Foaad Khosmood
California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo
Explaining Humour Style Classifications: An XAI Approach to Understanding Computational Humour Analysis
Jan 06, 2025Abstract:Humour styles can have either a negative or a positive impact on well-being. Given the importance of these styles to mental health, significant research has been conducted on their automatic identification. However, the automated machine learning models used for this purpose are black boxes, making their prediction decisions opaque. Clarity and transparency are vital in the field of mental health. This paper presents an explainable AI (XAI) framework for understanding humour style classification, building upon previous work in computational humour analysis. Using the best-performing single model (ALI+XGBoost) from prior research, we apply comprehensive XAI techniques to analyse how linguistic, emotional, and semantic features contribute to humour style classification decisions. Our analysis reveals distinct patterns in how different humour styles are characterised and misclassified, with particular emphasis on the challenges in distinguishing affiliative humour from other styles. Through detailed examination of feature importance, error patterns, and misclassification cases, we identify key factors influencing model decisions, including emotional ambiguity, context misinterpretation, and target identification. The framework demonstrates significant utility in understanding model behaviour, achieving interpretable insights into the complex interplay of features that define different humour styles. Our findings contribute to both the theoretical understanding of computational humour analysis and practical applications in mental health, content moderation, and digital humanities research.
A Two-Model Approach for Humour Style Recognition
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:Humour, a fundamental aspect of human communication, manifests itself in various styles that significantly impact social interactions and mental health. Recognising different humour styles poses challenges due to the lack of established datasets and machine learning (ML) models. To address this gap, we present a new text dataset for humour style recognition, comprising 1463 instances across four styles (self-enhancing, self-deprecating, affiliative, and aggressive) and non-humorous text, with lengths ranging from 4 to 229 words. Our research employs various computational methods, including classic machine learning classifiers, text embedding models, and DistilBERT, to establish baseline performance. Additionally, we propose a two-model approach to enhance humour style recognition, particularly in distinguishing between affiliative and aggressive styles. Our method demonstrates an 11.61% improvement in f1-score for affiliative humour classification, with consistent improvements in the 14 models tested. Our findings contribute to the computational analysis of humour in text, offering new tools for studying humour in literature, social media, and other textual sources.
Exploring Description-Augmented Dataless Intent Classification
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:In this work, we introduce several schemes to leverage description-augmented embedding similarity for dataless intent classification using current state-of-the-art (SOTA) text embedding models. We report results of our methods on four commonly used intent classification datasets and compare against previous works of a similar nature. Our work shows promising results for dataless classification scaling to a large number of unseen intents. We show competitive results and significant improvements (+6.12\% Avg.) over strong zero-shot baselines, all without training on labelled or task-specific data. Furthermore, we provide qualitative error analysis of the shortfalls of this methodology to help guide future research in this area.
Systematic Literature Review: Computational Approaches for Humour Style Classification
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:Understanding various humour styles is essential for comprehending the multifaceted nature of humour and its impact on fields such as psychology and artificial intelligence. This understanding has revealed that humour, depending on the style employed, can either have therapeutic or detrimental effects on an individual's health and relationships. Although studies dedicated exclusively to computational-based humour style analysis remain somewhat rare, an expansive body of research thrives within related task, particularly binary humour and sarcasm recognition. In this systematic literature review (SLR), we survey the landscape of computational techniques applied to these related tasks and also uncover their fundamental relevance to humour style analysis. Through this study, we unveil common approaches, illuminate various datasets and evaluation metrics, and effectively navigate the complex terrain of humour research. Our efforts determine potential research gaps and outlined promising directions. Furthermore, the SLR identifies a range of features and computational models that can seamlessly transition from related tasks like binary humour and sarcasm detection to invigorate humour style classification. These features encompass incongruity, sentiment and polarity analysis, ambiguity detection, acoustic nuances, visual cues, contextual insights, and more. The computational models that emerge contain traditional machine learning paradigms, neural network architectures, transformer-based models, and specialised models attuned to the nuances of humour. Finally, the SLR provides access to existing datasets related to humour and sarcasm, facilitating the work of future researchers.
Improving Startup Success with Text Analysis
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:Investors are interested in predicting future success of startup companies, preferably using publicly available data which can be gathered using free online sources. Using public-only data has been shown to work, but there is still much room for improvement. Two of the best performing prediction experiments use 17 and 49 features respectively, mostly numeric and categorical in nature. In this paper, we significantly expand and diversify both the sources and the number of features (to 171) to achieve better prediction. Data collected from Crunchbase, the Google Search API, and Twitter (now X) are used to predict whether a company will raise a round of funding within a fixed time horizon. Much of the new features are textual and the Twitter subset include linguistic metrics such as measures of passive voice and parts-of-speech. A total of ten machine learning models are also evaluated for best performance. The adaptable model can be used to predict funding 1-5 years into the future, with a variable cutoff threshold to favor either precision or recall. Prediction with comparable assumptions generally achieves F scores above 0.730 which outperforms previous attempts in the literature (0.531), and does so with fewer examples. Furthermore, we find that the vast majority of the performance impact comes from the top 18 of 171 features which are mostly generic company observations, including the best performing individual feature which is the free-form text description of the company.
An Empathetic AI Coach for Self-Attachment Therapy
Sep 17, 2022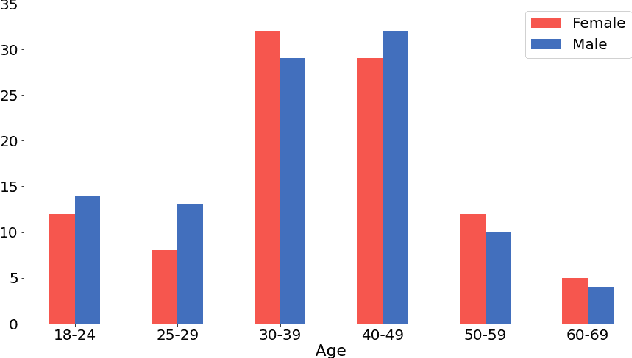

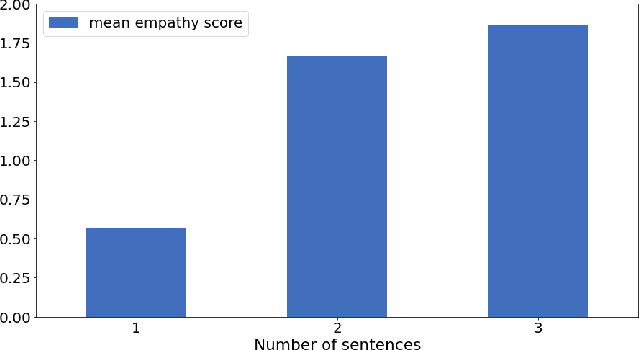

Abstract:In this work, we present a new dataset and a computational strategy for a digital coach that aims to guide users in practicing the protocols of self-attachment therapy. Our framework augments a rule-based conversational agent with a deep-learning classifier for identifying the underlying emotion in a user's text response, as well as a deep-learning assisted retrieval method for producing novel, fluent and empathetic utterances. We also craft a set of human-like personas that users can choose to interact with. Our goal is to achieve a high level of engagement during virtual therapy sessions. We evaluate the effectiveness of our framework in a non-clinical trial with N=16 participants, all of whom have had at least four interactions with the agent over the course of five days. We find that our platform is consistently rated higher for empathy, user engagement and usefulness than the simple rule-based framework. Finally, we provide guidelines to further improve the design and performance of the application, in accordance with the feedback received.
Evaluation of Automatic Text Summarization using Synthetic Facts
Apr 11, 2022


Abstract:Despite some recent advances, automatic text summarization remains unreliable, elusive, and of limited practical use in applications. Two main problems with current summarization methods are well known: evaluation and factual consistency. To address these issues, we propose a new automatic reference-less text summarization evaluation system that can measure the quality of any text summarization model with a set of generated facts based on factual consistency, comprehensiveness, and compression rate. As far as we know, our evaluation system is the first system that measures the overarching quality of the text summarization models based on factuality, information coverage, and compression rate.
Feature Engineering for US State Legislative Hearings: Stance, Affiliation, Engagement and Absentees
Sep 18, 2021



Abstract:In US State government legislatures, most of the activity occurs in committees made up of lawmakers discussing bills. When analyzing, classifying or summarizing these committee proceedings, some important features become broadly interesting. In this paper, we engineer four useful features, two applying to lawmakers (engagement and absence), and two to non-lawmakers (stance and affiliation). We propose a system to automatically track the affiliation of organizations in public comments and whether the organizational representative supports or opposes the bill. The model tracking affiliation achieves an F1 of 0.872 while the support determination has an F1 of 0.979. Additionally, a metric to compute legislator engagement and absenteeism is also proposed and as proof-of-concept, a list of the most and least engaged legislators over one full California legislative session is presented.
A Framework for Complementary Companion Character Behavior in Video Games
Aug 28, 2018



Abstract:We propose a game development framework capable of governing the behavior of complementary companions in a video game. A "complementary" action is contrasted with a mimicking action and is defined as any action by a friendly non-player character that furthers the player's strategy. This is determined through a combination of both player action and game state prediction processes while allowing the AI companion to experiment. We determine the location of interest for companion actions based on a dynamic set of regions customized to the individual player. A user study shows promising results; a majority of participants familiar with game design react positively to the companion behavior, stating that they would consider using the frame-work in future games themselves.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge