Fabrice Daniel
Comparative Evaluation of Anomaly Detection Methods for Fraud Detection in Online Credit Card Payments
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:This study explores the application of anomaly detection (AD) methods in imbalanced learning tasks, focusing on fraud detection using real online credit card payment data. We assess the performance of several recent AD methods and compare their effectiveness against standard supervised learning methods. Offering evidence of distribution shift within our dataset, we analyze its impact on the tested models' performances. Our findings reveal that LightGBM exhibits significantly superior performance across all evaluated metrics but suffers more from distribution shifts than AD methods. Furthermore, our investigation reveals that LightGBM also captures the majority of frauds detected by AD methods. This observation challenges the potential benefits of ensemble methods to combine supervised, and AD approaches to enhance performance. In summary, this research provides practical insights into the utility of these techniques in real-world scenarios, showing LightGBM's superiority in fraud detection while highlighting challenges related to distribution shifts.
Benchmarking Robustness of Deep Reinforcement Learning approaches to Online Portfolio Management
Jun 19, 2023


Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning approaches to Online Portfolio Selection have grown in popularity in recent years. The sensitive nature of training Reinforcement Learning agents implies a need for extensive efforts in market representation, behavior objectives, and training processes, which have often been lacking in previous works. We propose a training and evaluation process to assess the performance of classical DRL algorithms for portfolio management. We found that most Deep Reinforcement Learning algorithms were not robust, with strategies generalizing poorly and degrading quickly during backtesting.
Evaluating resampling methods on a real-life highly imbalanced online credit card payments dataset
Jun 27, 2022



Abstract:Various problems of any credit card fraud detection based on machine learning come from the imbalanced aspect of transaction datasets. Indeed, the number of frauds compared to the number of regular transactions is tiny and has been shown to damage learning performances, e.g., at worst, the algorithm can learn to classify all the transactions as regular. Resampling methods and cost-sensitive approaches are known to be good candidates to leverage this issue of imbalanced datasets. This paper evaluates numerous state-of-the-art resampling methods on a large real-life online credit card payments dataset. We show they are inefficient because methods are intractable or because metrics do not exhibit substantial improvements. Our work contributes to this domain in (1) that we compare many state-of-the-art resampling methods on a large-scale dataset and in (2) that we use a real-life online credit card payments dataset.
TracInAD: Measuring Influence for Anomaly Detection
May 04, 2022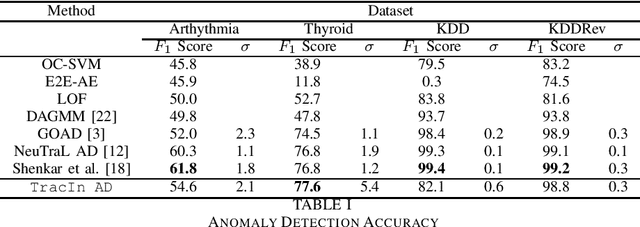
Abstract:As with many other tasks, neural networks prove very effective for anomaly detection purposes. However, very few deep-learning models are suited for detecting anomalies on tabular datasets. This paper proposes a novel methodology to flag anomalies based on TracIn, an influence measure initially introduced for explicability purposes. The proposed methods can serve to augment any unsupervised deep anomaly detection method. We test our approach using Variational Autoencoders and show that the average influence of a subsample of training points on a test point can serve as a proxy for abnormality. Our model proves to be competitive in comparison with state-of-the-art approaches: it achieves comparable or better performance in terms of detection accuracy on medical and cyber-security tabular benchmark data.
Evaluating categorical encoding methods on a real credit card fraud detection database
Dec 22, 2021



Abstract:Correctly dealing with categorical data in a supervised learning context is still a major issue. Furthermore, though some machine learning methods embody builtin methods to deal with categorical features, it is unclear whether they bring some improvements and how do they compare with usual categorical encoding methods. In this paper, we describe several well-known categorical encoding methods that are based on target statistics and weight of evidence. We apply them on a large and real credit card fraud detection database. Then, we train the encoded databases using state-of-the-art gradient boosting methods and evaluate their performances. We show that categorical encoding methods generally bring substantial improvements with respect to the absence of encoding. The contribution of this work is twofold: (1) we compare many state-of-the-art "lite" categorical encoding methods on a large scale database and (2) we use a real credit card fraud detection database.
Bayesian and Dempster-Shafer models for combining multiple sources of evidence in a fraud detection system
Apr 15, 2021



Abstract:Combining evidence from different sources can be achieved with Bayesian or Dempster-Shafer methods. The first requires an estimate of the priors and likelihoods while the second only needs an estimate of the posterior probabilities and enables reasoning with uncertain information due to imprecision of the sources and with the degree of conflict between them. This paper describes the two methods and how they can be applied to the estimation of a global score in the context of fraud detection.
Financial Time Series Data Processing for Machine Learning
Jul 03, 2019



Abstract:This article studies the financial time series data processing for machine learning. It introduces the most frequent scaling methods, then compares the resulting stationarity and preservation of useful information for trend forecasting. It proposes an empirical test based on the capability to learn simple data relationship with simple models. It also speaks about the data split method specific to time series, avoiding unwanted overfitting and proposes various labelling for classification and regression.
Seq2Seq and Multi-Task Learning for joint intent and content extraction for domain specific interpreters
Aug 01, 2018



Abstract:This study evaluates the performances of an LSTM network for detecting and extracting the intent and content of com- mands for a financial chatbot. It presents two techniques, sequence to sequence learning and Multi-Task Learning, which might improve on the previous task.
Stock Chart Pattern recognition with Deep Learning
Aug 01, 2018



Abstract:This study evaluates the performances of CNN and LSTM for recognizing common charts patterns in a stock historical data. It presents two common patterns, the method used to build the training set, the neural networks architectures and the accuracies obtained.
Using NLP on news headlines to predict index trends
Jun 22, 2018
Abstract:This paper attempts to provide a state of the art in trend prediction using news headlines. We present the research done on predicting DJIA trends using Natural Language Processing. We will explain the different algorithms we have used as well as the various embedding techniques attempted. We rely on statistical and deep learning models in order to extract information from the corpuses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge