Fabien Tarissan
The Neutrality Fallacy: When Algorithmic Fairness Interventions are (Not) Positive Action
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:Various metrics and interventions have been developed to identify and mitigate unfair outputs of machine learning systems. While individuals and organizations have an obligation to avoid discrimination, the use of fairness-aware machine learning interventions has also been described as amounting to 'algorithmic positive action' under European Union (EU) non-discrimination law. As the Court of Justice of the European Union has been strict when it comes to assessing the lawfulness of positive action, this would impose a significant legal burden on those wishing to implement fair-ml interventions. In this paper, we propose that algorithmic fairness interventions often should be interpreted as a means to prevent discrimination, rather than a measure of positive action. Specifically, we suggest that this category mistake can often be attributed to neutrality fallacies: faulty assumptions regarding the neutrality of fairness-aware algorithmic decision-making. Our findings raise the question of whether a negative obligation to refrain from discrimination is sufficient in the context of algorithmic decision-making. Consequently, we suggest moving away from a duty to 'not do harm' towards a positive obligation to actively 'do no harm' as a more adequate framework for algorithmic decision-making and fair ml-interventions.
Measuring Diversity in Heterogeneous Information Networks
Jan 10, 2020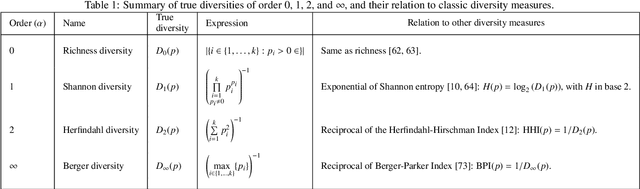
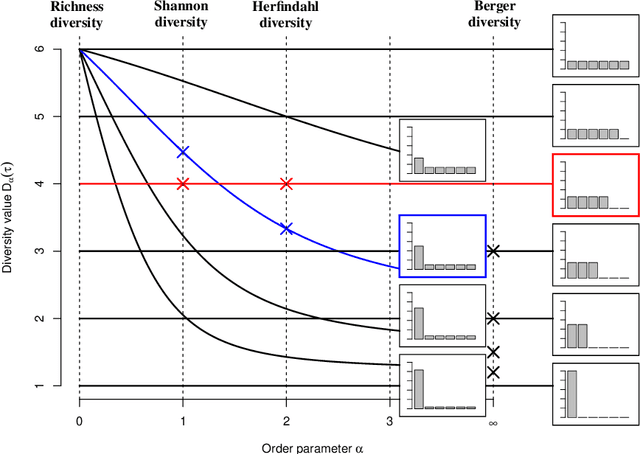
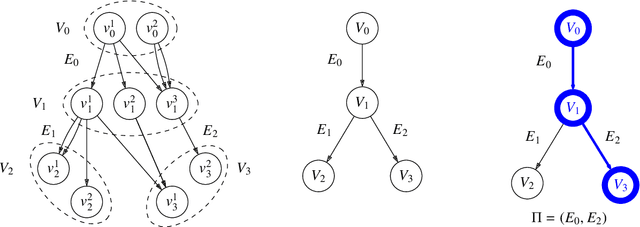

Abstract:Diversity is a concept relevant to numerous domains of research varying from ecology, to information theory, and to economics, to cite a few. It is a notion that is steadily gaining attention in the information retrieval, network analysis, and artificial neural networks communities. While the use of diversity measures in network-structured data counts a growing number of applications, no clear and comprehensive description is available for the different ways in which diversities can be measured. In this article, we develop a formal framework for the application of a large family of diversity measures to heterogeneous information networks (HINs), a flexible, widely-used network data formalism. This extends the application of diversity measures, from systems of classifications and apportionments, to more complex relations that can be better modeled by networks. In doing so, we not only provide an effective organization of multiple practices from different domains, but also unearth new observables in systems modeled by heterogeneous information networks. We illustrate the pertinence of our approach by developing different applications related to various domains concerned by both diversity and networks. In particular, we illustrate the usefulness of these new proposed observables in the domains of recommender systems and social media studies, among other fields.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge