Felix Ruppert
An Open-Source Modular Treadmill for Dynamic Force Measurement with Load Dependant Range Adjustment
Mar 25, 2023
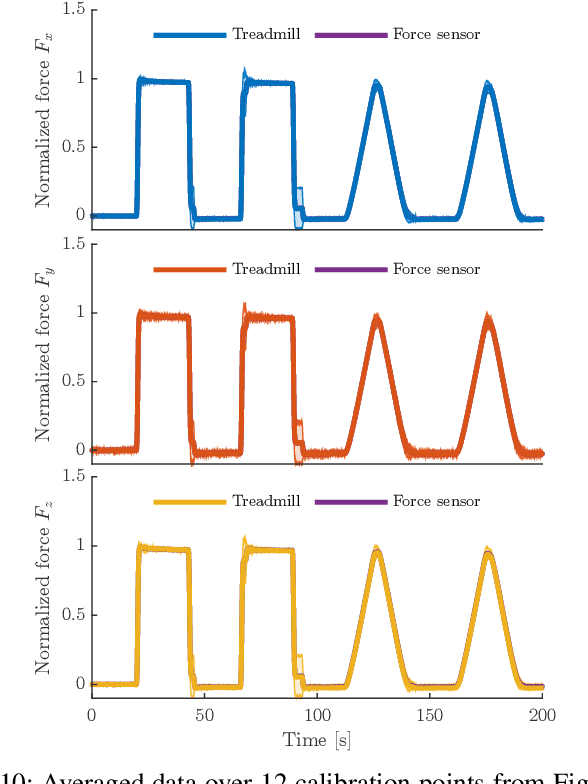

Abstract:Ground reaction force sensing is one of the key components of gait analysis in legged locomotion research. To measure continuous force data during locomotion, we present a novel compound instrumented treadmill design. The treadmill is 1.7m long, with a natural frequency of 170Hz and an adjustable range that can be used for humans and small robots alike. Here, we present the treadmill's design methodology and characterize it in its natural frequency, noise behavior and real-life performance. Additionally, we apply an ISO 376 norm conform calibration procedure for all spatial force directions and center of pressure position. We achieve a force accuracy of $\leq$5.6N for the ground reaction forces and $\leq$13mm in center of pressure position.
FootTile: a Rugged Foot Sensor for Force and Center of Pressure Sensing in Soft Terrain
May 18, 2020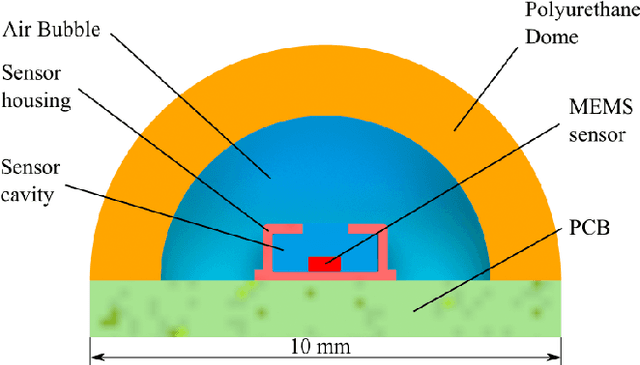
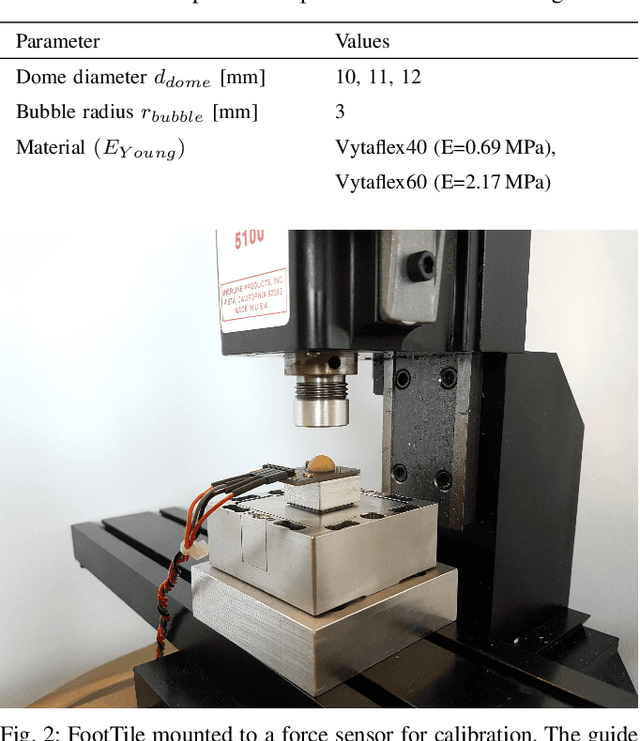
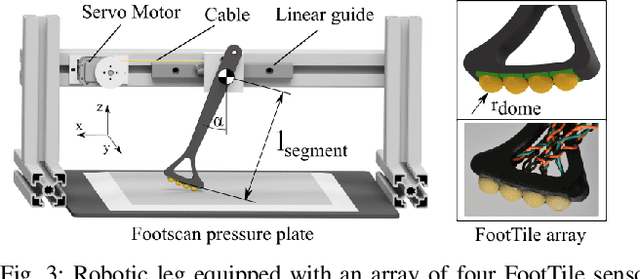
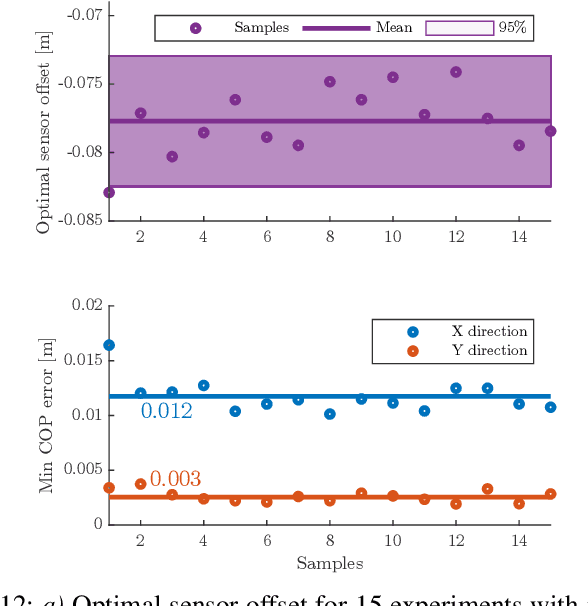
Abstract:In this paper we present FootTile, a foot sensor for reaction force and center of pressure sensing in challenging terrain. We compare our sensor design to standard biomechanical devices, force plates and pressure plates. We show that FootTile can accurately estimate force and pressure distribution during legged locomotion. FootTile weighs 0.9g, has a sampling rate of 330Hz, a footprint of 10 by 10mm and can easily be adapted in sensor range to the required load case. In three experiments we validate: first the performance of the individual sensor, second an array of FootTiles for center of pressure sensing and third the ground reaction force estimation during locomotion in granular substrate. We then go on to show the accurate sensing capabilities of the waterproof sensor in liquid mud, as a showcase for real world rough terrain use.
Shaping in Practice: Training Wheels to Learn Fast Hopping Directly in Hardware
Mar 07, 2018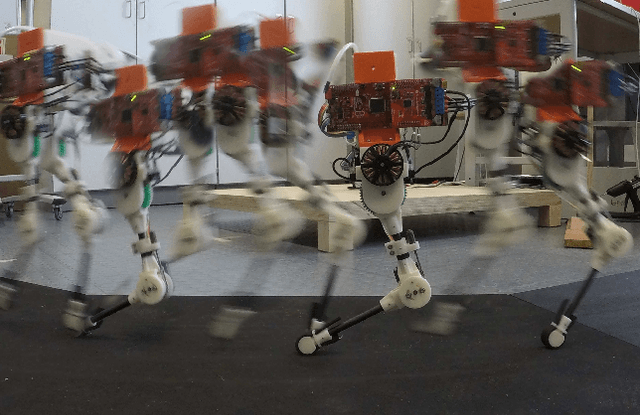
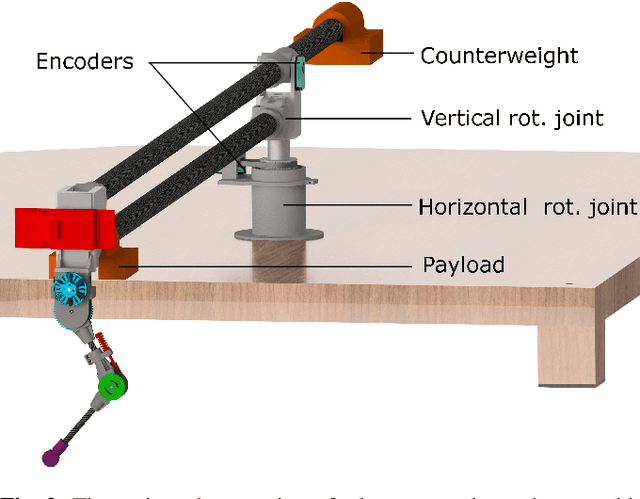
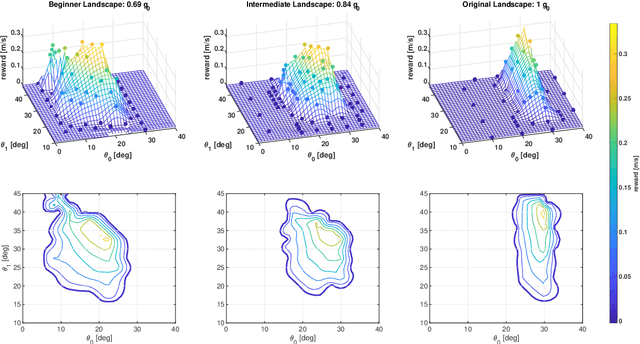
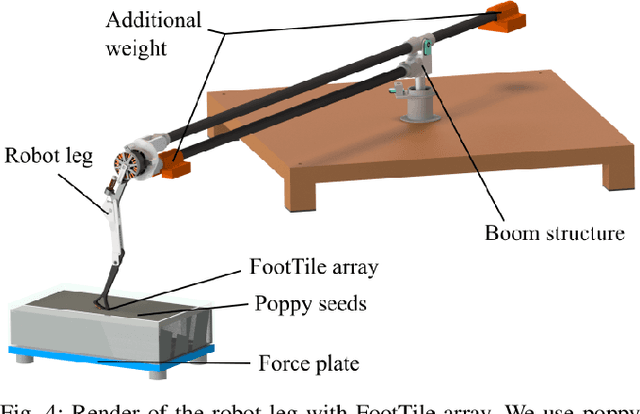
Abstract:Learning instead of designing robot controllers can greatly reduce engineering effort required, while also emphasizing robustness. Despite considerable progress in simulation, applying learning directly in hardware is still challenging, in part due to the necessity to explore potentially unstable parameters. We explore the concept of shaping the reward landscape with training wheels: temporary modifications of the physical hardware that facilitate learning. We demonstrate the concept with a robot leg mounted on a boom learning to hop fast. This proof of concept embodies typical challenges such as instability and contact, while being simple enough to empirically map out and visualize the reward landscape. Based on our results we propose three criteria for designing effective training wheels for learning in robotics. A video synopsis can be found at https://youtu.be/6iH5E3LrYh8.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge