Farzan Haddadi
Hybrid Quantum-Classical Selective State Space Artificial Intelligence
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Hybrid Quantum Classical (HQC) algorithms constitute one of the most effective paradigms for exploiting the computational advantages of quantum systems in large-scale numerical tasks. By operating in high-dimensional Hilbert spaces, quantum circuits enable exponential speed-ups and provide access to richer representations of cost landscapes compared to purely classical methods. These capabilities are particularly relevant for machine learning, where state-of-the-art models especially in Natural Language Processing (NLP) suffer from prohibitive time complexity due to massive matrix multiplications and high-dimensional optimization. In this manuscript, we propose a Hybrid Quantum Classical selection mechanism for the Mamba architecture, designed specifically for temporal sequence classification problems. Our approach leverages Variational Quantum Circuits (VQCs) as quantum gating modules that both enhance feature extraction and improve suppression of irrelevant information. This integration directly addresses the computational bottlenecks of deep learning architectures by exploiting quantum resources for more efficient representation learning. We analyze how introducing quantum subroutines into large language models (LLMs) impacts their generalization capability, expressivity, and parameter efficiency. The results highlight the potential of quantum-enhanced gating mechanisms as a path toward scalable, resource-efficient NLP models, in a limited simulation step. Within the first four epochs on a reshaped MNIST dataset with input format (batch, 784, d_model), our hybrid model achieved 24.6% accuracy while using one quantum layer and achieve higher expressivity, compared to 21.6% obtained by a purely classical selection mechanism. we state No founding
Matrix Completion via Nonsmooth Regularization of Fully Connected Neural Networks
Mar 15, 2024

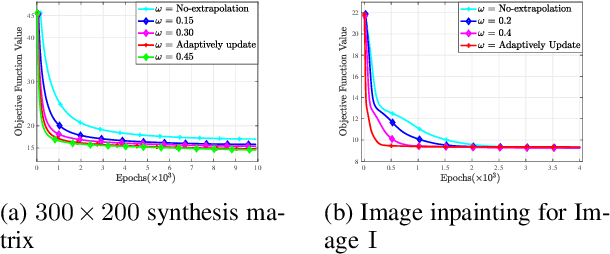
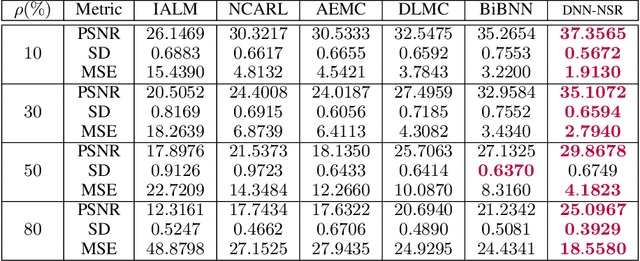
Abstract:Conventional matrix completion methods approximate the missing values by assuming the matrix to be low-rank, which leads to a linear approximation of missing values. It has been shown that enhanced performance could be attained by using nonlinear estimators such as deep neural networks. Deep fully connected neural networks (FCNNs), one of the most suitable architectures for matrix completion, suffer from over-fitting due to their high capacity, which leads to low generalizability. In this paper, we control over-fitting by regularizing the FCNN model in terms of the $\ell_{1}$ norm of intermediate representations and nuclear norm of weight matrices. As such, the resulting regularized objective function becomes nonsmooth and nonconvex, i.e., existing gradient-based methods cannot be applied to our model. We propose a variant of the proximal gradient method and investigate its convergence to a critical point. In the initial epochs of FCNN training, the regularization terms are ignored, and through epochs, the effect of that increases. The gradual addition of nonsmooth regularization terms is the main reason for the better performance of the deep neural network with nonsmooth regularization terms (DNN-NSR) algorithm. Our simulations indicate the superiority of the proposed algorithm in comparison with existing linear and nonlinear algorithms.
Double-detector for Sparse Signal Detection from One Bit Compressed Sensing Measurements
Jul 02, 2016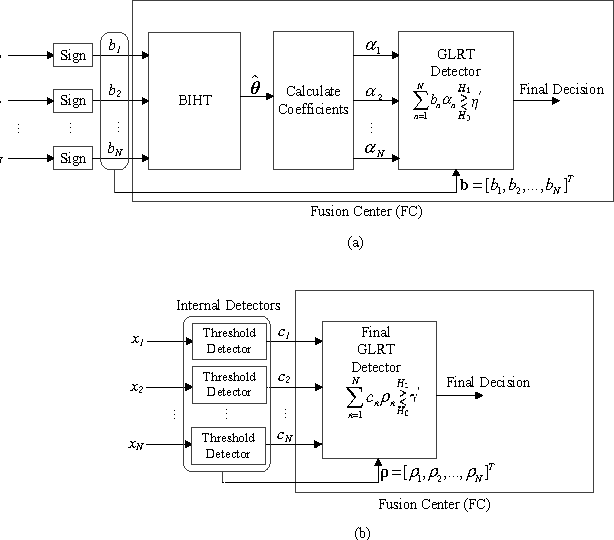
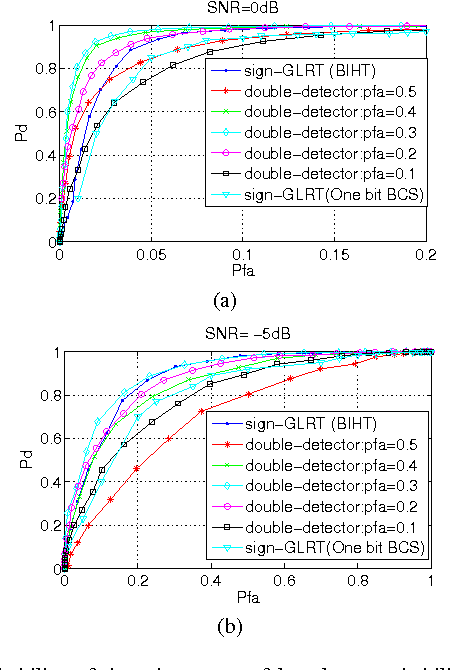
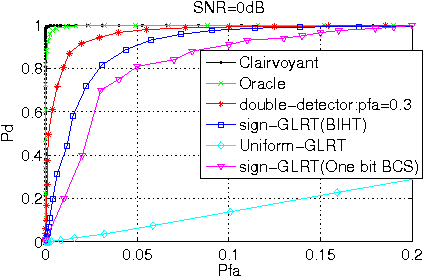
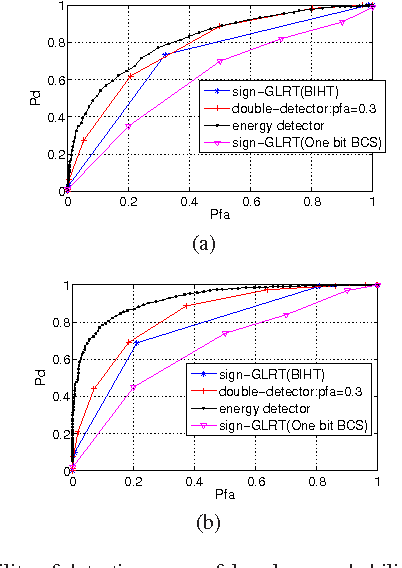
Abstract:This letter presents the sparse vector signal detection from one bit compressed sensing measurements, in contrast to the previous works which deal with scalar signal detection. In this letter, available results are extended to the vector case and the GLRT detector and the optimal quantizer design are obtained. Also, a double-detector scheme is introduced in which a sensor level threshold detector is integrated into network level GLRT to improve the performance. The detection criteria of oracle and clairvoyant detectors are also derived. Simulation results show that with careful design of the threshold detector, the overall detection performance of double-detector scheme would be better than the sign-GLRT proposed in [1] and close to oracle and clairvoyant detectors. Also, the proposed detector is applied to spectrum sensing and the results are near the well known energy detector which uses the real valued data while the proposed detector only uses the sign of the data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge