Fengpei Yuan
Integrating Reinforcement Learning and AI Agents for Adaptive Robotic Interaction and Assistance in Dementia Care
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:This study explores a novel approach to advancing dementia care by integrating socially assistive robotics, reinforcement learning (RL), large language models (LLMs), and clinical domain expertise within a simulated environment. This integration addresses the critical challenge of limited experimental data in socially assistive robotics for dementia care, providing a dynamic simulation environment that realistically models interactions between persons living with dementia (PLWDs) and robotic caregivers. The proposed framework introduces a probabilistic model to represent the cognitive and emotional states of PLWDs, combined with an LLM-based behavior simulation to emulate their responses. We further develop and train an adaptive RL system enabling humanoid robots, such as Pepper, to deliver context-aware and personalized interactions and assistance based on PLWDs' cognitive and emotional states. The framework also generalizes to computer-based agents, highlighting its versatility. Results demonstrate that the RL system, enhanced by LLMs, effectively interprets and responds to the complex needs of PLWDs, providing tailored caregiving strategies. This research contributes to human-computer and human-robot interaction by offering a customizable AI-driven caregiving platform, advancing understanding of dementia-related challenges, and fostering collaborative innovation in assistive technologies. The proposed approach has the potential to enhance the independence and quality of life for PLWDs while alleviating caregiver burden, underscoring the transformative role of interaction-focused AI systems in dementia care.
Learning-Based Strategy Design for Robot-Assisted Reminiscence Therapy Based on a Developed Model for People with Dementia
Sep 06, 2021
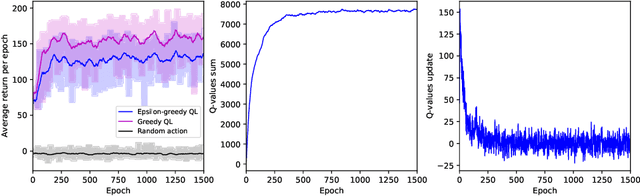
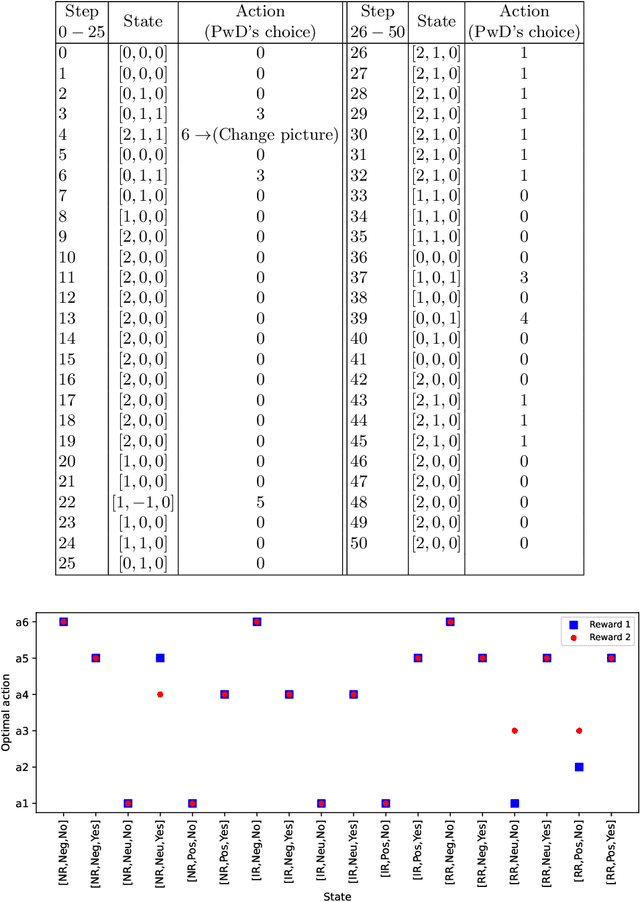
Abstract:In this paper, the robot-assisted Reminiscence Therapy (RT) is studied as a psychosocial intervention to persons with dementia (PwDs). We aim at a conversation strategy for the robot by reinforcement learning to stimulate the PwD to talk. Specifically, to characterize the stochastic reactions of a PwD to the robot's actions, a simulation model of a PwD is developed which features the transition probabilities among different PwD states consisting of the response relevance, emotion levels and confusion conditions. A Q-learning (QL) algorithm is then designed to achieve the best conversation strategy for the robot. The objective is to stimulate the PwD to talk as much as possible while keeping the PwD's states as positive as possible. In certain conditions, the achieved strategy gives the PwD choices to continue or change the topic, or stop the conversation, so that the PwD has a sense of control to mitigate the conversation stress. To achieve this, the standard QL algorithm is revised to deliberately integrate the impact of PwD's choices into the Q-value updates. Finally, the simulation results demonstrate the learning convergence and validate the efficacy of the achieved strategy. Tests show that the strategy is capable to duly adjust the difficulty level of prompt according to the PwD's states, take actions (e.g., repeat or explain the prompt, or comfort) to help the PwD out of bad states, and allow the PwD to control the conversation tendency when bad states continue.
Assessing the Acceptability of a Humanoid Robot for Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementia Care Using an Online Survey
Apr 26, 2021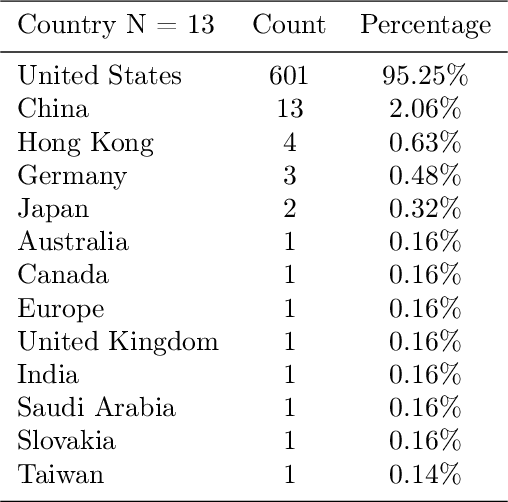
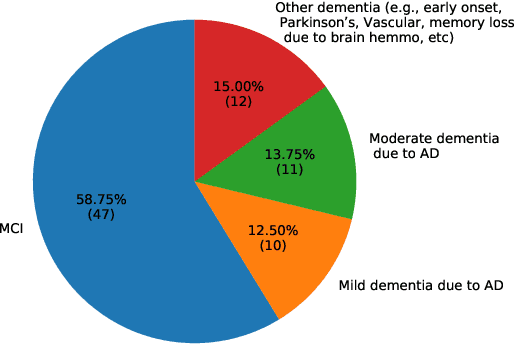
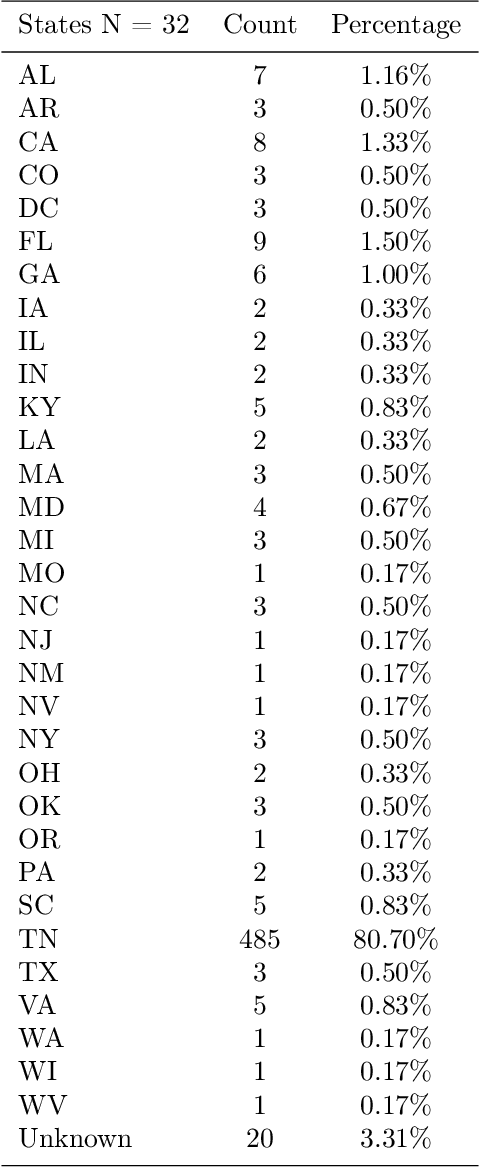
Abstract:In this work, an online survey was used to understand the acceptability of humanoid robots and users' needs in using these robots to assist with care among people with Alzheimer's disease and related dementias (ADRD), their family caregivers, health care professionals, and the general public. From November 12, 2020 to March 13, 2021, a total of 631 complete responses were collected, including 80 responses from people with mild cognitive impairment or ADRD, 245 responses from caregivers and health care professionals, and 306 responses from the general public. Overall, people with ADRD, caregivers, and the general public showed positive attitudes towards using the robot to assist with care for people with ADRD. The top three functions of robots required by the group of people with ADRD were reminders to take medicine, emergency call service, and helping contact medical services. Additional comments, suggestions, and concerns provided by caregivers and the general public are also discussed.
A Simulated Experiment to Explore Robotic Dialogue Strategies for People with Dementia
Apr 18, 2021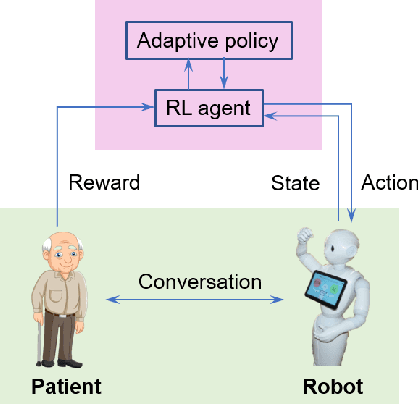
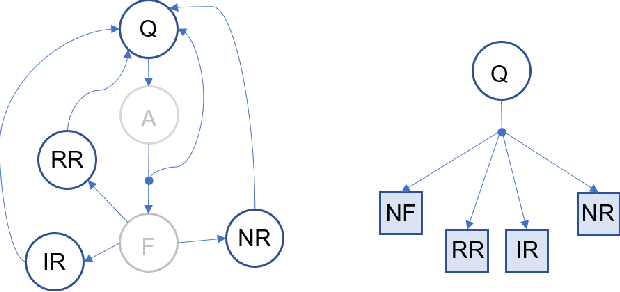
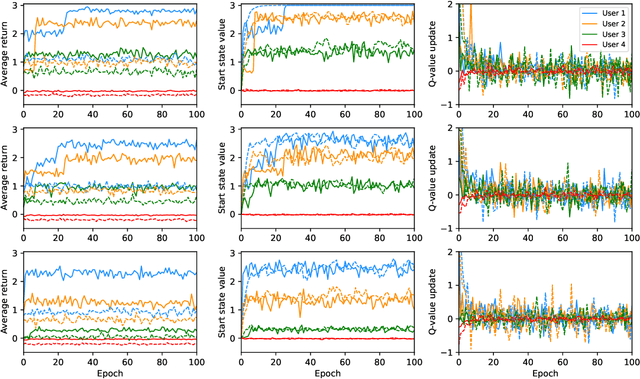

Abstract:People with Alzheimer's disease and related dementias (ADRD) often show the problem of repetitive questioning, which brings a great burden on persons with ADRD (PwDs) and their caregivers. Conversational robots hold promise of coping with this problem and hence alleviating the burdens on caregivers. In this paper, we proposed a partially observable markov decision process (POMDP) model for the PwD-robot interaction in the context of repetitive questioning, and used Q-learning to learn an adaptive conversation strategy (i.e., rate of follow-up question and difficulty of follow-up question) towards PwDs with different cognitive capabilities and different engagement levels. The results indicated that Q-learning was helpful for action selection for the robot. This may be a useful step towards the application of conversational social robots to cope with repetitive questioning in PwDs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge