Eunji Chong
Detecting Attended Visual Targets in Video
Mar 30, 2020



Abstract:We address the problem of detecting attention targets in video. Our goal is to identify where each person in each frame of a video is looking, and correctly handle the case where the gaze target is out-of-frame. Our novel architecture models the dynamic interaction between the scene and head features and infers time-varying attention targets. We introduce a new annotated dataset, VideoAttentionTarget, containing complex and dynamic patterns of real-world gaze behavior. Our experiments show that our model can effectively infer dynamic attention in videos. In addition, we apply our predicted attention maps to two social gaze behavior recognition tasks, and show that the resulting classifiers significantly outperform existing methods. We achieve state-of-the-art performance on three datasets: GazeFollow (static images), VideoAttentionTarget (videos), and VideoCoAtt (videos), and obtain the first results for automatically classifying clinically-relevant gaze behavior without wearable cameras or eye trackers.
Connecting Gaze, Scene, and Attention: Generalized Attention Estimation via Joint Modeling of Gaze and Scene Saliency
Jul 27, 2018
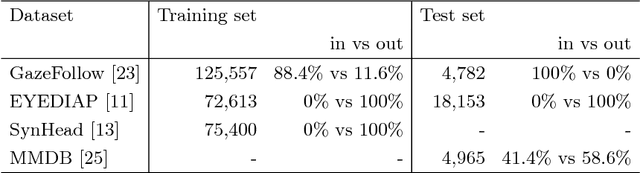
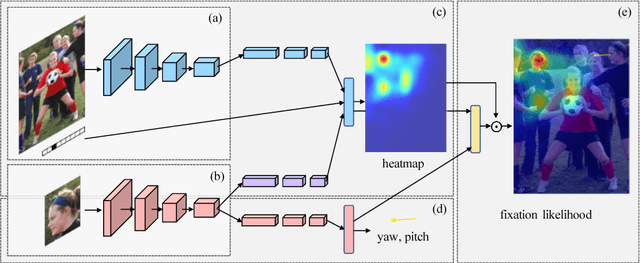
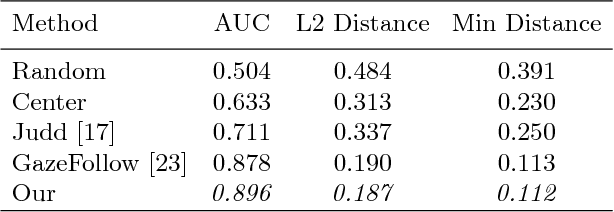
Abstract:This paper addresses the challenging problem of estimating the general visual attention of people in images. Our proposed method is designed to work across multiple naturalistic social scenarios and provides a full picture of the subject's attention and gaze. In contrast, earlier works on gaze and attention estimation have focused on constrained problems in more specific contexts. In particular, our model explicitly represents the gaze direction and handles out-of-frame gaze targets. We leverage three different datasets using a multi-task learning approach. We evaluate our method on widely used benchmarks for single-tasks such as gaze angle estimation and attention-within-an-image, as well as on the new challenging task of generalized visual attention prediction. In addition, we have created extended annotations for the MMDB and GazeFollow datasets which are used in our experiments, which we will publicly release.
Fine-Grained Head Pose Estimation Without Keypoints
Apr 13, 2018



Abstract:Estimating the head pose of a person is a crucial problem that has a large amount of applications such as aiding in gaze estimation, modeling attention, fitting 3D models to video and performing face alignment. Traditionally head pose is computed by estimating some keypoints from the target face and solving the 2D to 3D correspondence problem with a mean human head model. We argue that this is a fragile method because it relies entirely on landmark detection performance, the extraneous head model and an ad-hoc fitting step. We present an elegant and robust way to determine pose by training a multi-loss convolutional neural network on 300W-LP, a large synthetically expanded dataset, to predict intrinsic Euler angles (yaw, pitch and roll) directly from image intensities through joint binned pose classification and regression. We present empirical tests on common in-the-wild pose benchmark datasets which show state-of-the-art results. Additionally we test our method on a dataset usually used for pose estimation using depth and start to close the gap with state-of-the-art depth pose methods. We open-source our training and testing code as well as release our pre-trained models.
* Accepted to Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2018 IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 2018
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge