Francesco Denti
On the intrinsic dimensionality of Covid-19 data: a global perspective
Mar 08, 2022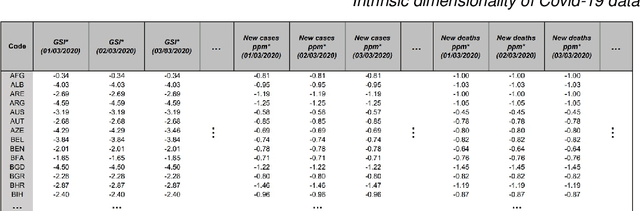
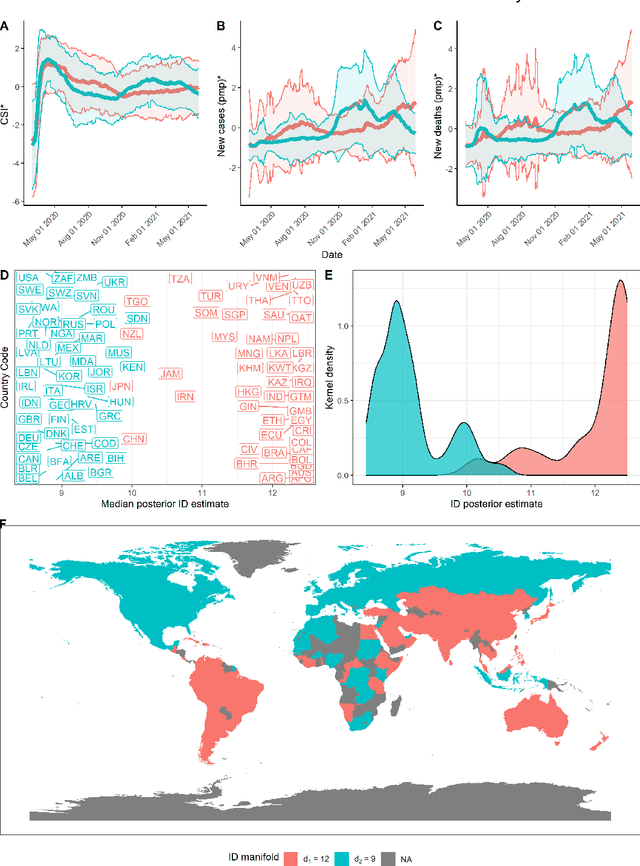
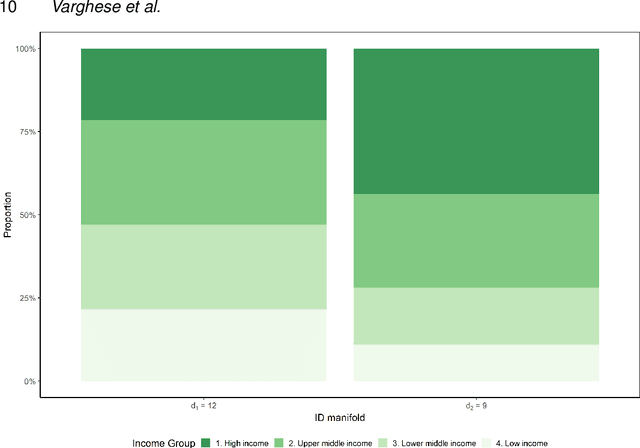
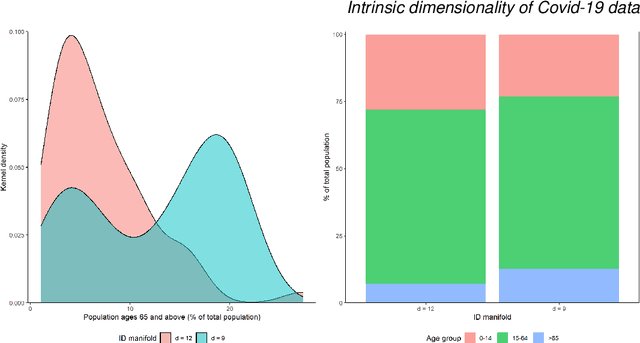
Abstract:This paper aims to develop a global perspective of the complexity of the relationship between the standardised per-capita growth rate of Covid-19 cases, deaths, and the OxCGRT Covid-19 Stringency Index, a measure describing a country's stringency of lockdown policies. To achieve our goal, we use a heterogeneous intrinsic dimension estimator implemented as a Bayesian mixture model, called Hidalgo. We identify that the Covid-19 dataset may project onto two low-dimensional manifolds without significant information loss. The low dimensionality suggests strong dependency among the standardised growth rates of cases and deaths per capita and the OxCGRT Covid-19 Stringency Index for a country over 2020-2021. Given the low dimensional structure, it may be feasible to model observable Covid-19 dynamics with few parameters. Importantly, we identify spatial autocorrelation in the intrinsic dimension distribution worldwide. Moreover, we highlight that high-income countries are more likely to lie on low-dimensional manifolds, likely arising from aging populations, comorbidities, and increased per capita mortality burden from Covid-19. Finally, we temporally stratify the dataset to examine the intrinsic dimension at a more granular level throughout the Covid-19 pandemic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge