Frank Proske
On the Theoretical Properties of Noise Correlation in Stochastic Optimization
Sep 19, 2022



Abstract:Studying the properties of stochastic noise to optimize complex non-convex functions has been an active area of research in the field of machine learning. Prior work has shown that the noise of stochastic gradient descent improves optimization by overcoming undesirable obstacles in the landscape. Moreover, injecting artificial Gaussian noise has become a popular idea to quickly escape saddle points. Indeed, in the absence of reliable gradient information, the noise is used to explore the landscape, but it is unclear what type of noise is optimal in terms of exploration ability. In order to narrow this gap in our knowledge, we study a general type of continuous-time non-Markovian process, based on fractional Brownian motion, that allows for the increments of the process to be correlated. This generalizes processes based on Brownian motion, such as the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process. We demonstrate how to discretize such processes which gives rise to the new algorithm fPGD. This method is a generalization of the known algorithms PGD and Anti-PGD. We study the properties of fPGD both theoretically and empirically, demonstrating that it possesses exploration abilities that, in some cases, are favorable over PGD and Anti-PGD. These results open the field to novel ways to exploit noise for training machine learning models.
Anticorrelated Noise Injection for Improved Generalization
Feb 06, 2022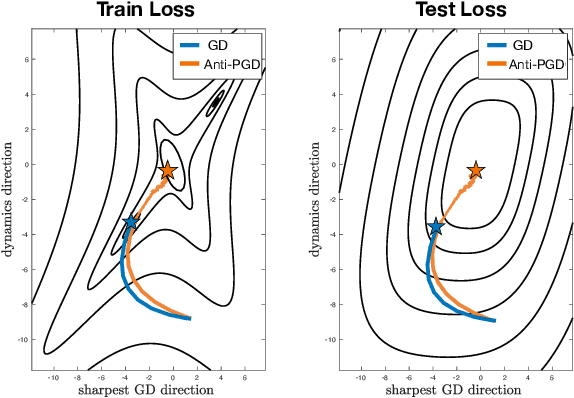
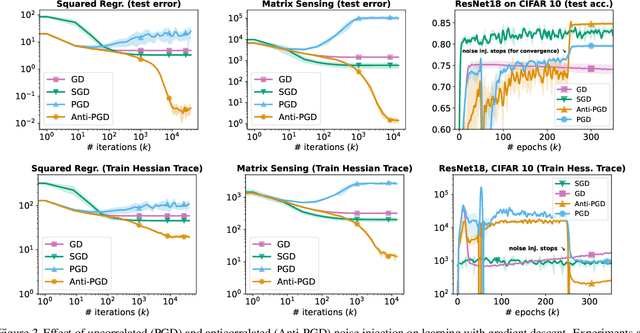
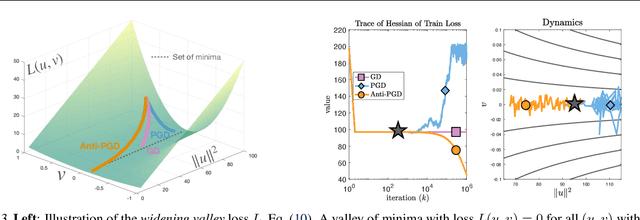
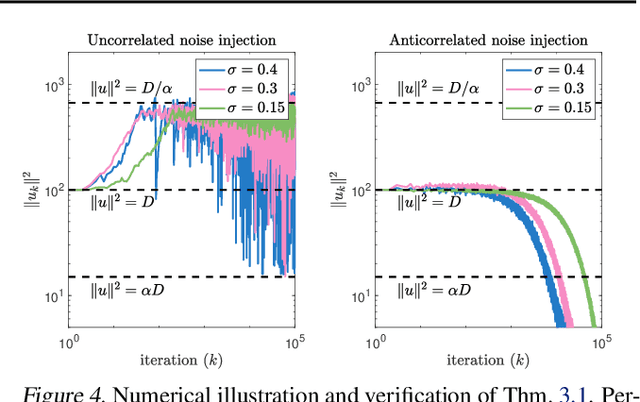
Abstract:Injecting artificial noise into gradient descent (GD) is commonly employed to improve the performance of machine learning models. Usually, uncorrelated noise is used in such perturbed gradient descent (PGD) methods. It is, however, not known if this is optimal or whether other types of noise could provide better generalization performance. In this paper, we zoom in on the problem of correlating the perturbations of consecutive PGD steps. We consider a variety of objective functions for which we find that GD with anticorrelated perturbations ("Anti-PGD") generalizes significantly better than GD and standard (uncorrelated) PGD. To support these experimental findings, we also derive a theoretical analysis that demonstrates that Anti-PGD moves to wider minima, while GD and PGD remain stuck in suboptimal regions or even diverge. This new connection between anticorrelated noise and generalization opens the field to novel ways to exploit noise for training machine learning models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge