Florian Eichin
Linear Script Representations in Speech Foundation Models Enable Zero-Shot Transliteration
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Multilingual speech foundation models such as Whisper are trained on web-scale data, where data for each language consists of a myriad of regional varieties. However, different regional varieties often employ different scripts to write the same language, rendering speech recognition output also subject to non-determinism in the output script. To mitigate this problem, we show that script is linearly encoded in the activation space of multilingual speech models, and that modifying activations at inference time enables direct control over output script. We find the addition of such script vectors to activations at test time can induce script change even in unconventional language-script pairings (e.g. Italian in Cyrillic and Japanese in Latin script). We apply this approach to inducing post-hoc control over the script of speech recognition output, where we observe competitive performance across all model sizes of Whisper.
Grokking ExPLAIND: Unifying Model, Data, and Training Attribution to Study Model Behavior
May 26, 2025Abstract:Post-hoc interpretability methods typically attribute a model's behavior to its components, data, or training trajectory in isolation. This leads to explanations that lack a unified view and may miss key interactions. While combining existing methods or applying them at different training stages offers broader insights, these approaches usually lack theoretical support. In this work, we present ExPLAIND, a unified framework that integrates all three perspectives. First, we generalize recent work on gradient path kernels, which reformulate models trained by gradient descent as a kernel machine, to more realistic training settings. Empirically, we find that both a CNN and a Transformer model are replicated accurately by this reformulation. Second, we derive novel parameter- and step-wise influence scores from the kernel feature maps. We show their effectiveness in parameter pruning that is comparable to existing methods, reinforcing their value for model component attribution. Finally, jointly interpreting model components and data over the training process, we leverage ExPLAIND to analyze a Transformer that exhibits Grokking. Among other things, our findings support previously proposed stages of Grokking, while refining the final phase as one of alignment of input embeddings and final layers around a representation pipeline learned after the memorization phase. Overall, ExPLAIND provides a theoretically grounded, unified framework to interpret model behavior and training dynamics.
What's the Difference? Supporting Users in Identifying the Effects of Prompt and Model Changes Through Token Patterns
Apr 22, 2025



Abstract:Prompt engineering for large language models is challenging, as even small prompt perturbations or model changes can significantly impact the generated output texts. Existing evaluation methods, either automated metrics or human evaluation, have limitations, such as providing limited insights or being labor-intensive. We propose Spotlight, a new approach that combines both automation and human analysis. Based on data mining techniques, we automatically distinguish between random (decoding) variations and systematic differences in language model outputs. This process provides token patterns that describe the systematic differences and guide the user in manually analyzing the effects of their prompt and model changes efficiently. We create three benchmarks to quantitatively test the reliability of token pattern extraction methods and demonstrate that our approach provides new insights into established prompt data. From a human-centric perspective, through demonstration studies and a user study, we show that our token pattern approach helps users understand the systematic differences of language model outputs, and we are able to discover relevant differences caused by prompt and model changes (e.g. related to gender or culture), thus supporting the prompt engineering process and human-centric model behavior research.
Probing LLMs for Multilingual Discourse Generalization Through a Unified Label Set
Mar 13, 2025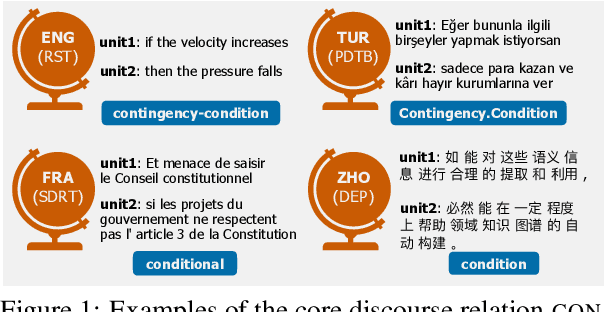
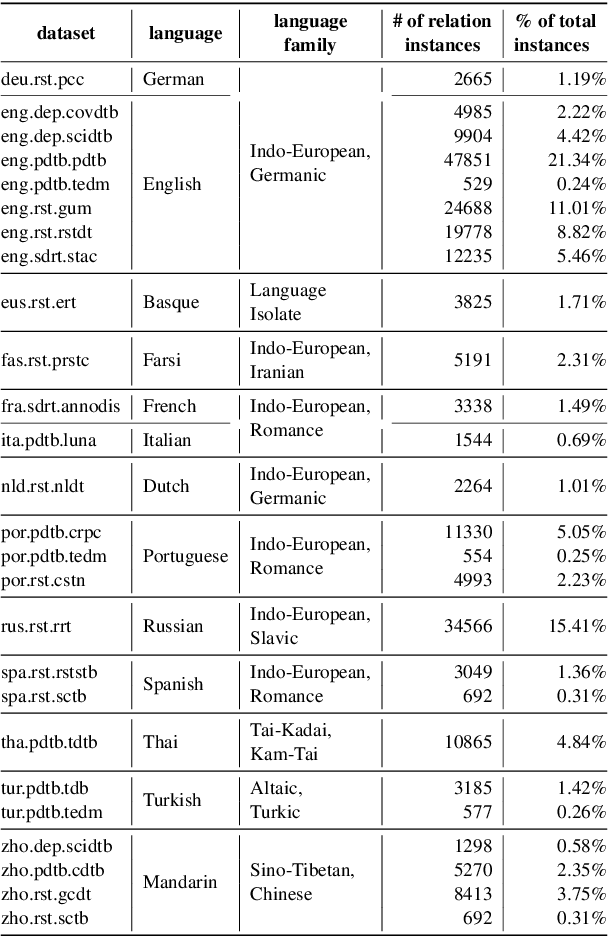
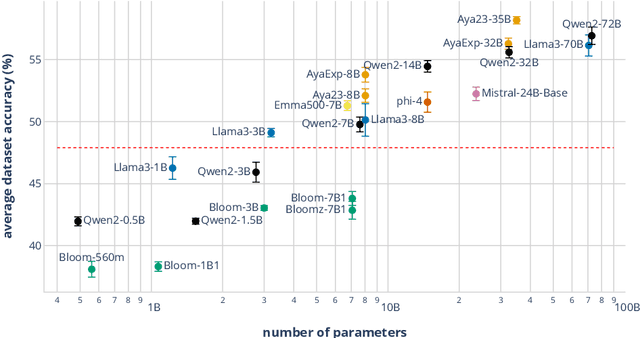
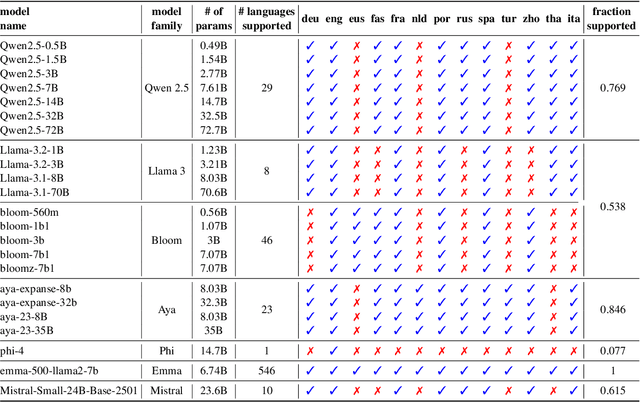
Abstract:Discourse understanding is essential for many NLP tasks, yet most existing work remains constrained by framework-dependent discourse representations. This work investigates whether large language models (LLMs) capture discourse knowledge that generalizes across languages and frameworks. We address this question along two dimensions: (1) developing a unified discourse relation label set to facilitate cross-lingual and cross-framework discourse analysis, and (2) probing LLMs to assess whether they encode generalizable discourse abstractions. Using multilingual discourse relation classification as a testbed, we examine a comprehensive set of 23 LLMs of varying sizes and multilingual capabilities. Our results show that LLMs, especially those with multilingual training corpora, can generalize discourse information across languages and frameworks. Further layer-wise analyses reveal that language generalization at the discourse level is most salient in the intermediate layers. Lastly, our error analysis provides an account of challenging relation classes.
Semantic Component Analysis: Discovering Patterns in Short Texts Beyond Topics
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Topic modeling is a key method in text analysis, but existing approaches are limited by assuming one topic per document or fail to scale efficiently for large, noisy datasets of short texts. We introduce Semantic Component Analysis (SCA), a novel topic modeling technique that overcomes these limitations by discovering multiple, nuanced semantic components beyond a single topic in short texts which we accomplish by introducing a decomposition step to the clustering-based topic modeling framework. Evaluated on multiple Twitter datasets, SCA matches the state-of-the-art method BERTopic in coherence and diversity, while uncovering at least double the semantic components and maintaining a noise rate close to zero while staying scalable and effective across languages, including an underrepresented one.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge