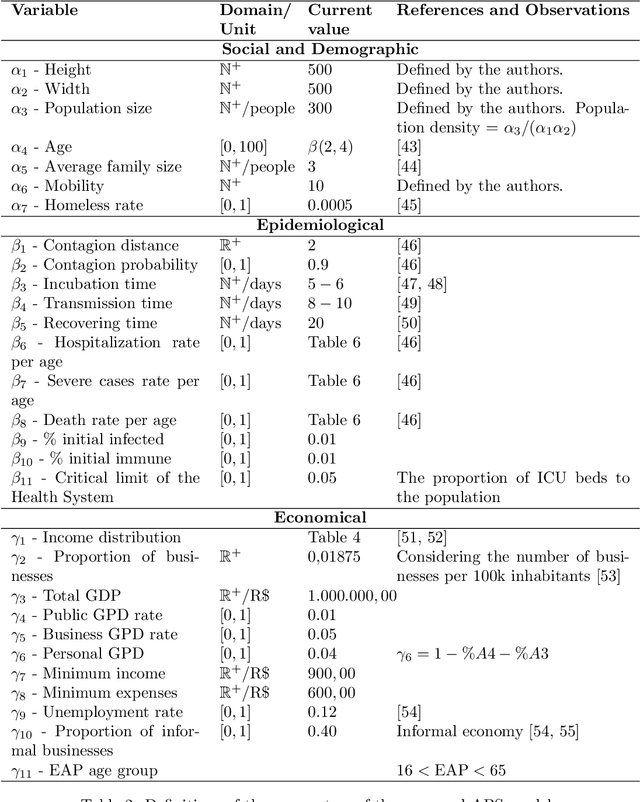
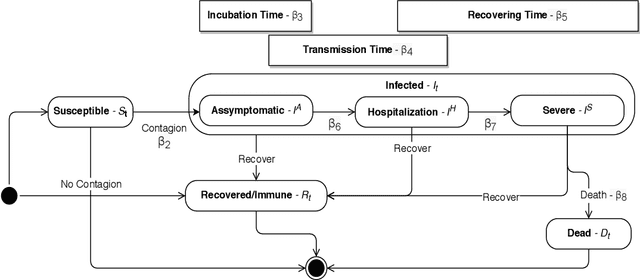
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic due to the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus have directly impacted the public health and economy. To overcome this problem, the countries have adopted different policies for controlling the spread of the virus. This paper proposes the COVID-ABS, a new SEIR agent-based model that aims to simulate the pandemic dynamics using a society of agents emulating people, business and government. Seven different scenarios varying epidemiological and economical effects of social distance interventions were performed, which are: (1) do nothing, (2) lockdown, (3) conditional lockdown, (4) vertical isolation, (5) partial isolation, (6) use of face masks, and (7) use of face masks together with 50% of adhesion to social isolation. In the impossibility of implementing scenarios with lockdown which present the lowest number of deaths and highest impact on the economy, scenarios combining the use of face masks and partial isolation can be the more realistic for implementation in terms of social cooperation. The model can be easily extended to new societies by varying the parameters as well as allows the creating of a multitude of other scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge