Ferdian Jovan
Optimising TinyML with Quantization and Distillation of Transformer and Mamba Models for Indoor Localisation on Edge Devices
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:This paper proposes small and efficient machine learning models (TinyML) for resource-constrained edge devices, specifically for on-device indoor localisation. Typical approaches for indoor localisation rely on centralised remote processing of data transmitted from lower powered devices such as wearables. However, there are several benefits for moving this to the edge device itself, including increased battery life, enhanced privacy, reduced latency and lowered operational costs, all of which are key for common applications such as health monitoring. The work focuses on model compression techniques, including quantization and knowledge distillation, to significantly reduce the model size while maintaining high predictive performance. We base our work on a large state-of-the-art transformer-based model and seek to deploy it within low-power MCUs. We also propose a state-space-based architecture using Mamba as a more compact alternative to the transformer. Our results show that the quantized transformer model performs well within a 64 KB RAM constraint, achieving an effective balance between model size and localisation precision. Additionally, the compact Mamba model has strong performance under even tighter constraints, such as a 32 KB of RAM, without the need for model compression, making it a viable option for more resource-limited environments. We demonstrate that, through our framework, it is feasible to deploy advanced indoor localisation models onto low-power MCUs with restricted memory limitations. The application of these TinyML models in healthcare has the potential to revolutionize patient monitoring by providing accurate, real-time location data while minimizing power consumption, increasing data privacy, improving latency and reducing infrastructure costs.
Multimodal Indoor Localisation in Parkinson's Disease for Detecting Medication Use: Observational Pilot Study in a Free-Living Setting
Aug 03, 2023



Abstract:Parkinson's disease (PD) is a slowly progressive, debilitating neurodegenerative disease which causes motor symptoms including gait dysfunction. Motor fluctuations are alterations between periods with a positive response to levodopa therapy ("on") and periods marked by re-emergency of PD symptoms ("off") as the response to medication wears off. These fluctuations often affect gait speed and they increase in their disabling impact as PD progresses. To improve the effectiveness of current indoor localisation methods, a transformer-based approach utilising dual modalities which provide complementary views of movement, Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) and accelerometer data from wearable devices, is proposed. A sub-objective aims to evaluate whether indoor localisation, including its in-home gait speed features (i.e. the time taken to walk between rooms), could be used to evaluate motor fluctuations by detecting whether the person with PD is taking levodopa medications or withholding them. To properly evaluate our proposed method, we use a free-living dataset where the movements and mobility are greatly varied and unstructured as expected in real-world conditions. 24 participants lived in pairs (consisting of one person with PD, one control) for five days in a smart home with various sensors. Our evaluation on the resulting dataset demonstrates that our proposed network outperforms other methods for indoor localisation. The sub-objective evaluation shows that precise room-level localisation predictions, transformed into in-home gait speed features, produce accurate predictions on whether the PD participant is taking or withholding their medications.
* 11 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables
Multimodal Indoor Localisation for Measuring Mobility in Parkinson's Disease using Transformers
May 12, 2022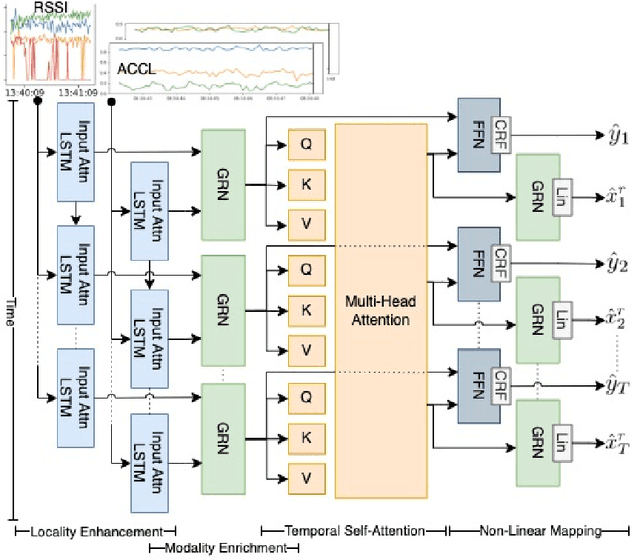
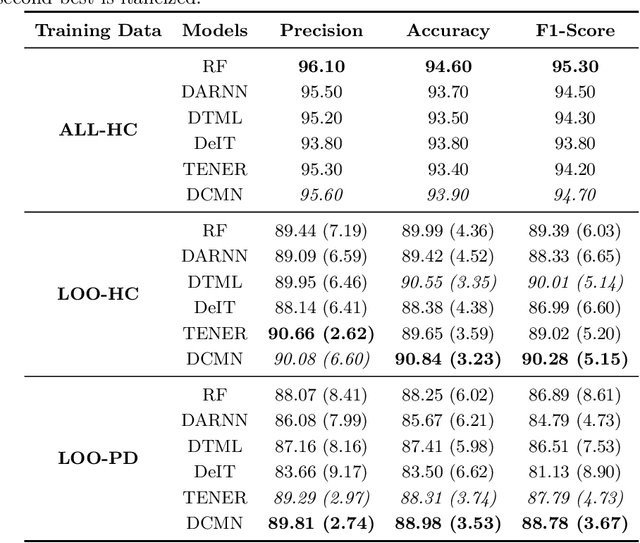
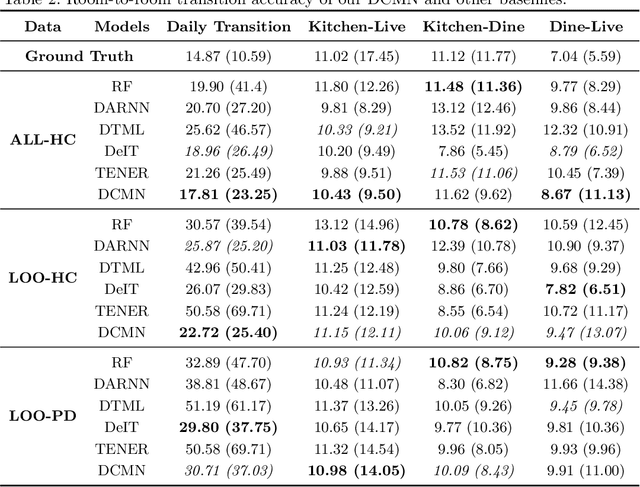
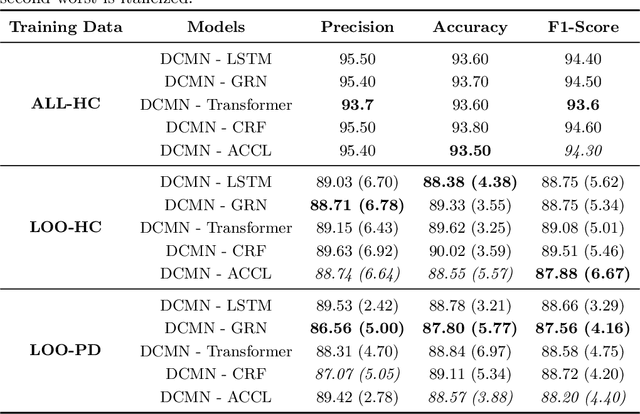
Abstract:Parkinson's disease (PD) is a slowly progressive debilitating neurodegenerative disease which is prominently characterised by motor symptoms. Indoor localisation, including number and speed of room to room transitions, provides a proxy outcome which represents mobility and could be used as a digital biomarker to quantify how mobility changes as this disease progresses. We use data collected from 10 people with Parkinson's, and 10 controls, each of whom lived for five days in a smart home with various sensors. In order to more effectively localise them indoors, we propose a transformer-based approach utilizing two data modalities, Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) and accelerometer data from wearable devices, which provide complementary views of movement. Our approach makes asymmetric and dynamic correlations by a) learning temporal correlations at different scales and levels, and b) utilizing various gating mechanisms to select relevant features within modality and suppress unnecessary modalities. On a dataset with real patients, we demonstrate that our proposed method gives an average accuracy of 89.9%, outperforming competitors. We also show that our model is able to better predict in-home mobility for people with Parkinson's with an average offset of 1.13 seconds to ground truth.
The STRANDS Project: Long-Term Autonomy in Everyday Environments
Oct 14, 2016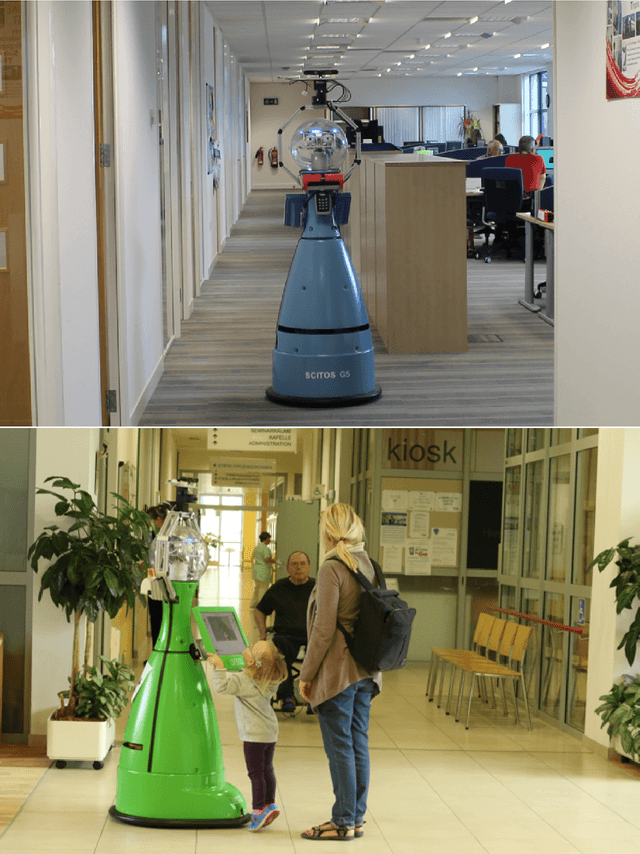
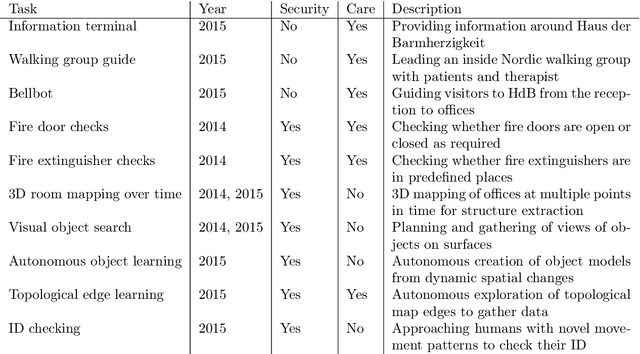
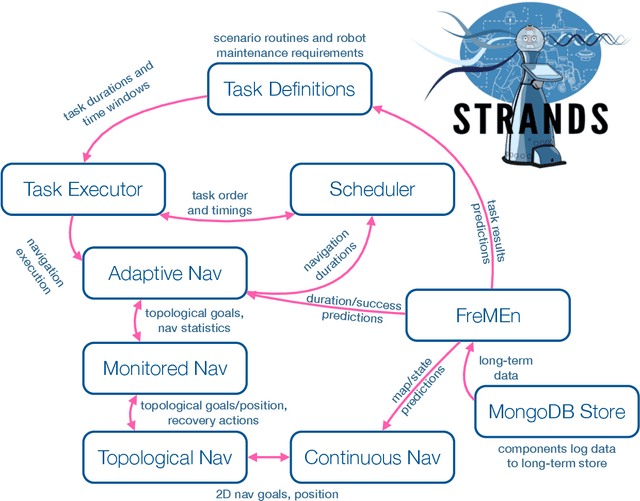
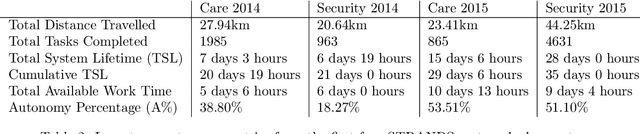
Abstract:Thanks to the efforts of the robotics and autonomous systems community, robots are becoming ever more capable. There is also an increasing demand from end-users for autonomous service robots that can operate in real environments for extended periods. In the STRANDS project we are tackling this demand head-on by integrating state-of-the-art artificial intelligence and robotics research into mobile service robots, and deploying these systems for long-term installations in security and care environments. Over four deployments, our robots have been operational for a combined duration of 104 days autonomously performing end-user defined tasks, covering 116km in the process. In this article we describe the approach we have used to enable long-term autonomous operation in everyday environments, and how our robots are able to use their long run times to improve their own performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge