Francisco J. González-Castaño
Optimal word order for non-causal text generation with Large Language Models: the Spanish case
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Natural Language Generation (NLG) popularity has increased owing to the progress in Large Language Models (LLMs), with zero-shot inference capabilities. However, most neural systems utilize decoder-only causal (unidirectional) transformer models, which are effective for English but may reduce the richness of languages with less strict word order, subject omission, or different relative clause attachment preferences. This is the first work that analytically addresses optimal text generation order for non-causal language models. We present a novel Viterbi algorithm-based methodology for maximum likelihood word order estimation. We analyze the non-causal most-likelihood order probability for NLG in Spanish and, then, the probability of generating the same phrases with Spanish causal NLG. This comparative analysis reveals that causal NLG prefers English-like SVO structures. We also analyze the relationship between optimal generation order and causal left-to-right generation order using Spearman's rank correlation. Our results demonstrate that the ideal order predicted by the maximum likelihood estimator is not closely related to the causal order and may be influenced by the syntactic structure of the target sentence.
Explainable cognitive decline detection in free dialogues with a Machine Learning approach based on pre-trained Large Language Models
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:Cognitive and neurological impairments are very common, but only a small proportion of affected individuals are diagnosed and treated, partly because of the high costs associated with frequent screening. Detecting pre-illness stages and analyzing the progression of neurological disorders through effective and efficient intelligent systems can be beneficial for timely diagnosis and early intervention. We propose using Large Language Models to extract features from free dialogues to detect cognitive decline. These features comprise high-level reasoning content-independent features (such as comprehension, decreased awareness, increased distraction, and memory problems). Our solution comprises (i) preprocessing, (ii) feature engineering via Natural Language Processing techniques and prompt engineering, (iii) feature analysis and selection to optimize performance, and (iv) classification, supported by automatic explainability. We also explore how to improve Chatgpt's direct cognitive impairment prediction capabilities using the best features in our models. Evaluation metrics obtained endorse the effectiveness of a mixed approach combining feature extraction with Chatgpt and a specialized Machine Learning model to detect cognitive decline within free-form conversational dialogues with older adults. Ultimately, our work may facilitate the development of an inexpensive, non-invasive, and rapid means of detecting and explaining cognitive decline.
Predictability and Causality in Spanish and English Natural Language Generation
Aug 26, 2024Abstract:In recent years, the field of Natural Language Generation (NLG) has been boosted by the recent advances in deep learning technologies. Nonetheless, these new data-intensive methods introduce language-dependent disparities in NLG as the main training data sets are in English. Also, most neural NLG systems use decoder-only (causal) transformer language models, which work well for English, but were not designed with other languages in mind. In this work we depart from the hypothesis that they may introduce generation bias in target languages with less rigid word ordering, subject omission, or different attachment preferences for relative clauses, so that for these target languages other language generation strategies may be more desirable. This paper first compares causal and non-causal language modeling for English and Spanish, two languages with different grammatical structures and over 1.5 billion and 0.5 billion speakers, respectively. For this purpose, we define a novel metric of average causal and non-causal context-conditioned entropy of the grammatical category distribution for both languages as an information-theoretic a priori approach. The evaluation of natural text sources (such as training data) in both languages reveals lower average non-causal conditional entropy in Spanish and lower causal conditional entropy in English. According to this experiment, Spanish is more predictable than English given a non-causal context. Then, by applying a conditional relative entropy metric to text generation experiments, we obtain as insights that the best performance is respectively achieved with causal NLG in English, and with non-causal NLG in Spanish. These insights support further research in NLG in Spanish using bidirectional transformer language models.
Unsupervised explainable activity prediction in competitive Nordic Walking from experimental data
Jun 18, 2024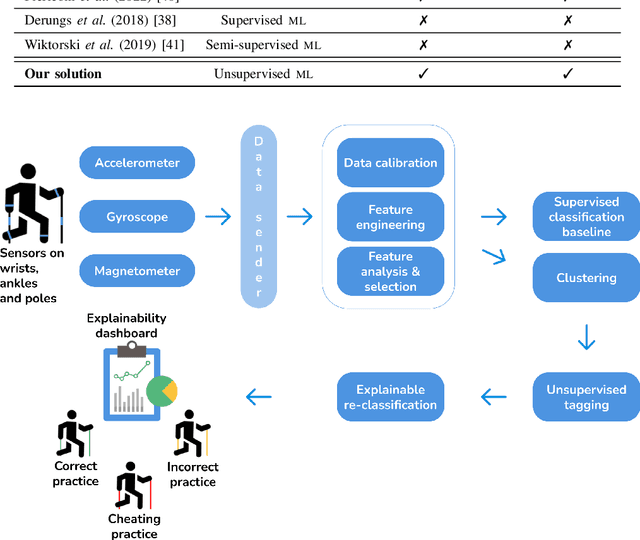


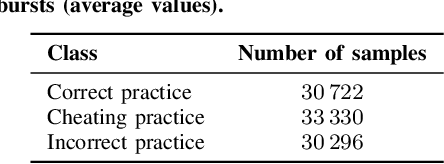
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has found application in Human Activity Recognition (HAR) in competitive sports. To date, most Machine Learning (ML) approaches for HAR have relied on offline (batch) training, imposing higher computational and tagging burdens compared to online processing unsupervised approaches. Additionally, the decisions behind traditional ML predictors are opaque and require human interpretation. In this work, we apply an online processing unsupervised clustering approach based on low-cost wearable Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs). The outcomes generated by the system allow for the automatic expansion of limited tagging available (e.g., by referees) within those clusters, producing pertinent information for the explainable classification stage. Specifically, our work focuses on achieving automatic explainability for predictions related to athletes' activities, distinguishing between correct, incorrect, and cheating practices in Nordic Walking. The proposed solution achieved performance metrics of close to 100 % on average.
Automatic generation of insights from workers' actions in industrial workflows with explainable Machine Learning
Jun 18, 2024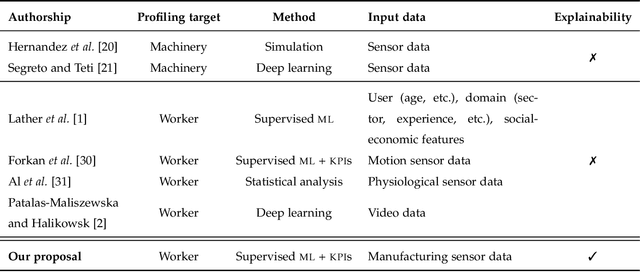
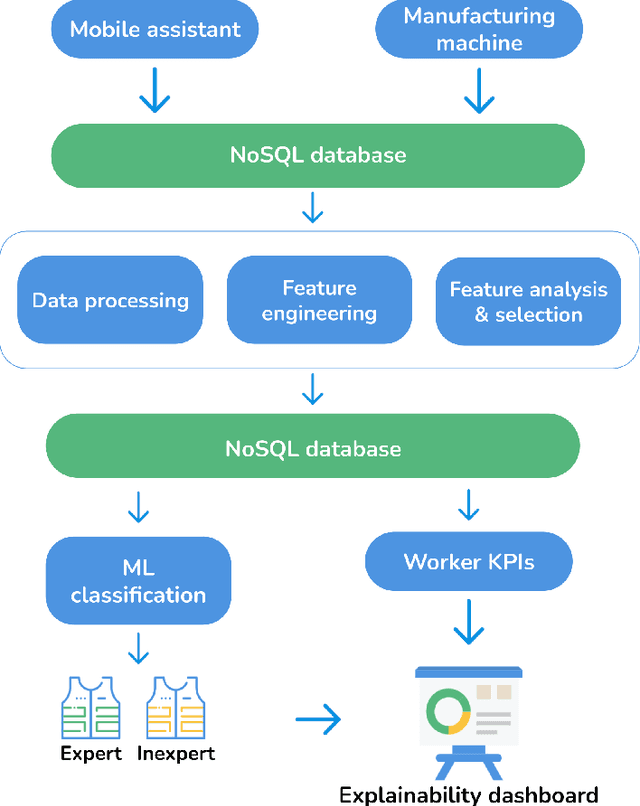
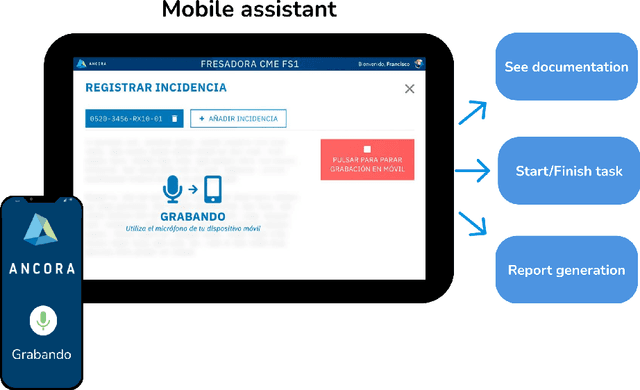
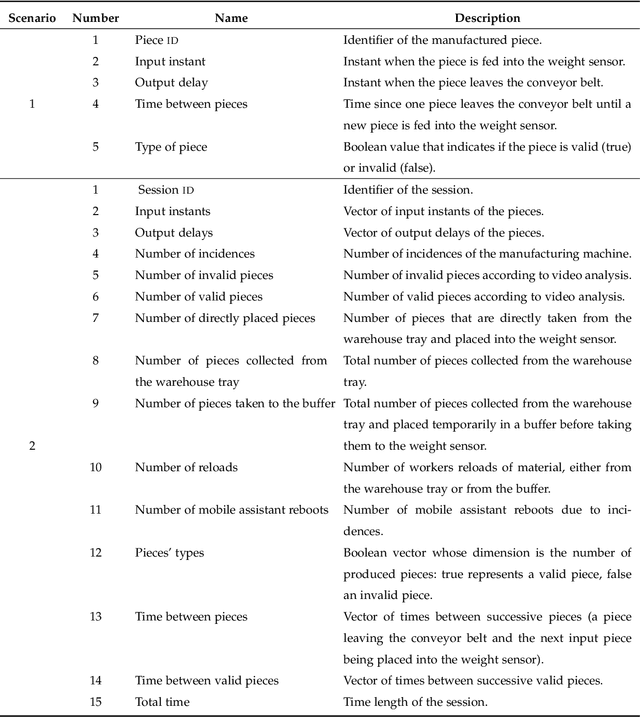
Abstract:New technologies such as Machine Learning (ML) gave great potential for evaluating industry workflows and automatically generating key performance indicators (KPIs). However, despite established standards for measuring the efficiency of industrial machinery, there is no precise equivalent for workers' productivity, which would be highly desirable given the lack of a skilled workforce for the next generation of industry workflows. Therefore, an ML solution combining data from manufacturing processes and workers' performance for that goal is required. Additionally, in recent times intense effort has been devoted to explainable ML approaches that can automatically explain their decisions to a human operator, thus increasing their trustworthiness. We propose to apply explainable ML solutions to differentiate between expert and inexpert workers in industrial workflows, which we validate at a quality assessment industrial workstation. Regarding the methodology used, input data are captured by a manufacturing machine and stored in a NoSQL database. Data are processed to engineer features used in automatic classification and to compute workers' KPIs to predict their level of expertise (with all classification metrics exceeding 90 %). These KPIs, and the relevant features in the decisions are textually explained by natural language expansion on an explainability dashboard. These automatic explanations made it possible to infer knowledge from expert workers for inexpert workers. The latter illustrates the interest of research in self-explainable ML for automatically generating insights to improve productivity in industrial workflows.
Explainable assessment of financial experts' credibility by classifying social media forecasts and checking the predictions with actual market data
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Social media include diverse interaction metrics related to user popularity, the most evident example being the number of user followers. The latter has raised concerns about the credibility of the posts by the most popular creators. However, most existing approaches to assess credibility in social media strictly consider this problem a binary classification, often based on a priori information, without checking if actual real-world facts back the users' comments. In addition, they do not provide automatic explanations of their predictions to foster their trustworthiness. In this work, we propose a credibility assessment solution for financial creators in social media that combines Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning. The reputation of the contributors is assessed by automatically classifying their forecasts on asset values by type and verifying these predictions with actual market data to approximate their probability of success. The outcome of this verification is a continuous credibility score instead of a binary result, an entirely novel contribution by this work. Moreover, social media metrics (i.e., user context) are exploited by calculating their correlation with the credibility rankings, providing insights on the interest of the end-users in financial posts and their forecasts (i.e., drop or rise). Finally, the system provides natural language explanations of its decisions based on a model-agnostic analysis of relevant features.
Automatic detection of cognitive impairment in elderly people using an entertainment chatbot with Natural Language Processing capabilities
May 28, 2024Abstract:Previous researchers have proposed intelligent systems for therapeutic monitoring of cognitive impairments. However, most existing practical approaches for this purpose are based on manual tests. This raises issues such as excessive caretaking effort and the white-coat effect. To avoid these issues, we present an intelligent conversational system for entertaining elderly people with news of their interest that monitors cognitive impairment transparently. Automatic chatbot dialogue stages allow assessing content description skills and detecting cognitive impairment with Machine Learning algorithms. We create these dialogue flows automatically from updated news items using Natural Language Generation techniques. The system also infers the gold standard of the answers to the questions, so it can assess cognitive capabilities automatically by comparing these answers with the user responses. It employs a similarity metric with values in [0, 1], in increasing level of similarity. To evaluate the performance and usability of our approach, we have conducted field tests with a test group of 30 elderly people in the earliest stages of dementia, under the supervision of gerontologists. In the experiments, we have analysed the effect of stress and concentration in these users. Those without cognitive impairment performed up to five times better. In particular, the similarity metric varied between 0.03, for stressed and unfocused participants, and 0.36, for relaxed and focused users. Finally, we developed a Machine Learning algorithm based on textual analysis features for automatic cognitive impairment detection, which attained accuracy, F-measure and recall levels above 80%. We have thus validated the automatic approach to detect cognitive impairment in elderly people based on entertainment content.
Explainable machine learning multi-label classification of Spanish legal judgements
May 27, 2024
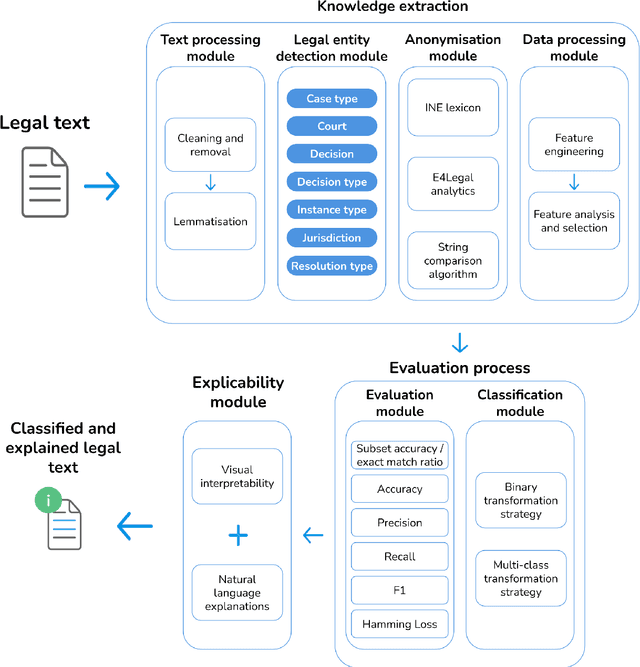

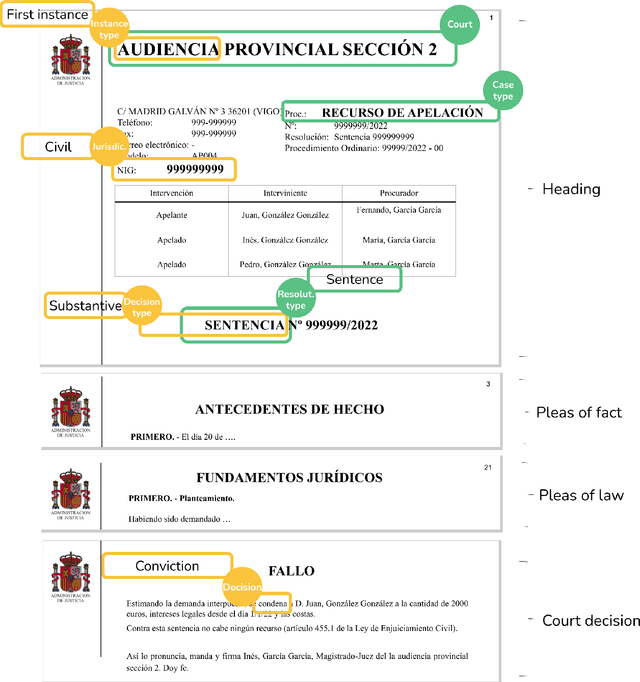
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence techniques such as Machine Learning (ML) have not been exploited to their maximum potential in the legal domain. This has been partially due to the insufficient explanations they provided about their decisions. Automatic expert systems with explanatory capabilities can be specially useful when legal practitioners search jurisprudence to gather contextual knowledge for their cases. Therefore, we propose a hybrid system that applies ML for multi-label classification of judgements (sentences) and visual and natural language descriptions for explanation purposes, boosted by Natural Language Processing techniques and deep legal reasoning to identify the entities, such as the parties, involved. We are not aware of any prior work on automatic multi-label classification of legal judgements also providing natural language explanations to the end-users with comparable overall quality. Our solution achieves over 85 % micro precision on a labelled data set annotated by legal experts. This endorses its interest to relieve human experts from monotonous labour-intensive legal classification tasks.
Explainable automatic industrial carbon footprint estimation from bank transaction classification using natural language processing
May 23, 2024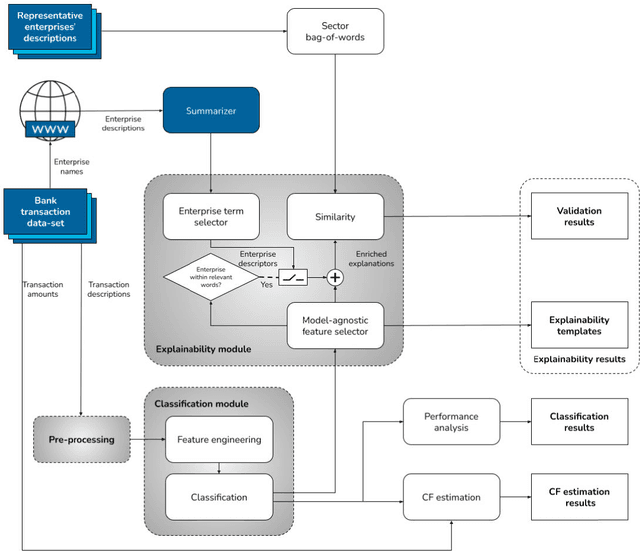
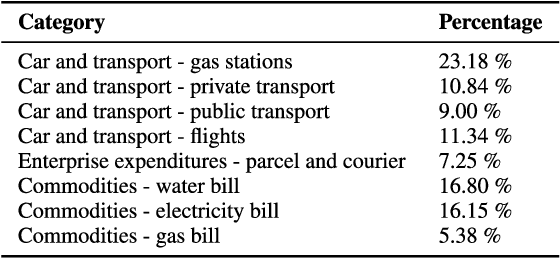
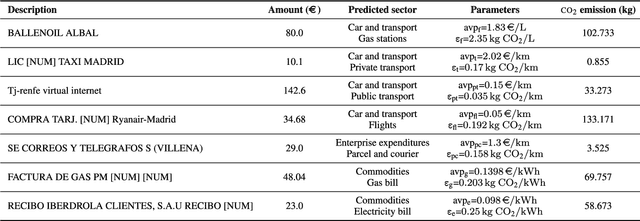
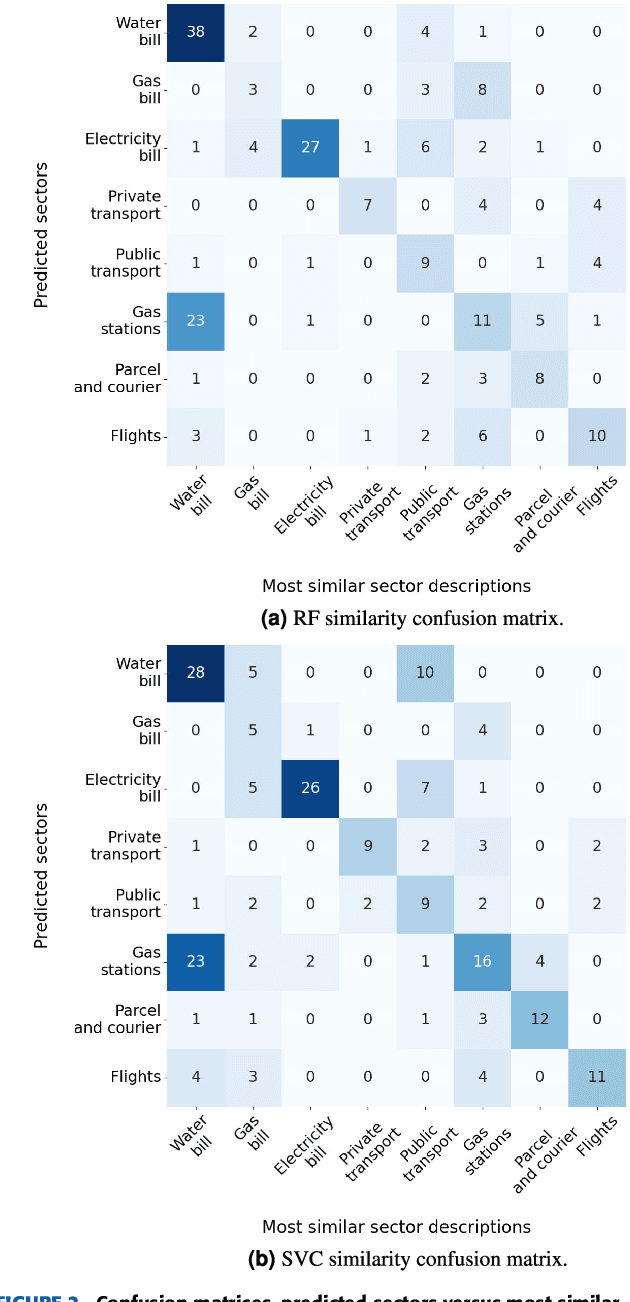
Abstract:Concerns about the effect of greenhouse gases have motivated the development of certification protocols to quantify the industrial carbon footprint (CF). These protocols are manual, work-intensive, and expensive. All of the above have led to a shift towards automatic data-driven approaches to estimate the CF, including Machine Learning (ML) solutions. Unfortunately, the decision-making processes involved in these solutions lack transparency from the end user's point of view, who must blindly trust their outcomes compared to intelligible traditional manual approaches. In this research, manual and automatic methodologies for CF estimation were reviewed, taking into account their transparency limitations. This analysis led to the proposal of a new explainable ML solution for automatic CF calculations through bank transaction classification. Consideration should be given to the fact that no previous research has considered the explainability of bank transaction classification for this purpose. For classification, different ML models have been employed based on their promising performance in the literature, such as Support Vector Machine, Random Forest, and Recursive Neural Networks. The results obtained were in the 90 % range for accuracy, precision, and recall evaluation metrics. From their decision paths, the proposed solution estimates the CO2 emissions associated with bank transactions. The explainability methodology is based on an agnostic evaluation of the influence of the input terms extracted from the descriptions of transactions using locally interpretable models. The explainability terms were automatically validated using a similarity metric over the descriptions of the target categories. Conclusively, the explanation performance is satisfactory in terms of the proximity of the explanations to the associated activity sector descriptions.
Automatic explanation of the classification of Spanish legal judgments in jurisdiction-dependent law categories with tree estimators
Mar 30, 2024



Abstract:Automatic legal text classification systems have been proposed in the literature to address knowledge extraction from judgments and detect their aspects. However, most of these systems are black boxes even when their models are interpretable. This may raise concerns about their trustworthiness. Accordingly, this work contributes with a system combining Natural Language Processing (NLP) with Machine Learning (ML) to classify legal texts in an explainable manner. We analyze the features involved in the decision and the threshold bifurcation values of the decision paths of tree structures and present this information to the users in natural language. This is the first work on automatic analysis of legal texts combining NLP and ML along with Explainable Artificial Intelligence techniques to automatically make the models' decisions understandable to end users. Furthermore, legal experts have validated our solution, and this knowledge has also been incorporated into the explanation process as "expert-in-the-loop" dictionaries. Experimental results on an annotated data set in law categories by jurisdiction demonstrate that our system yields competitive classification performance, with accuracy values well above 90%, and that its automatic explanations are easily understandable even to non-expert users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge