Fatemeh Tahmasbi
Scaling Laws for Discriminative Classification in Large Language Models
May 24, 2024



Abstract:Modern large language models (LLMs) represent a paradigm shift in what can plausibly be expected of machine learning models. The fact that LLMs can effectively generate sensible answers to a diverse range of queries suggests that they would be useful in customer support applications. While powerful, LLMs have been observed to be prone to hallucination which unfortunately makes their near term use in customer support applications challenging. To address this issue we present a system that allows us to use an LLM to augment our customer support advocates by re-framing the language modeling task as a discriminative classification task. In this framing, we seek to present the top-K best template responses for a customer support advocate to use when responding to a customer. We present the result of both offline and online experiments where we observed offline gains and statistically significant online lifts for our experimental system. Along the way, we present observed scaling curves for validation loss and top-K accuracy, resulted from model parameter ablation studies. We close by discussing the space of trade-offs with respect to model size, latency, and accuracy as well as and suggesting future applications to explore.
Feels Bad Man: Dissecting Automated Hateful Meme Detection Through the Lens of Facebook's Challenge
Feb 17, 2022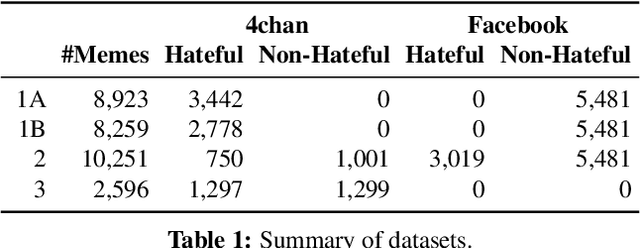
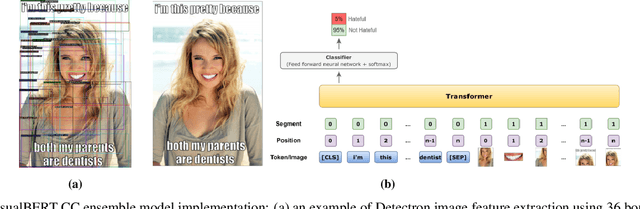

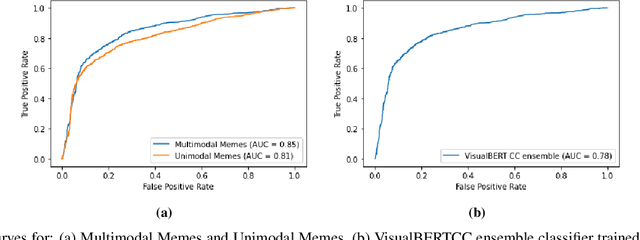
Abstract:Internet memes have become a dominant method of communication; at the same time, however, they are also increasingly being used to advocate extremism and foster derogatory beliefs. Nonetheless, we do not have a firm understanding as to which perceptual aspects of memes cause this phenomenon. In this work, we assess the efficacy of current state-of-the-art multimodal machine learning models toward hateful meme detection, and in particular with respect to their generalizability across platforms. We use two benchmark datasets comprising 12,140 and 10,567 images from 4chan's "Politically Incorrect" board (/pol/) and Facebook's Hateful Memes Challenge dataset to train the competition's top-ranking machine learning models for the discovery of the most prominent features that distinguish viral hateful memes from benign ones. We conduct three experiments to determine the importance of multimodality on classification performance, the influential capacity of fringe Web communities on mainstream social platforms and vice versa, and the models' learning transferability on 4chan memes. Our experiments show that memes' image characteristics provide a greater wealth of information than its textual content. We also find that current systems developed for online detection of hate speech in memes necessitate further concentration on its visual elements to improve their interpretation of underlying cultural connotations, implying that multimodal models fail to adequately grasp the intricacies of hate speech in memes and generalize across social media platforms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge