Francisco M. López
Hierarchical Residuals Exploit Brain-Inspired Compositionality
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:We present Hierarchical Residual Networks (HiResNets), deep convolutional neural networks with long-range residual connections between layers at different hierarchical levels. HiResNets draw inspiration on the organization of the mammalian brain by replicating the direct connections from subcortical areas to the entire cortical hierarchy. We show that the inclusion of hierarchical residuals in several architectures, including ResNets, results in a boost in accuracy and faster learning. A detailed analysis of our models reveals that they perform hierarchical compositionality by learning feature maps relative to the compressed representations provided by the skip connections.
Self-Supervised Learning of Color Constancy
Apr 11, 2024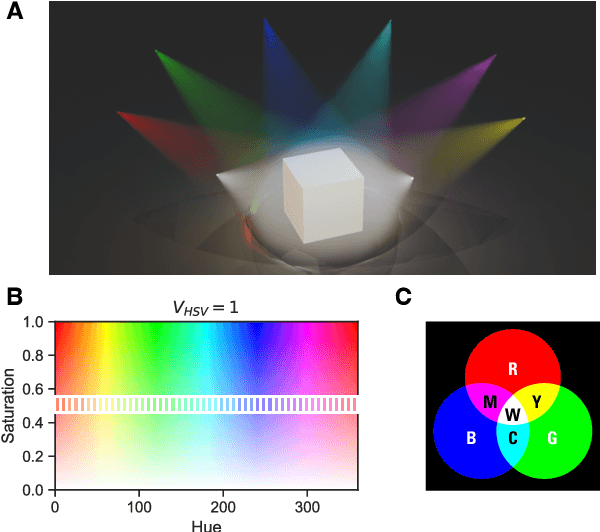
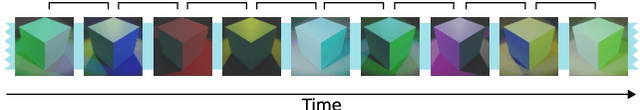
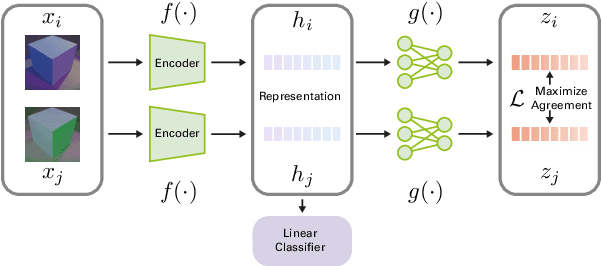
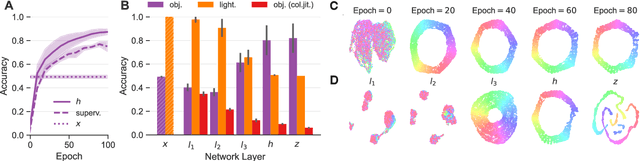
Abstract:Color constancy (CC) describes the ability of the visual system to perceive an object as having a relatively constant color despite changes in lighting conditions. While CC and its limitations have been carefully characterized in humans, it is still unclear how the visual system acquires this ability during development. Here, we present a first study showing that CC develops in a neural network trained in a self-supervised manner through an invariance learning objective. During learning, objects are presented under changing illuminations, while the network aims to map subsequent views of the same object onto close-by latent representations. This gives rise to representations that are largely invariant to the illumination conditions, offering a plausible example of how CC could emerge during human cognitive development via a form of self-supervised learning.
MIMo: A Multi-Modal Infant Model for Studying Cognitive Development
Dec 07, 2023Abstract:Human intelligence and human consciousness emerge gradually during the process of cognitive development. Understanding this development is an essential aspect of understanding the human mind and may facilitate the construction of artificial minds with similar properties. Importantly, human cognitive development relies on embodied interactions with the physical and social environment, which is perceived via complementary sensory modalities. These interactions allow the developing mind to probe the causal structure of the world. This is in stark contrast to common machine learning approaches, e.g., for large language models, which are merely passively ``digesting'' large amounts of training data, but are not in control of their sensory inputs. However, computational modeling of the kind of self-determined embodied interactions that lead to human intelligence and consciousness is a formidable challenge. Here we present MIMo, an open-source multi-modal infant model for studying early cognitive development through computer simulations. MIMo's body is modeled after an 18-month-old child with detailed five-fingered hands. MIMo perceives its surroundings via binocular vision, a vestibular system, proprioception, and touch perception through a full-body virtual skin, while two different actuation models allow control of his body. We describe the design and interfaces of MIMo and provide examples illustrating its use. All code is available at https://github.com/trieschlab/MIMo .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge