Federica Cena
From psychological traits to safety warnings: three studies on recommendations in a smart home environment
Jun 09, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we report on three experiments we have carried out in the context of the EMPATHY project, with the aim of helping users make better configuration choices in a smart home environment, and discuss our results. We found that there are psychological traits, such as Need for Cognition, which influence the way individuals tend to use recommendations, that there are non obvious relationships between the perceived usefulness of recommendations in different domains and individuals' ability to exploit suggestions on configuration choices, and that detailed, easy-to-understand security explanations are more persuasive than simple security warnings, when it comes to make decisions on the applicability of rules which might cause privacy and security risks.
Cloud-based user modeling for social robots: a first attempt
Sep 25, 2022
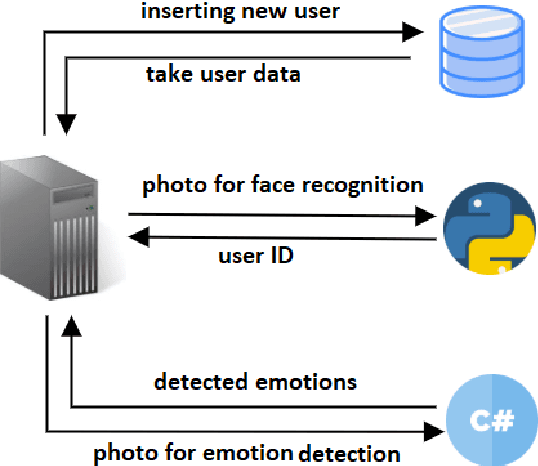
Abstract:A social robot is an autonomous robot that interact with people by engaging in social emotive behaviors, skills, capacities, and rules attached to its collaborative role. In order to achieve these goals we believe that modeling the interaction with the user and adapt the robot behavior to the user herself are fundamental for its social role. This paper presents our first attempt to integrate user modeling features in social and affective robots. We propose a cloud-based architecture for modeling the user-robot interaction in order to reuse the approach with different kind of social robots.
Using consumer feedback from location-based services in PoI recommender systems for people with autism
Apr 21, 2022
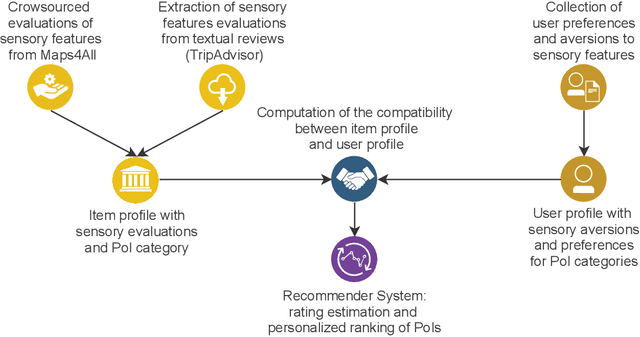
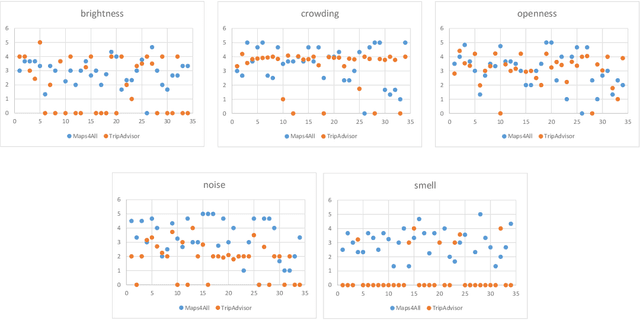
Abstract:When suggesting Points of Interest (PoIs) to people with autism spectrum disorders, we must take into account that they have idiosyncratic sensory aversions to noise, brightness and other features that influence the way they perceive places. Therefore, recommender systems must deal with these aspects. However, the retrieval of sensory data about PoIs is a real challenge because most geographical information servers fail to provide this data. Moreover, ad-hoc crowdsourcing campaigns do not guarantee to cover large geographical areas and lack sustainability. Thus, we investigate the extraction of sensory data about places from the consumer feedback collected by location-based services, on which people spontaneously post reviews from all over the world. Specifically, we propose a model for the extraction of sensory data from the reviews about PoIs, and its integration in recommender systems to predict item ratings by considering both user preferences and compatibility information. We tested our approach with autistic and neurotypical people by integrating it into diverse recommendation algorithms. For the test, we used a dataset built in a crowdsourcing campaign and another one extracted from TripAdvisor reviews. The results show that the algorithms obtain the highest accuracy and ranking capability when using TripAdvisor data. Moreover, by jointly using these two datasets, the algorithms further improve their performance. These results encourage the use of consumer feedback as a reliable source of information about places in the development of inclusive recommender systems.
User modeling for social and affective robots
Aug 05, 2021Abstract:This paper presents our first attempt to integrate user modeling features in social and affective robots. We propose a cloud-based architecture for modeling the user-robot interaction in order to re-use the approach with different kind of social robots.
Personalized Recommendation of PoIs to People with Autism
Apr 27, 2020
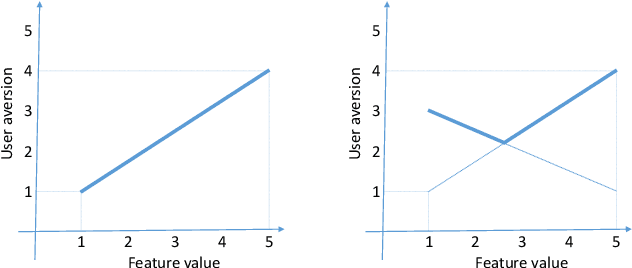
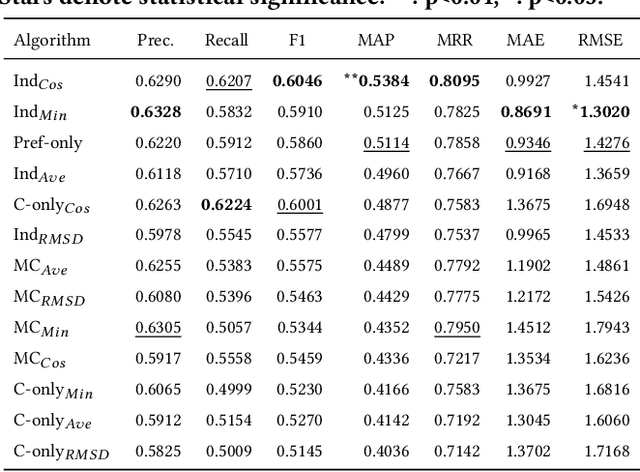
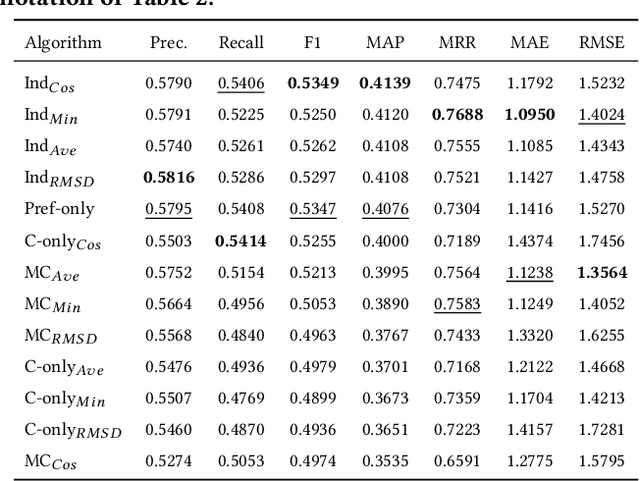
Abstract:The suggestion of Points of Interest to people with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) challenges recommender systems research because these users' perception of places is influenced by idiosyncratic sensory aversions which can mine their experience by causing stress and anxiety. Therefore, managing individual preferences is not enough to provide these people with suitable recommendations. In order to address this issue, we propose a Top-N recommendation model that combines the user's idiosyncratic aversions with her/his preferences in a personalized way to suggest the most compatible and likable Points of Interest for her/him. We are interested in finding a user-specific balance of compatibility and interest within a recommendation model that integrates heterogeneous evaluation criteria to appropriately take these aspects into account. We tested our model on both ASD and "neurotypical" people. The evaluation results show that, on both groups, our model outperforms in accuracy and ranking capability the recommender systems based on item compatibility, on user preferences, or which integrate these two aspects by means of a uniform evaluation model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge