Francisca Gil-Ureta
DPA-Net: Structured 3D Abstraction from Sparse Views via Differentiable Primitive Assembly
Apr 02, 2024
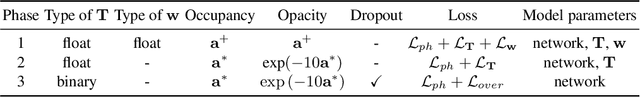

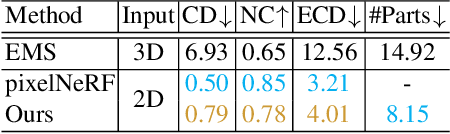
Abstract:We present a differentiable rendering framework to learn structured 3D abstractions in the form of primitive assemblies from sparse RGB images capturing a 3D object. By leveraging differentiable volume rendering, our method does not require 3D supervision. Architecturally, our network follows the general pipeline of an image-conditioned neural radiance field (NeRF) exemplified by pixelNeRF for color prediction. As our core contribution, we introduce differential primitive assembly (DPA) into NeRF to output a 3D occupancy field in place of density prediction, where the predicted occupancies serve as opacity values for volume rendering. Our network, coined DPA-Net, produces a union of convexes, each as an intersection of convex quadric primitives, to approximate the target 3D object, subject to an abstraction loss and a masking loss, both defined in the image space upon volume rendering. With test-time adaptation and additional sampling and loss designs aimed at improving the accuracy and compactness of the obtained assemblies, our method demonstrates superior performance over state-of-the-art alternatives for 3D primitive abstraction from sparse views.
HAL3D: Hierarchical Active Learning for Fine-Grained 3D Part Labeling
Jan 25, 2023
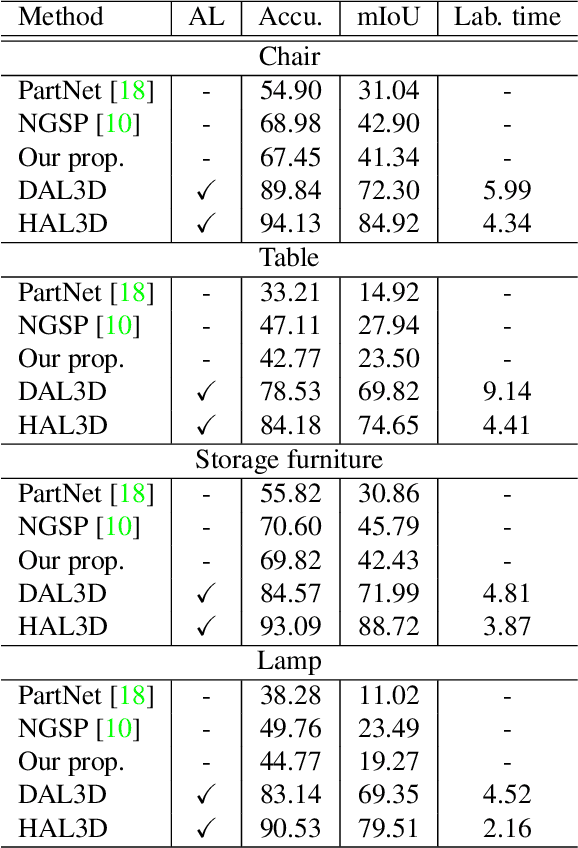
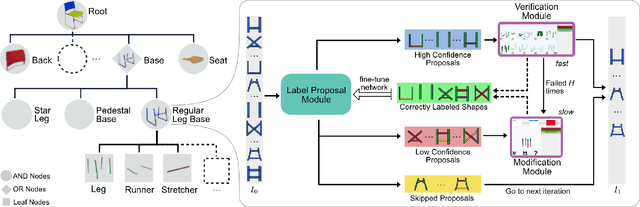
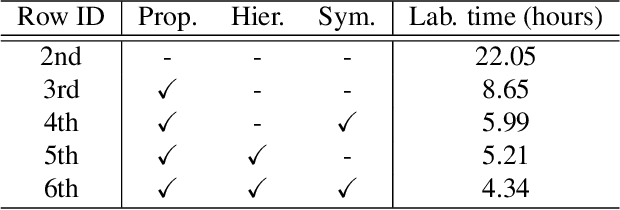
Abstract:We present the first active learning tool for fine-grained 3D part labeling, a problem which challenges even the most advanced deep learning (DL) methods due to the significant structural variations among the small and intricate parts. For the same reason, the necessary data annotation effort is tremendous, motivating approaches to minimize human involvement. Our labeling tool iteratively verifies or modifies part labels predicted by a deep neural network, with human feedback continually improving the network prediction. To effectively reduce human efforts, we develop two novel features in our tool, hierarchical and symmetry-aware active labeling. Our human-in-the-loop approach, coined HAL3D, achieves 100% accuracy (barring human errors) on any test set with pre-defined hierarchical part labels, with 80% time-saving over manual effort.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge