Freba Ahmaddy
Automatic Liver and Tumor Segmentation of CT and MRI Volumes using Cascaded Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Feb 23, 2017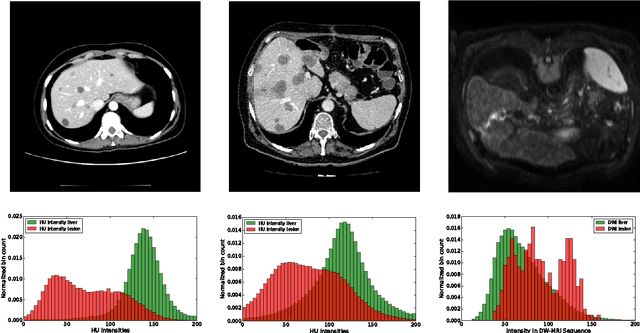
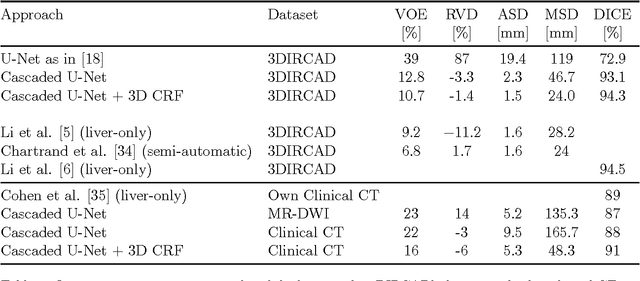
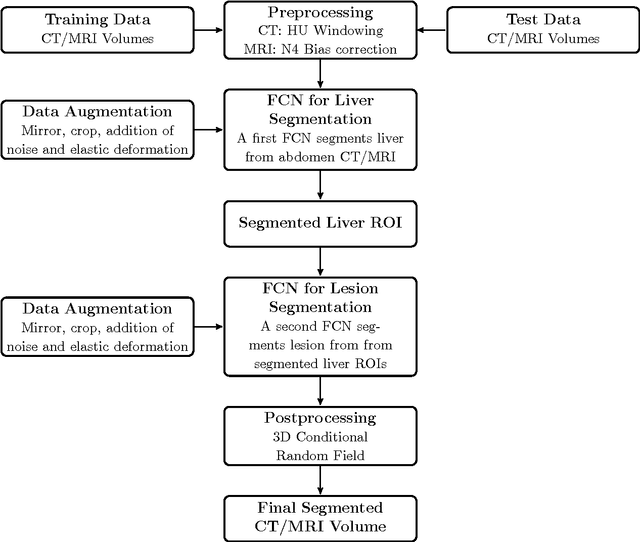
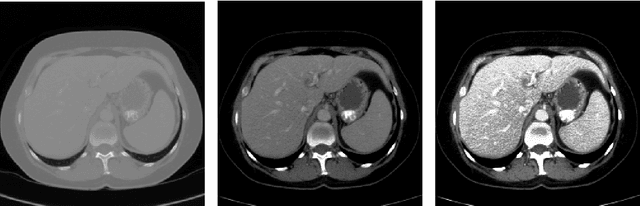
Abstract:Automatic segmentation of the liver and hepatic lesions is an important step towards deriving quantitative biomarkers for accurate clinical diagnosis and computer-aided decision support systems. This paper presents a method to automatically segment liver and lesions in CT and MRI abdomen images using cascaded fully convolutional neural networks (CFCNs) enabling the segmentation of a large-scale medical trial or quantitative image analysis. We train and cascade two FCNs for a combined segmentation of the liver and its lesions. In the first step, we train a FCN to segment the liver as ROI input for a second FCN. The second FCN solely segments lesions within the predicted liver ROIs of step 1. CFCN models were trained on an abdominal CT dataset comprising 100 hepatic tumor volumes. Validations on further datasets show that CFCN-based semantic liver and lesion segmentation achieves Dice scores over 94% for liver with computation times below 100s per volume. We further experimentally demonstrate the robustness of the proposed method on an 38 MRI liver tumor volumes and the public 3DIRCAD dataset.
SurvivalNet: Predicting patient survival from diffusion weighted magnetic resonance images using cascaded fully convolutional and 3D convolutional neural networks
Feb 20, 2017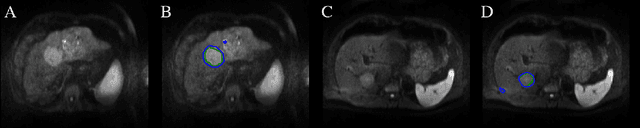

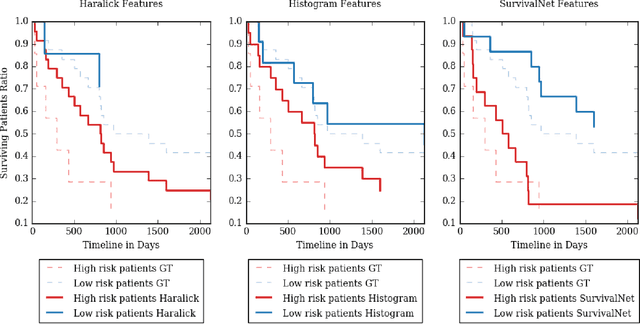
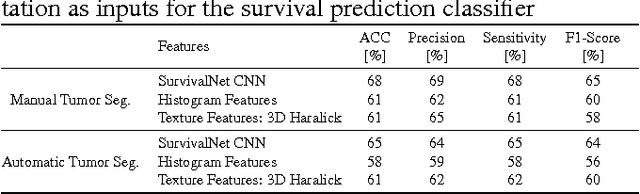
Abstract:Automatic non-invasive assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) malignancy has the potential to substantially enhance tumor treatment strategies for HCC patients. In this work we present a novel framework to automatically characterize the malignancy of HCC lesions from DWI images. We predict HCC malignancy in two steps: As a first step we automatically segment HCC tumor lesions using cascaded fully convolutional neural networks (CFCN). A 3D neural network (SurvivalNet) then predicts the HCC lesions' malignancy from the HCC tumor segmentation. We formulate this task as a classification problem with classes being "low risk" and "high risk" represented by longer or shorter survival times than the median survival. We evaluated our method on DWI of 31 HCC patients. Our proposed framework achieves an end-to-end accuracy of 65% with a Dice score for the automatic lesion segmentation of 69% and an accuracy of 68% for tumor malignancy classification based on expert annotations. We compared the SurvivalNet to classical handcrafted features such as Histogram and Haralick and show experimentally that SurvivalNet outperforms the handcrafted features in HCC malignancy classification. End-to-end assessment of tumor malignancy based on our proposed fully automatic framework corresponds to assessment based on expert annotations with high significance (p>0.95).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge