Self-Supervised Learning of Color Constancy
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2024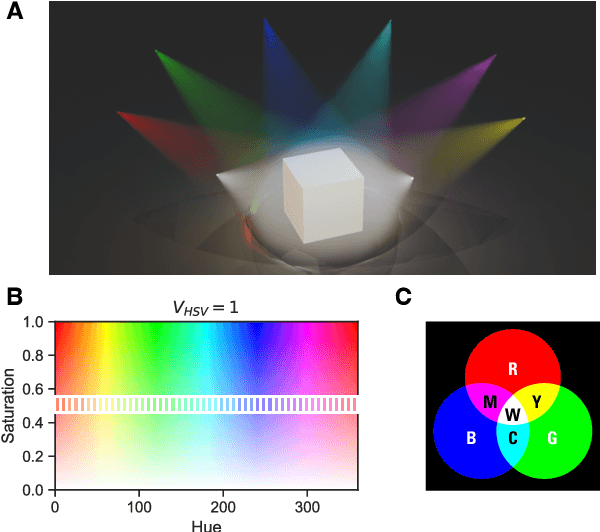
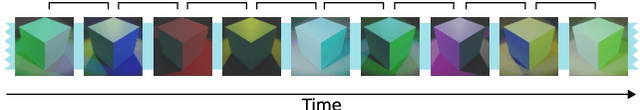
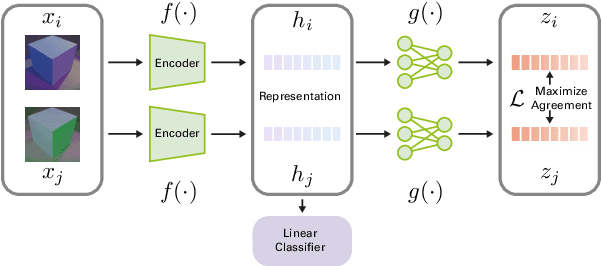
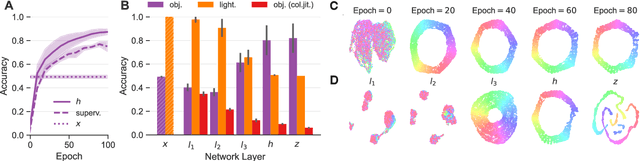
Color constancy (CC) describes the ability of the visual system to perceive an object as having a relatively constant color despite changes in lighting conditions. While CC and its limitations have been carefully characterized in humans, it is still unclear how the visual system acquires this ability during development. Here, we present a first study showing that CC develops in a neural network trained in a self-supervised manner through an invariance learning objective. During learning, objects are presented under changing illuminations, while the network aims to map subsequent views of the same object onto close-by latent representations. This gives rise to representations that are largely invariant to the illumination conditions, offering a plausible example of how CC could emerge during human cognitive development via a form of self-supervised learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge